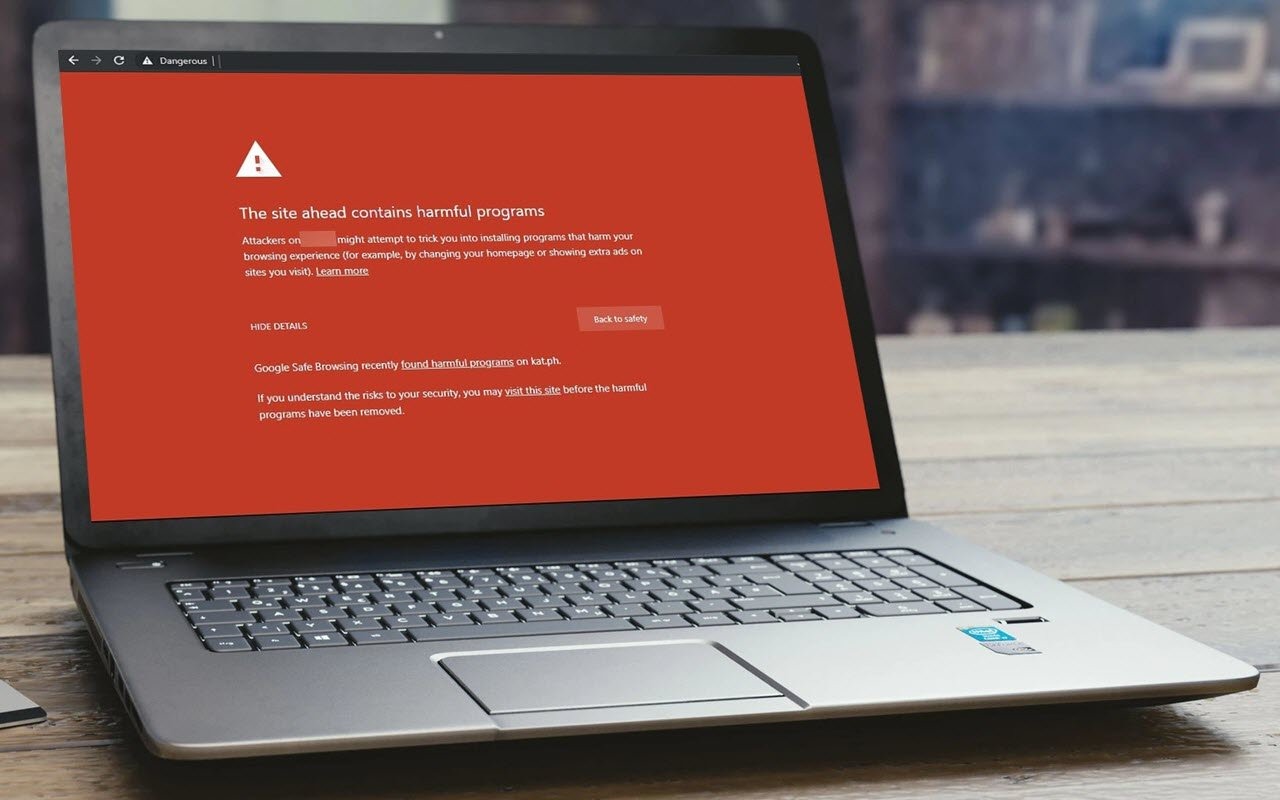
Importance of Avoiding Dangerous Websites
Dangerous websites pose serious threats to internet users, and being aware of the risks they present is crucial for maintaining online security. These websites can be a breeding ground for malware, viruses, scams, and identity theft. Furthermore, they can also compromise the privacy and personal information of individuals. Therefore, it is essential to understand the importance of avoiding such websites and taking preventive measures to protect oneself.
One of the primary reasons for avoiding dangerous websites is to ensure the security of your devices and personal data. Malicious websites often contain harmful software or codes that can infect your computer or mobile device, leading to data breaches or unauthorized access to your personal information. This can result in financial loss, identity theft, or even compromising the security of your online accounts.
Another crucial aspect is protecting yourself from online scams. Dangerous websites are often used as platforms to deceive users into providing sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, or social security numbers. Falling victim to these scams can lead to financial devastation and even ruin your credit history.
Moreover, dangerous websites can also expose you to cyberattacks through phishing attempts. Phishing is a fraudulent tactic used by cybercriminals to trick users into revealing personal information by posing as trustworthy entities. Avoiding these websites can significantly decrease your chances of becoming a victim of such attacks, ensuring your online safety and peace of mind.
Furthermore, keeping away from dangerous websites also helps prevent the spread of malware and viruses. When you visit infected websites, these malicious programs can be secretly downloaded onto your device, causing it to slow down, crash, or even become inaccessible. Additionally, malware can also spread to other devices within your network, putting not only your own data but also the data of others at risk.
Lastly, by avoiding dangerous websites, you contribute to the overall improvement of online security. Websites containing malware or engaging in illegal activities thrive when users unwittingly visit and interact with them. By choosing to steer clear of such websites, you discourage cybercriminals and lessen their impact on the digital world.
Types of Dangerous Websites
Dangerous websites come in various forms, each with its own level of risk and potential harm. Being aware of the different types of dangerous websites can help you recognize and avoid them effectively. Here are some common types to watch out for:
- Phishing Websites: These websites are designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal details. They often mimic legitimate websites and use deceptive tactics to convince users to share their information.
- Malware-Infected Websites: These websites contain malicious software that can infect your device and compromise your data and privacy. The malware can be disguised as innocent-looking downloads, ads, or pop-ups, and visiting such websites can lead to automatic installation of harmful software.
- Scam Websites: Scam websites are created to deceive users into providing money or personal information through fraudulent schemes. Examples of scam websites include fake online stores, lottery scams, or bogus charity websites.
- Adult Content Websites: While not all adult websites are dangerous, some may contain explicit content that can be used as a bait to lure users into downloading malware or unauthorized payment requests.
- Unsecured Websites: These are websites that lack essential security measures, such as encryption or secure socket layer (SSL) certificates. Visiting unsecured websites can put your data at risk as it can be intercepted by hackers or unauthorized third parties.
- Fake News Websites: Fake news websites spread misinformation, disinformation, and propaganda. These websites can manipulate public opinion, spread conspiracy theories, or exploit sensitive topics for personal gain.
It’s essential to note that dangerous websites can evolve and often overlap in their traits. Therefore, it is crucial to stay vigilant and employ caution when browsing the internet.
Signs of a Dangerous Website
Recognizing the signs of a dangerous website is crucial for protecting yourself and your data while browsing the internet. Here are some common indicators that can help you identify potentially hazardous websites:
- Unsecure Connection: One of the first things to look for is an unsecure connection. If a website doesn’t have the padlock icon or starts with “https://” instead of “http://”, it indicates that the website does not have proper encryption and may not be safe.
- Poor Website Design: Pay attention to the overall design and layout of the website. If it looks poorly designed, contains numerous ads, or has strange and suspicious elements, it could be an indication of an unsafe website.
- Lack of Contact Information: Legitimate websites often provide clear contact information, such as an address, phone number, or email. If you can’t find any contact details or they seem vague and unreliable, it’s a red flag.
- Too Good to Be True Offers: Be wary of websites that offer incredibly low prices or unbelievable deals that seem too good to be true. Scammers often use these tactics to lure users into providing their personal or financial information.
- Spelling and Grammar Errors: Pay attention to the quality of the website’s content. If you notice frequent spelling and grammar mistakes, it may indicate that the website is not professionally maintained or trustworthy.
- Excessive Pop-ups and Ads: Websites bombarded with excessive pop-ups, flashy ads, or suspicious banner ads can be indicators of a dangerous website. These ads may contain malicious links or redirect you to unsafe web pages.
- Unsolicited Emails or Messages: If you receive unsolicited emails or messages containing links to a website, exercise caution before clicking on them. These messages may be phishing attempts or attempts to deliver malware to your device.
- Warnings from Antivirus Software: Trusted antivirus software can often detect and warn you about dangerous websites. If your antivirus or security software alerts you about potential threats, it’s best to avoid accessing the website.
- User Reviews and Ratings: Before visiting a website, check for user reviews and ratings to get an idea of its reputation. If you come across multiple negative reviews or warnings about security issues, it’s best to steer clear of that website.
Remember, it’s better to be cautious and avoid potentially dangerous websites than to risk your security and privacy online.
Setting Up Security Measures
Protecting yourself from dangerous websites involves setting up effective security measures. By following these steps, you can significantly enhance your online safety:
- Install Antivirus and Firewall: Ensure that you have reliable antivirus software installed on your computer, tablet, or smartphone. It will help detect and remove malware, viruses, and other threats. Additionally, enable the built-in firewall on your device to provide an extra layer of protection.
- Keep Operating Systems Updated: Regularly update your device’s operating system (OS) to ensure that you have the latest security patches. Manufacturers frequently release updates to address vulnerabilities and strengthen security measures.
- Use Strong and Unique Passwords: Create strong and unique passwords for each of your online accounts. Avoid using common passwords and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Consider using a password manager to securely store and generate complex passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Activate two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible. This additional security layer requires you to provide a second verification, such as a unique code sent to your phone, in addition to your password.
- Be Cautious of Public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing sensitive information or logging into accounts while connected to public Wi-Fi networks. Hackers can intercept data on these networks, potentially exposing your personal information.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): When using public Wi-Fi, consider using a VPN to encrypt your internet connection and protect your data from potential eavesdroppers. A VPN creates a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, ensuring your privacy.
- Regularly Back Up Your Data: Backup your important files regularly to an external hard drive or a cloud storage service. In case of a security breach or device failure, having backups ensures that you don’t lose valuable information.
- Enable Automatic Updates: Keep your web browser, plugins, and extensions up to date by enabling automatic updates. Often, these updates include important security fixes that protect you against the latest threats.
- Be Mindful of Clicking Suspicious Links: Avoid clicking on links in emails, messages, or advertisements that appear suspicious or are from unknown sources. These links could lead you to dangerous websites or trigger malware downloads.
- Regularly Clear Your Browser Cache: Clear your browser cache regularly to remove temporary internet files and cookies. This helps prevent tracking and minimizes the risk of websites accessing your browsing history or personal information.
By implementing these security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of encountering dangerous websites and protect your online presence.
Keeping Software Updated
Keeping your software up to date is a critical step in maintaining a secure online environment. It involves regularly updating your operating system, web browsers, plugins, and other software applications to ensure they have the latest security patches and bug fixes. Here’s why this practice is vital:
Firstly, software updates often address security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals. As technology advances, new threats emerge, and software developers continuously work to identify and fix these vulnerabilities. By keeping your software updated, you benefit from the latest security enhancements, making it harder for hackers to exploit known weaknesses.
Secondly, outdated software can be a gateway for malware and other cyber threats. Cybercriminals often exploit security holes in older or unsupported software versions to deliver malicious payloads to unsuspecting users. By regularly updating your software, you close these doors, ensuring a safer online experience.
Thirdly, software updates also bring new features and performance improvements. Developers are constantly working on enhancing their software to deliver better functionality and user experience. By updating your software, you not only gain access to these improvements but also reduce the chances of encountering software bugs or glitches that could compromise your digital activities.
It’s important to note that software updates come from trusted sources, such as the official websites or the built-in update mechanisms provided by the software itself. Avoid downloading software or updates from unfamiliar or unverified sources, as they may contain malware or other harmful elements.
Setting your devices or software to automatically check for and install updates is a good practice, as it ensures that you don’t miss critical updates. However, it’s also important to review and research updates before installation, especially for major updates or for software that may have compatibility issues with your system.
Using Strong and Unique Passwords
Passwords are the first line of defense in protecting your online accounts and personal information. Using strong and unique passwords is crucial for maintaining the security of your digital identity. Here’s why it is important and how to create and manage strong passwords:
A strong password is one that is not easily guessable by others. It should be a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using common words, personal information, or sequential patterns as they can be easily cracked by cybercriminals using automated tools.
Using the same password across multiple accounts is a common mistake that puts your online security at risk. If one account is compromised, all your other accounts become vulnerable. Therefore, it is essential to use unique passwords for each online account you have.
It can be challenging to remember multiple complex passwords. Consider using a password manager tool to store and generate strong, unique passwords for your accounts. Password managers securely encrypt your passwords, making them accessible across devices with a single master password or biometric authentication.
When creating passwords, aim for a length of at least 12 characters. The longer and more complex the password, the harder it is for hackers to crack it. Avoid using easily guessable information such as your name, birthdate, or common dictionary words.
Periodically changing your passwords is also a good practice, especially for critical accounts and sensitive information. Set reminders to update your passwords every few months or whenever you suspect a security breach.
Phishing attacks are a common method used by cybercriminals to steal passwords. Avoid clicking on suspicious links or providing your password in response to emails or messages asking for your login credentials. Legitimate organizations will never ask for your password directly.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever available. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to provide a second form of verification, such as a unique code sent to your phone, in addition to your password.
Lastly, exercise caution when entering passwords on public or shared computers. Use virtual keyboards when possible and ensure that there are no keyloggers or malicious software present that can record your keystrokes and steal your password.
By using strong and unique passwords, you significantly reduce the risk of account compromise and protect your online identity and sensitive information.
Avoiding Suspicious Links and Emails
One of the common methods cybercriminals use to deceive and exploit internet users is through suspicious links and emails. Falling victim to phishing scams or clicking on malicious links can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and the compromise of personal data. It is essential to be cautious and follow these guidelines to avoid falling into these traps:
Firstly, be vigilant when receiving emails from unknown or untrusted sources. Check for telltale signs of a phishing attempt, such as spelling or grammatical errors, generic greetings, or urgent requests for personal information. Legitimate organizations will not ask for sensitive data via email.
Don’t click on links or download attachments from emails unless you are certain they are from a trusted source. Hover over any links to reveal the URL before clicking on them, and ensure it matches the domain of the website you are expecting to visit.
If you receive an email or message claiming to be from a reputable organization – such as a bank or online service provider – requesting sensitive information, do not respond directly. Instead, manually visit the official website through a trusted browser and contact the organization using the contact information provided there to verify the request.
Be cautious of unexpected prize winnings, lottery notifications, or “too good to be true” offers. Scammers often use enticing offers to lure individuals into providing personal information or making payments. Remember that legitimate offers and promotions are rarely distributed through unsolicited emails.
It’s crucial to keep your web browser, email client, and operating system up to date. Developers regularly release security patches and updates to protect against known vulnerabilities that scammers may exploit.
Install reliable antivirus and anti-malware software on your devices. These tools can help detect and quarantine suspicious links or emails that may contain harmful content or phishing attempts.
Exercise caution when clicking on links from social media platforms, chat platforms, or other websites. Be wary of shortened URLs or links that redirect to unfamiliar websites, as they can lead to phishing sites or malware downloads. Consider using a URL-expanding service to preview the full URL before accessing a link.
When visiting websites, check for HTTPS encryption and a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar. This indicates that the website has a secure connection and is more likely to be trustworthy.
Lastly, trust your instincts. If something feels suspicious or too good to be true, it probably is. Err on the side of caution and avoid engaging with suspicious links or emails.
By staying vigilant and following these guidelines, you can protect yourself from falling victim to scams, phishing attempts, and malicious links.
Verifying Websites Before Sharing Personal Information
Before sharing personal information on a website, it is crucial to verify its legitimacy and security to protect against identity theft, fraud, and other types of cybercrime. Here are some steps you can take to ensure the website is trustworthy:
Firstly, examine the website’s URL or web address. Legitimate websites typically have a domain name that corresponds to the organization or service they represent. Avoid websites with suspicious or unusual domain names, as they may be indicators of phishing attempts or fake websites.
Check for HTTPS encryption and a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar. The “S” in HTTPS stands for secure, indicating that the data transmitted between your device and the website is encrypted. This makes it more difficult for hackers to intercept and access your personal information.
Research the website and organization. Look for reviews, ratings, and any history of security breaches or scams associated with the website. Trusted review platforms, online forums, and cybersecurity websites can provide valuable insights and help you determine if the website is trustworthy.
Find and review the website’s privacy policy and terms of service. Legitimate websites typically have these documents easily accessible and provide detailed information on how they collect, use, and protect user data. Ensure that the website has clear policies in place to safeguard your personal information.
Look for contact information on the website. Genuine websites usually provide multiple ways to get in touch with them, such as a physical address, phone number, or email. Verify the provided information to ensure it is valid and corresponds to a legitimate organization.
Be wary of websites that request excessive or unnecessary personal information. Only provide the information that is absolutely necessary for the specific transaction or purpose. Legitimate websites typically follow privacy best practices and do not ask for irrelevant data.
Consider using payment methods with buyer protection and a trusted third-party payment processor when making online transactions. This adds an extra layer of security and can help resolve potential issues with fraudulent websites or unauthorized transactions.
Use web browser extensions or security software that can help identify and block suspicious or malicious websites. These tools can provide warnings or alerts if you unknowingly visit a dangerous website or encounter known phishing attempts.
Be cautious when accessing websites through external links, especially in emails, social media posts, or instant messages. Scammers often use deceptive techniques to trick users into visiting malicious websites that mimic legitimate ones. Instead, manually type the URL or use a trusted bookmark.
Trust your instincts. If something feels off or if you have any doubts about the legitimacy or security of a website, it’s better to err on the side of caution and avoid sharing personal information.
By taking these precautionary measures and verifying the legitimacy and security of a website before sharing personal information, you can mitigate the risk of falling victim to identity theft, fraud, or other malicious activities.
Limiting the Use of Public Wi-Fi
While public Wi-Fi can be convenient, especially when traveling or working from cafes, it poses significant security risks. Being aware of these risks and taking precautions can help safeguard your personal information and sensitive data. Here are some important steps to limit the use of public Wi-Fi:
Firstly, avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi networks unless absolutely necessary. Instead, opt for using your mobile data or a personal hotspot, as these connections are generally more secure. Reserve public Wi-Fi usage for non-sensitive activities, such as browsing the web or accessing general information.
When you do need to use public Wi-Fi, verify the network’s legitimacy. Scammers often set up fake hotspots with names similar to legitimate establishments, such as cafes or hotels. Confirm the correct network name with the staff or signage, or ask for the network credentials from a trusted source.
Choose known and trusted Wi-Fi networks whenever possible. If you frequent the same places, such as your favorite coffee shop or library, pay attention to the network names and remember them for future use. Be cautious of unknown or ad-hoc networks that may appear suspicious.
Make sure your device’s firewall is enabled. Firewalls help filter and monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic, acting as a barrier between your device and potential threats on public Wi-Fi networks.
Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when connecting to public Wi-Fi. A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it much more difficult for hackers to intercept and access your data. It creates a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, protecting your online activities and privacy.
Avoid accessing sensitive information or logging into accounts that contain personal or financial data when connected to public Wi-Fi. These include online banking, shopping, or accessing work-related accounts. Wait until you are on a secure network or use a trusted VPN connection to ensure the confidentiality of your information.
Be cautious of Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. These attacks involve intercepting information between the user and the network. To avoid such attacks, ensure the websites you visit have HTTPS encryption and always confirm you are on the correct website.
Disable automatic Wi-Fi connectivity on your devices to prevent them from automatically connecting to open or unsecured networks without your knowledge. This gives you more control over which networks you connect to and reduces the risk of accidentally connecting to malicious networks.
Regularly update your device’s software, including the operating system and applications. These updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit, improving your device’s overall security.
By following these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with using public Wi-Fi and help protect your personal information from falling into the wrong hands.
Utilizing Web Filters and Security Extensions
Web filters and security extensions are valuable tools that can enhance your online safety by blocking malicious content, filtering out harmful websites, and providing additional layers of protection. Here’s why you should consider utilizing web filters and security extensions:
Web filters are software programs or browser settings that block or restrict access to certain websites, content categories, or specific types of content. They can help prevent exposure to potentially dangerous or inappropriate material, especially for children or in professional settings.
Web filters work by analyzing website content, URL reputations, and other factors to determine if a website or its contents should be accessible. They can be managed through parental control software, internet service provider (ISP) settings, or third-party applications. By using web filters, you can limit access to malicious websites, adult content, gambling sites, or other categories as per your preferences or organizational policies.
Security extensions or browser add-ons can provide an extra layer of protection when browsing the internet. These extensions often come with features such as anti-phishing, anti-malware, and ad blocking functionalities.
Anti-phishing features help identify and warn against accessing malicious websites or falling victim to phishing attempts. They can detect fake websites designed to steal personal information or mimic legitimate websites to deceive users into providing sensitive data.
Anti-malware features within security extensions scan websites and files for potential threats, blocking malicious content and downloads. They can also provide real-time protection by identifying and blocking known malware sources.
Ad-blocking features not only eliminate annoying ads, but they also reduce the risk of malicious ads leading to dangerous or compromised websites. Some ads can contain malicious code or redirect users to phishing websites, making ad-blocking extensions an important tool for safeguarding against these threats.
Utilizing web filters and security extensions can help safeguard your devices, personal information, and online activities. They provide an added layer of security against a wide range of cyber threats, reduce exposure to harmful content, and improve browsing performance by blocking unwanted ads.
When choosing web filters or security extensions, opt for reputable and well-reviewed options from trusted sources. Pay attention to the permissions you are granting to these extensions and regularly update them to ensure they have the latest security features and enhancements.
By incorporating web filters and security extensions into your online experience, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with malicious websites, phishing attempts, malware infections, and intrusive advertisements.
Educating Children and Teenagers
As technology continues to play a central role in our lives, it becomes increasingly important to educate children and teenagers about online safety and responsible internet usage. By providing them with the necessary knowledge and skills, we empower them to navigate the digital world confidently and protect themselves from potential online threats. Here are some key aspects to consider when educating young individuals about internet safety:
1. Online Privacy and Personal Information: Teach children and teenagers about the importance of safeguarding personal information online. Encourage them to be cautious about sharing personal details, such as full names, addresses, phone numbers, school names, or social media account information. Explain the potential risks that can arise from sharing such information with strangers or on unsecured platforms.
2. Cyberbullying and Online Behavior: Discuss the harmful impact of cyberbullying and emphasize the importance of treating others with respect and empathy online. Teach children and teenagers how to recognize and report cyberbullying incidents, and encourage open communication if they or their peers experience such behavior.
3. Awareness of Online Threats: Educate young individuals about common online threats, such as phishing scams, malware, and identity theft. Teach them how to identify suspicious emails, links, or websites and emphasize the importance of not clicking on unfamiliar or potentially dangerous content.
4. Social Media Etiquette: Guide children and teenagers on responsible social media usage. Teach them about the potential consequences of sharing inappropriate content, the importance of respecting others’ privacy, and the impact of their online reputation on future endeavors such as college admissions or job applications.
5. Strangers and Online Interactions: Emphasize the significance of being cautious when interacting with strangers online. Teach them about the potential risks of sharing personal information or meeting individuals they’ve only met online. Encourage them to discuss any online interactions and seek guidance from a trusted adult if needed.
6. Critical Thinking and Media Literacy: Foster critical thinking skills by teaching children and teenagers how to evaluate the credibility and reliability of online information sources. Encourage them to question and verify information before accepting it as true, promoting a healthy skepticism that helps them avoid falling for misinformation or scams.
7. Open Communication and Trust: Maintain open lines of communication with children and teenagers about their online experiences. Encourage them to share any concerns, incidents, or encounters that make them uncomfortable or raise suspicions. Build a foundation of trust and assure them that they can seek guidance and support without fear of judgment or punishment.
8. Setting Healthy Boundaries: Teach children and teenagers to establish healthy boundaries for their online activities, such as limiting screen time, avoiding excessive sharing of personal information, or taking breaks from social media platforms when necessary. Encourage them to cultivate a healthy balance between their online and offline lives.
9. Keeping Personal Devices Secure: Instruct children and teenagers on the importance of device security measures, such as locking their devices with strong passwords or biometric authentication. Teach them to keep their operating systems, apps, and antivirus software up to date to protect against potential vulnerabilities.
10. Leading by Example: Model responsible internet usage and digital citizenship. Children and teenagers often learn by observing the behavior of adults around them. Practicing good online habits and demonstrating responsible behavior online will reinforce the importance of online safety and inspire them to do the same.
By addressing these fundamental aspects of online safety and ensuring ongoing communication and support, we empower children and teenagers to navigate the digital landscape confidently and make informed decisions while embracing the benefits of the internet.
Reporting Dangerous Websites
Reporting dangerous websites is an essential step in combating online threats and protecting other internet users from potential harm. By reporting suspicious or malicious websites, you contribute to creating a safer online environment for everyone. Here’s why reporting dangerous websites is important and how to do it:
1. Preventing Further Damage: Reporting dangerous websites promptly can help prevent others from falling victim to scams, malware infections, or other cybercrimes. By alerting relevant authorities or organizations, you enable them to take necessary action to shut down these websites, disrupt criminal activities, or block access to malicious content.
2. Gathering Intelligence for Security Organizations: Reporting dangerous websites provides valuable insights to security organizations and law enforcement agencies. These reports help them understand evolving cyber threats, track patterns, and identify trends to develop effective strategies for combating online crime.
3. Supporting Victims: Reporting dangerous websites can lead to the identification and apprehension of the individuals or organizations behind them. This, in turn, helps victims seek justice and recover from any financial losses or privacy breaches they may have experienced.
4. Raising Awareness: Reporting dangerous websites helps raise awareness among the general public about the threats lurking on the internet. Sharing information about these websites, their methods, and the potential consequences can empower others to stay vigilant and avoid falling into similar traps.
5. How to Report: Reporting methods may vary depending on the nature and jurisdiction of the website. Here are some common reporting avenues:
a. Contacting Local Law Enforcement: If you believe a website is involved in illegal activities, such as child exploitation, financial fraud, or trafficking, report it to your local law enforcement agency. They have the authority to investigate and take appropriate action.
b. Reporting to Internet Service Providers (ISPs): Many ISPs have mechanisms in place for reporting dangerous websites hosted on their platforms. Contact the respective ISP’s abuse department or support channels to notify them of the suspicious or malicious website.
c. Alerting Web Browsers and Search Engines: Major web browsers and search engines often have options to report dangerous websites. They utilize this information to warn users about potentially harmful websites and prevent them from accessing these websites through their platforms.
d. Reporting to Anti-Phishing Organizations: Anti-phishing organizations, such as the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG), accept reports of phishing websites. They work collaboratively with industry stakeholders to dismantle fraudulent websites and disrupt phishing campaigns.
e. Utilizing Online Reporting Tools: Online reporting platforms, such as the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), provide a centralized system for reporting cybercrimes. They gather information and refer reports to the appropriate authorities for investigation.
Note: When reporting dangerous websites, provide as much information as possible, including the website URL, a description of the suspicious activities, and any supporting evidence or screenshots if available. This helps authorities and organizations assess the severity of the threat and take appropriate action.
By reporting dangerous websites, you play an active role in combating cyber threats and protecting fellow internet users. Your actions can make a significant difference in creating a safer online environment for everyone.