Why Change Sleep Settings in Windows?
Sleep mode is a built-in feature in Windows that helps conserve energy by putting your computer into a low-power state after a period of inactivity. However, depending on your usage habits and preferences, you may find that the default sleep settings are not ideal for your needs. Changing the sleep settings in Windows allows you to customize how and when your computer goes to sleep, providing a better user experience and optimizing energy efficiency.
There are several reasons why you might want to change the sleep settings in Windows:
1. Energy conservation: By adjusting the sleep settings, you can ensure that your computer goes into sleep mode more quickly when it’s not in use. This helps reduce energy consumption and extends the battery life of laptops and other portable devices.
2. Convenience: If you frequently step away from your computer but want it to remain active for certain tasks, such as downloads or streaming music, you can adjust the sleep settings to prevent the computer from going to sleep during those times.
3. Productivity: If you often work with large files or perform resource-intensive tasks, such as rendering videos or running simulations, having your computer go to sleep too quickly can interrupt the progress and slow down your workflow. Customizing the sleep settings allows you to prevent unnecessary interruptions and maintain productivity.
4. System updates and backups: Regular system updates and backups are essential for keeping your computer secure and protecting your data. Adjusting the sleep settings ensures that these processes can run uninterrupted, especially if they require long periods of time to complete.
5. Gaming and multimedia: Gamers and multimedia enthusiasts may want to change the sleep settings to prevent the computer from going to sleep while playing games or watching movies. This ensures a seamless and uninterrupted experience without any sudden interruptions.
By understanding the benefits of changing the sleep settings in Windows, you can tailor the sleep mode behavior to suit your specific needs and preferences. Whether it’s conserving energy, improving convenience, enhancing productivity, or optimizing your gaming and multimedia experience, customizing the sleep settings allows you to take greater control over your computer’s performance.
How to Open the Power & Sleep Settings
To change the sleep settings in Windows, you’ll need to access the Power & Sleep settings. Here’s how:
Method 1: Using the Start Menu:
- Click on the Start button in the bottom-left corner of the screen.
- Select Settings (the gear icon).
- In the Settings window, click on System.
- From the left sidebar, choose Power & Sleep.
Method 2: Using the Control Panel:
- Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Type control and press Enter.
- In the Control Panel window, click on System and Security.
- Under the Power Options section, click on Change when the computer sleeps.
Once you’ve accessed the Power & Sleep settings, you’ll be able to adjust the sleep settings to meet your requirements.
Note: The exact steps may vary slightly depending on the version of Windows you’re using. If you’re using an older version of Windows, such as Windows 7 or Windows 8, you may need to navigate to the Control Panel directly to access the Power & Sleep settings.
Now that you know how to access the Power & Sleep settings, you’re ready to make changes to the sleep settings according to your preferences. Let’s explore how to customize the sleep options in the next section.
Adjusting the Sleep Settings
Once you’ve accessed the Power & Sleep settings in Windows, you can start adjusting the sleep settings to better suit your needs. Here’s how you can do it:
- Sleep Timer: Under the “Sleep” section, you’ll see a dropdown menu labeled “On battery power, turn off after” and “When plugged in, turn off after.” Use these dropdown menus to select the desired time interval before your computer goes to sleep. You can choose anything from a few minutes to several hours.
- Sleep on Battery: By default, Windows uses different sleep settings when your device is running on battery power. You can adjust these settings independently by selecting the desired sleep timer in the “On battery power, turn off after” dropdown menu.
- Screen Turn-off Timer: If you want to conserve power but keep your computer running in the background, you can adjust the screen turn-off time separately from the sleep timer. Under the “Screen” section, you’ll find a dropdown menu labeled “On battery power, turn off after” and “When plugged in, turn off after.” Choose the desired time interval for the screen to turn off after inactivity.
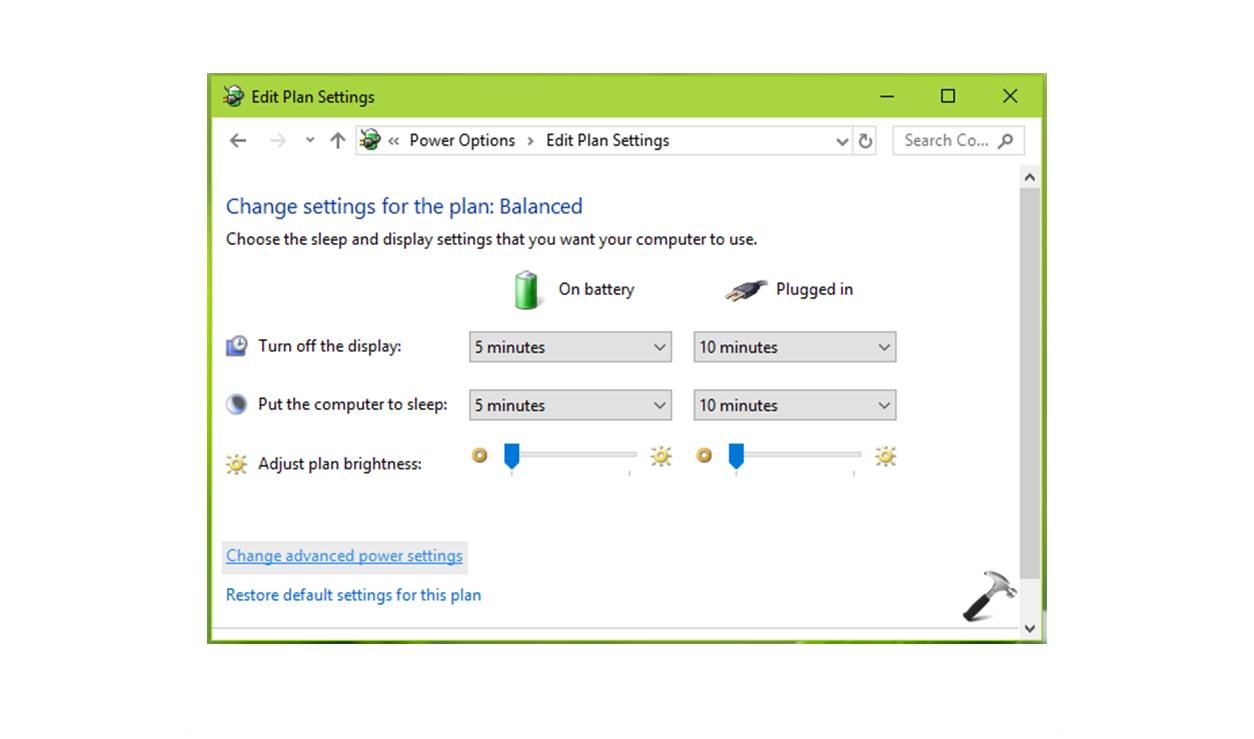
- Additional Power Settings: To access more advanced power settings, click on the “Additional Power Settings” link. This will open the Power Options window where you can further customize the power plan settings, including the behavior of the power buttons, sleep options for different components, and more.
By adjusting the sleep settings, you can ensure that your computer goes to sleep or turns off the screen after a specific period of inactivity, optimizing energy consumption and extending the battery life for laptops and other portable devices. It also allows you to strike a balance between power conservation and convenience, ensuring that your computer remains active when you need it most.
Now that you know how to adjust the sleep settings, let’s explore how you can customize the sleep options for different scenarios in the next section.
Changing the Sleep Settings for Plugged In and On Battery
Windows provides the flexibility to adjust sleep settings separately for when your device is plugged in and when it’s running on battery power. This allows you to customize the sleep behavior according to your specific needs and preferences in different scenarios. Here’s how you can change the sleep settings for both modes:
1. Sleep Settings for Plugged In:
- Go to the Power & Sleep settings as described in the previous section.
- Under the “Sleep” section, locate the dropdown menu labeled “When plugged in, turn off after.”
- Select the desired time interval from the dropdown menu to determine how long your computer should remain idle before it goes to sleep while plugged in.
- Optionally, adjust the screen turn-off timer under the “Screen” section by selecting the appropriate time interval from the corresponding dropdown menu.
2. Sleep Settings for On Battery Power:
- In the Power & Sleep settings, find the dropdown menu labeled “On battery power, turn off after.”
- Choose the desired time interval from the dropdown menu to set the idle time limit before your computer goes to sleep while running on battery power.
- If necessary, adjust the screen turn-off timer under the “Screen” section by selecting the suitable time interval from the related dropdown menu.
By customizing sleep settings independently for both plugged-in and battery modes, you can ensure optimal power management and keep your computer running efficiently in different situations. For example, you might want to extend the sleep timer when the device is plugged in to allow for longer periods of inactivity without turning off, while using shorter sleep intervals to preserve battery life when running on battery power.
Now that you know how to change the sleep settings for plugged in and on battery, let’s dive into customizing sleep options for different scenarios in the next section.
Customizing the Sleep Options for Different Situations
Windows allows you to customize sleep options for different situations, ensuring that your computer’s sleep behavior aligns with your specific needs and preferences. Here are some scenarios where you might want to customize the sleep options:
1. Presentation Mode: When giving presentations or sharing your screen, you wouldn’t want your computer to go to sleep and interrupt the flow. To prevent this, you can enable presentation mode. Presentation mode temporarily disables sleep so that your computer remains active during important presentations or meetings. You can enable presentation mode by going to the Power & Sleep settings and checking the box for “Don’t turn off the display” and “Don’t put the computer to sleep” options.
2. Media Playback: If you’re watching a movie or listening to music on your computer, you may want to customize the sleep options to ensure uninterrupted playback. To do this, access the Power & Sleep settings and increase the sleep timer or select the “Never” option for both plugged-in and battery modes. Additionally, you can adjust the screen turn-off timer to keep the display on while media is playing.
3. Downloading or Transferring Files: When downloading large files or transferring data, you may want to prevent your computer from going to sleep to ensure uninterrupted progress. Adjust the sleep settings to extend the sleep timer or choose the “Never” option so that your computer remains active during file transfers.
4. Background Tasks: There may be instances where you need your computer to perform background tasks, such as system updates or backup processes. To avoid any interruptions, customize the sleep options to prevent your computer from going to sleep during these tasks. You can adjust the sleep timer accordingly or choose the “Never” option during the update or backup process.
5. Different User Preferences: If multiple users share a computer, they may have different preferences for sleep settings. Windows allows each user to have their own sleep settings, ensuring that each user’s experience is tailored to their liking. To customize sleep settings for individual users, go to the Power & Sleep settings, click on the “Additional power settings” link, and select “Change plan settings” for the desired user.
By customizing the sleep options for different situations, you can ensure that your computer behaves in a way that suits your specific needs. Whether it’s for presentations, media playback, file transfers, background tasks, or individual user preferences, customizing sleep options helps optimize your computing experience.
Disabling Sleep Mode Altogether
While sleep mode can be useful for conserving energy and extending battery life, there may be situations where you prefer to have your computer remain active at all times. Windows allows you to disable sleep mode altogether if you desire. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open the Power & Sleep settings by following the steps outlined in the previous sections.
- Under the “Sleep” section, select the dropdown menu for both “On battery power, turn off after” and “When plugged in, turn off after.”
- Choose the option “Never” from the dropdown menus to disable sleep mode entirely for both plugged-in and battery modes.
By disabling sleep mode, your computer will stay active indefinitely until manually shut down or restarted. This can be useful for situations like running continuous programs, hosting server services, or performing tasks that require uninterrupted operation.
Note: Disabling sleep mode will significantly increase power consumption, reduce battery life, and may lead to higher energy usage. It’s recommended to only disable sleep mode when necessary and monitor your computer’s temperature and performance to ensure optimal functionality.
If you do disable sleep mode, it’s important to take regular breaks and allow your computer to rest to prevent overheating. Also, keep in mind that your computer will not automatically enter a low-power state, so it’s essential to manually shut it down or use hibernation mode if you want to conserve energy when not in use for an extended period.
Now that you know how to disable sleep mode, you have the flexibility to keep your computer active at all times when needed. However, it’s important to use this feature judiciously and consider the potential impact on energy consumption and system performance.
Troubleshooting Sleep Issues
If you encounter any issues with sleep mode on your Windows computer, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try to resolve the problem. Here are some common solutions to fix sleep issues:
1. Update Drivers: Outdated or incompatible drivers can sometimes cause sleep problems. Update your device drivers, especially the graphics and network drivers, to ensure compatibility and smooth sleep transitions. You can do this by visiting the manufacturer’s website or using a driver update software.
2. Check Power Settings: Verify that your power settings are properly configured. Go to the Power & Sleep settings and ensure that the sleep timers are set to the desired values. If necessary, reset the settings to default and then customize them again to see if that resolves the issue.
3. Disable Hybrid Sleep: Hybrid sleep is a combination of sleep and hibernation modes. If you are experiencing sleep issues, disabling hybrid sleep can help. Go to the Power Options in the Control Panel, select your power plan, and click on “Change plan settings.” Then, click on “Change advanced power settings” and expand the “Sleep” section. Disable hybrid sleep if it’s enabled.
4. Disable Fast Startup: Fast Startup is a feature that helps Windows boot up faster by saving the system state to a hibernation file. However, it can sometimes interfere with sleep mode. To disable Fast Startup, go to the Power Options in the Control Panel, click on “Choose what the power buttons do,” and then click on “Change settings that are currently unavailable.” Uncheck the box next to “Turn on fast startup” and save the changes.
5. Run Power Troubleshooter: Windows has a built-in troubleshooter for power-related issues. Go to the Control Panel, search for “Troubleshooting,” and select “View all” from the left sidebar. Choose “Power” and run the troubleshooter to automatically detect and fix sleep issues.
6. Update Windows: Keeping your Windows operating system up to date can help resolve known sleep-related bugs and issues. Make sure to install the latest Windows updates by going to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and clicking on “Check for updates.”
If none of these troubleshooting steps resolve the sleep issues, you may want to consider seeking additional technical support or contacting the manufacturer for further assistance. Keep in mind that sleep problems can also be caused by hardware malfunctions or third-party software conflicts, so it’s important to consider all possible factors when troubleshooting.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you can identify and resolve sleep issues on your Windows computer, ensuring smooth and efficient sleep mode functionality.
Tips for Optimizing Sleep Settings for Better Performance
Optimizing sleep settings can not only help conserve energy but also improve the overall performance of your Windows computer. By following these tips, you can fine-tune your sleep settings for better efficiency and user experience:
1. Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance tasks on your computer, such as running disk cleanup, disk defragmentation, and removing unnecessary files. This helps keep your computer running smoothly and can prevent slow wake-up times from sleep mode.
2. Adjust Sleep Timers: Customize the sleep timers based on your usage patterns. If you frequently step away from your computer for short periods, consider reducing the sleep timer to conserve energy. Conversely, if you need longer periods of uninterrupted work, increase the sleep timer accordingly.
3. Use Sleep Mode for Short Breaks: If you’re taking short breaks from your computer, such as during lunch or meetings, putting your computer into sleep mode can be more energy-efficient than keeping it running at full capacity. This helps conserve power while ensuring a quick wake-up when you return.
4. Use Hibernation for Extended Periods: For longer periods of inactivity, consider using hibernation mode instead of sleep mode. Hibernation saves the current state of your computer to the hard drive and shuts it down completely, providing greater power savings while still allowing for a quick boot-up when you’re ready to use it again.
5. Manage Background Processes: Check the applications and processes running in the background. Some applications and services may prevent your computer from entering sleep mode or wake it up unnecessarily. Use the Task Manager to identify and manage these processes to optimize sleep performance.
6. Update Firmware: Keep your computer’s firmware, including the system BIOS and hardware drivers, up to date. Manufacturers often release updates to improve power management and sleep mode functionalities, ensuring better performance and compatibility.
7. Avoid Sleep Issues: Be mindful of any software or hardware that may cause sleep issues. Certain applications and peripheral devices may prevent your computer from entering sleep mode or cause it to wake up unexpectedly. Troubleshoot and address these issues promptly to optimize sleep performance.
8. Use Sleep Settings Profiles: If you have different usage scenarios, create multiple sleep settings profiles. Customize the sleep and power settings for each profile based on your needs, allowing you to quickly switch between profiles depending on your current activities.
9. Experiment and Adjust: Sleep settings can be unique to individual preferences and computer configurations. Experiment with different sleep settings and monitor the impact on performance and battery life. Adjust the settings accordingly to strike the right balance between energy conservation and performance optimization.
By implementing these tips, you can ensure that your sleep settings are optimized for better performance, energy efficiency, and personal preferences. Striking the right balance between power management and system responsiveness enhances your overall computing experience.