Why Do You Need Ethernet on a Mac?
Ethernet is a crucial means of connecting your Mac to the internet. While Wi-Fi is convenient and widely used, Ethernet provides several benefits that make it indispensable in certain scenarios.
One of the key advantages of using Ethernet on a Mac is the stability and reliability it offers. Unlike Wi-Fi, which can be affected by factors like distance, signal interference, and network congestion, Ethernet provides a direct and dedicated connection between your Mac and the network. This results in a more stable and consistent internet connection, which is especially crucial for tasks that require high-speed and uninterrupted data transfer, such as video conferencing, online gaming, and large file downloads.
In addition to its stability, Ethernet also offers faster speeds compared to Wi-Fi. While Wi-Fi speeds may vary depending on your distance from the router and network congestion, Ethernet delivers consistent and high-speed connectivity, allowing for smoother browsing, faster downloads, and quicker uploads. This makes Ethernet an ideal choice for professionals who rely on fast and efficient internet access for their work, such as graphic designers, video editors, and software developers.
Another advantage of Ethernet is its security. While Wi-Fi connections are susceptible to unauthorized access, Ethernet provides a more secure and private connection. This is particularly important for businesses and individuals who deal with sensitive data and require a secure network connection to protect their information from potential cyber threats.
Furthermore, Ethernet is essential for establishing a local area network (LAN) connection. LANs allow you to connect multiple devices, such as printers, scanners, and other computers, to share resources and collaborate more effectively. Ethernet provides the necessary infrastructure to create a reliable and high-speed network for seamless communication and file sharing within a LAN.
Overall, while Wi-Fi offers convenience and flexibility, Ethernet is the go-to solution when stability, speed, and security are paramount. Whether you’re a professional requiring fast internet access or an individual seeking a reliable connection for various activities, having Ethernet on your Mac ensures enhanced performance and productivity.
Types of Ethernet Connections for Mac
When it comes to connecting Ethernet to your Mac, there are a few different options available. These options cater to different Mac models and user preferences, providing flexibility and convenience. Here are the primary types of Ethernet connections you can make with your Mac:
- Built-in Ethernet port: Many Mac desktop models come equipped with a built-in Ethernet port. These ports, usually located on the back of the Mac, allow you to directly connect an Ethernet cable to establish a wired connection. This option offers a straightforward and hassle-free way to connect to a network.
- Ethernet Adapter: For Mac laptops that don’t have a built-in Ethernet port, you can use an Ethernet adapter to establish a wired connection. These adapters typically connect to your Mac’s USB or Thunderbolt ports, and provide an Ethernet port to connect the cable. This option is convenient for MacBook Air and MacBook Pro users who require an Ethernet connection on the go.
- Thunderbolt Dock: Thunderbolt docks are versatile devices that offer multiple connectivity options, including Ethernet. By connecting your Mac to a Thunderbolt dock, you can gain access to an Ethernet port, along with additional USB ports, HDMI outputs, and more. This option is particularly useful for those who need a centralized hub for their various peripherals.
It’s important to note that when choosing an Ethernet connection for your Mac, you should ensure compatibility with your specific Mac model and operating system. Additionally, consider factors such as port availability, convenience, and the need for additional connectivity options when deciding which Ethernet connection method to use.
Ultimately, regardless of the type of Ethernet connection you choose, the goal is to establish a fast, stable, and secure wired connection that enhances your Mac’s networking capabilities.
Using an Ethernet Adapter with a MacBook
If you own a MacBook that lacks a built-in Ethernet port, don’t worry – you can still enjoy the benefits of a wired Ethernet connection by using an Ethernet adapter.
An Ethernet adapter is a small device that connects to your MacBook’s USB or Thunderbolt port, providing an Ethernet port for connecting an Ethernet cable. This allows you to establish a reliable wired connection, even on the go.
To use an Ethernet adapter with your MacBook, follow these simple steps:
- Identify the appropriate Ethernet adapter for your MacBook model. There are various adapters available, so ensure compatibility with your specific MacBook model and the version of macOS you’re running.
- Connect the Ethernet adapter to your MacBook’s USB or Thunderbolt port. Once plugged in, your MacBook should recognize the adapter.
- Take an Ethernet cable and insert one end into the Ethernet port on the adapter. The other end should be connected to a available LAN port on your network router or modem.
- Your MacBook will automatically detect the Ethernet connection, and you should see the network icon in the menu bar change to indicate the wired connection.
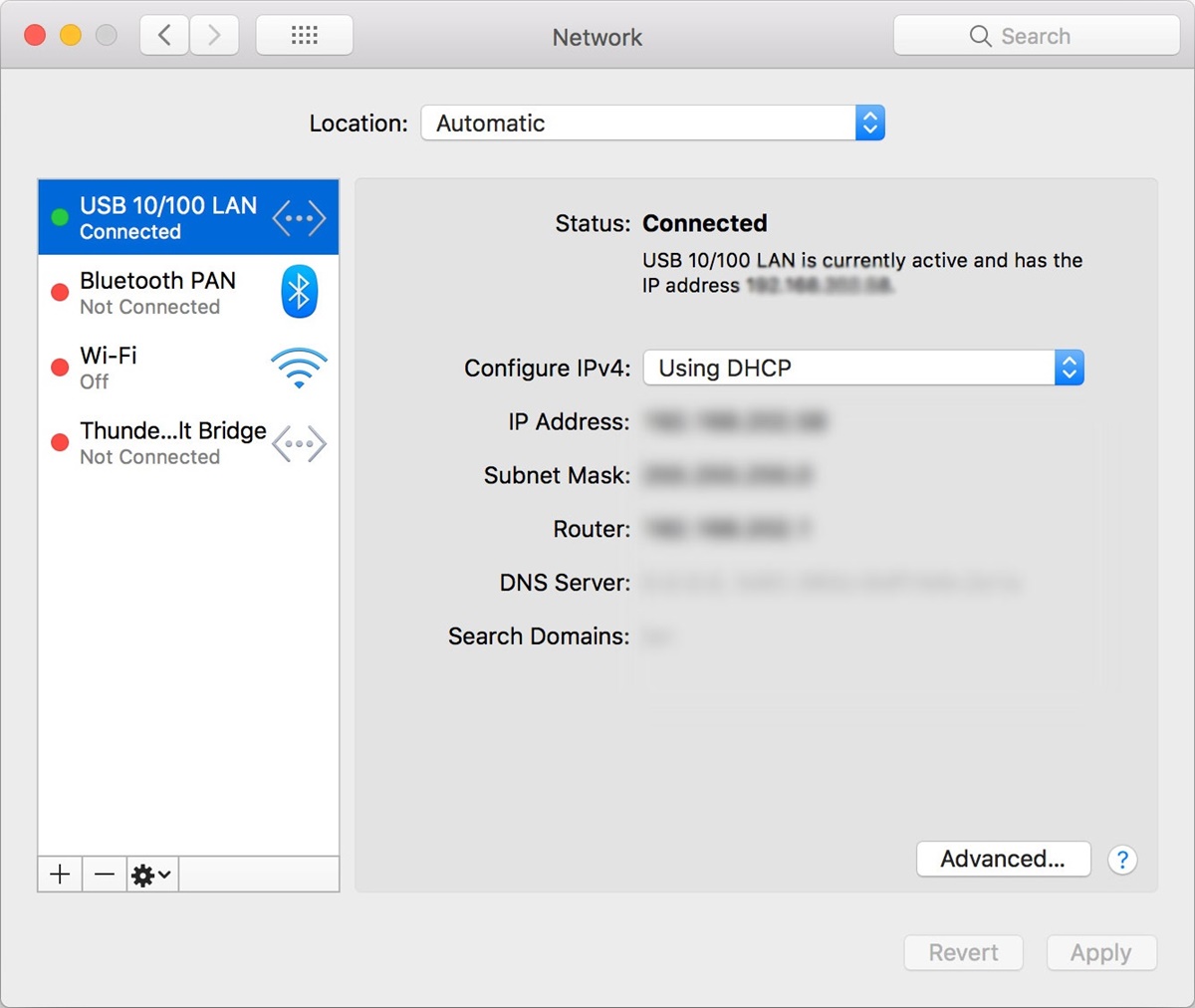
- To confirm that you’re connected via Ethernet, go to the “Network” settings in your MacBook’s System Preferences. You should see the Ethernet adapter listed and marked as “Connected.”
Once you’ve successfully set up the Ethernet adapter, you can enjoy the benefits of a stable and high-speed wired connection on your MacBook. This is particularly useful in situations where Wi-Fi connectivity may be unreliable or when you require a more secure and faster connection.
Remember to disconnect the Ethernet adapter when not in use, as it can drain your MacBook’s battery if left connected for long periods. Keeping it in your laptop bag or desk drawer ensures it’s readily available when you need it.
With the convenience of an Ethernet adapter, you can bring the advantages of a wired Ethernet connection to your MacBook, enhancing your productivity and online experience.
Setting Up Ethernet on a Mac
Setting up Ethernet on a Mac is a straightforward process that allows you to establish a wired connection for fast and reliable internet access. Whether your Mac has a built-in Ethernet port or you’re using an Ethernet adapter, here’s how you can set up Ethernet on your Mac:
- Ensure you have an Ethernet cable and either a built-in Ethernet port on your Mac or an Ethernet adapter compatible with your MacBook model.
- If your Mac has a built-in Ethernet port, simply connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the port and the other end to an available LAN port on your network router or modem.
- If you’re using an Ethernet adapter, connect it to your MacBook’s USB or Thunderbolt port. Then, insert one end of the Ethernet cable into the Ethernet port on the adapter and the other end into an available LAN port on your network router or modem.
- Once the Ethernet cable is connected, your Mac should automatically detect the wired connection. The network icon in the menu bar should change to indicate the Ethernet connection.
- Open the “Network” settings in your Mac’s System Preferences. You should see the Ethernet connection listed and marked as “Connected.”
- Click on the “Advanced” button to access additional settings. Here, you can configure IP address settings, DNS servers, and other network-related options. In most cases, the default settings should work fine.
- Test your Ethernet connection by opening a web browser or accessing other online services. You should experience a stable and fast internet connection.
Setting up Ethernet on your Mac provides you with a reliable and high-speed connection, ideal for activities that require a consistent and uninterrupted internet connection. It’s particularly beneficial for tasks like online gaming, video streaming, and large file transfers.
Remember that Ethernet connections offer enhanced security compared to Wi-Fi, making it a suitable choice when dealing with sensitive data or when you need a secure network connection.
By following these simple steps, you can set up Ethernet on your Mac and enjoy the benefits that come with a wired connection.
Troubleshooting Ethernet Connection Issues on a Mac
While setting up an Ethernet connection on your Mac is usually a straightforward process, there may be instances where you encounter issues with the connection. Here are some common troubleshooting steps to help you resolve Ethernet connection issues on your Mac:
- Check cable connections: Ensure that the Ethernet cable is securely plugged into both your Mac’s Ethernet port or adapter and the LAN port on your network router or modem. Sometimes, loose connections can lead to connectivity problems.
- Restart your devices: Power cycle your Mac, network router, and modem by turning them off and then back on. This helps refresh the network settings and can resolve temporary connectivity issues.
- Reset network settings: In the “Network” settings of your Mac’s System Preferences, click on the Ethernet connection and then click on the minus (-) button to remove it. Restart your Mac, go back to the “Network” settings, and click on the plus (+) button to re-add the Ethernet connection. This can help resolve any software-related issues that may be affecting the connection.
- Check for software updates: Ensure that your Mac’s operating system is up to date. Software updates often include bug fixes and improvements that can resolve connectivity issues.
- Disable Wi-Fi: If your Mac is simultaneously connected to Wi-Fi, it may prioritize the wireless connection over Ethernet. Disable Wi-Fi temporarily through the Wi-Fi menu in the menu bar to ensure that your Mac exclusively uses the Ethernet connection.
- Try a different Ethernet cable or adapter: If possible, test the Ethernet connection with a different cable or adapter to check if the issue lies with the hardware. Faulty cables or adapters can cause intermittent or no connection.
- Reset network preferences: If all else fails, you can try resetting your Mac’s network preferences. This removes all network settings and configurations, so proceed with caution. To do this, go to “System Preferences,” then “Network,” and select “Advanced.” Click on the “Reset” button to reset your network preferences to their default settings.
If you’ve exhausted these troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing Ethernet connection issues on your Mac, it may be helpful to seek further assistance from Apple support or consult with a professional network technician.
Remember to document any error messages or specific connectivity issues you encounter, as this can aid in pinpointing the cause of the problem and finding a suitable solution.
Tips for Maximizing Ethernet Performance on a Mac
When utilizing Ethernet on your Mac, there are several strategies you can employ to optimize performance and ensure the best possible wired connection. These tips will help you maximize the benefits of Ethernet on your Mac:
- Use quality Ethernet cables: Invest in high-quality Ethernet cables that are capable of delivering optimal performance. Look for cables with good shielding and higher category ratings, such as Cat 5e or Cat 6, to ensure faster speeds and minimal interference.
- Keep cables away from electrical interference: Avoid routing Ethernet cables in close proximity to electrical cables, power outlets, or devices that emit electromagnetic interference. This can help reduce signal interference and maintain a stable connection.
- Eliminate cable length limitations: Ethernet cables have a length limitation before signal degradation occurs. To boost performance, minimize the length of the cable between your Mac and the network router or switch. Additionally, use quality Ethernet switches or routers to maintain signal integrity over longer distances.
- Update network drivers: Keep your Mac’s network drivers up to date to ensure compatibility and take advantage of any performance enhancements provided by the manufacturer. Check for driver updates on the manufacturer’s website or through your Mac’s software update mechanism.
- Optimize your network configuration: Adjusting network settings can have a positive impact on Ethernet performance. For instance, disabling unnecessary network services, prioritizing network traffic, and configuring your Mac’s DNS settings can help improve overall performance.
- Secure your network: Utilize strong network security measures to protect your Ethernet connection from unauthorized access. Set up strong passwords, enable encryption, and consider using a firewall to safeguard your network and data.
- Regularly update your Mac’s operating system: Periodically check for software updates and install the latest version of macOS. These updates often include bug fixes, performance improvements, and security patches that can enhance your Mac’s overall performance and stability.
By implementing these tips, you can ensure that your Ethernet connection on your Mac is operating at its full potential. This will result in faster speeds, improved stability, and a more reliable wired network connection.
Remember that the overall performance of your Ethernet connection may also depend on factors beyond your control, such as ISP speeds and network congestion. However, by following these best practices, you can maximize the performance of Ethernet on your Mac and enjoy a superior wired internet experience.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ethernet on a Mac
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about Ethernet on a Mac:
- Can I connect my MacBook to Ethernet?
- Is Ethernet faster than Wi-Fi on a Mac?
- How do I check if my Mac is connected to Ethernet?
- Do all Mac models have a built-in Ethernet port?
- Can I use Wi-Fi and Ethernet simultaneously on a Mac?
- Can I connect multiple devices to Ethernet using my Mac?
- Do I need special cables for Ethernet?
Yes, you can connect your MacBook to Ethernet by using an Ethernet adapter. This adapter connects to your MacBook’s USB or Thunderbolt port, allowing you to establish a wired Ethernet connection.
Generally, Ethernet provides faster speeds and more stable connectivity compared to Wi-Fi. While Wi-Fi is convenient and suitable for most tasks, Ethernet is ideal for activities that require high-speed and uninterrupted data transfer, such as online gaming, video streaming, and large file downloads.
To check if your Mac is connected to Ethernet, go to the “Network” settings in your Mac’s System Preferences. If your Ethernet connection is active, you will see it listed and marked as “Connected.”
No, not all Mac models have a built-in Ethernet port. Many newer MacBook models, such as the MacBook Air and some MacBook Pro models, do not come with a built-in Ethernet port. However, you can still connect these models to Ethernet by using an Ethernet adapter.
Yes, you can use Wi-Fi and Ethernet simultaneously on a Mac. However, by default, macOS may prioritize Wi-Fi over Ethernet. To ensure your Mac uses the Ethernet connection, disable Wi-Fi temporarily through the Wi-Fi menu in the menu bar.
Yes, you can connect multiple devices to Ethernet by using your Mac as a bridge or by connecting them to a network switch. This allows you to create a local area network (LAN) and share the Ethernet connection among various devices.
For standard Ethernet connections, you can use Cat 5e or Cat 6 Ethernet cables. These cables are widely available and suitable for most residential and small office networks. However, for high-speed connections or longer cable runs, you may need higher category cables, such as Cat 6a or Cat 7.
These are just a few common questions about Ethernet on a Mac. If you have more specific inquiries or encounter any issues, consult the documentation provided with your Mac or seek assistance from Apple support or a professional network technician.