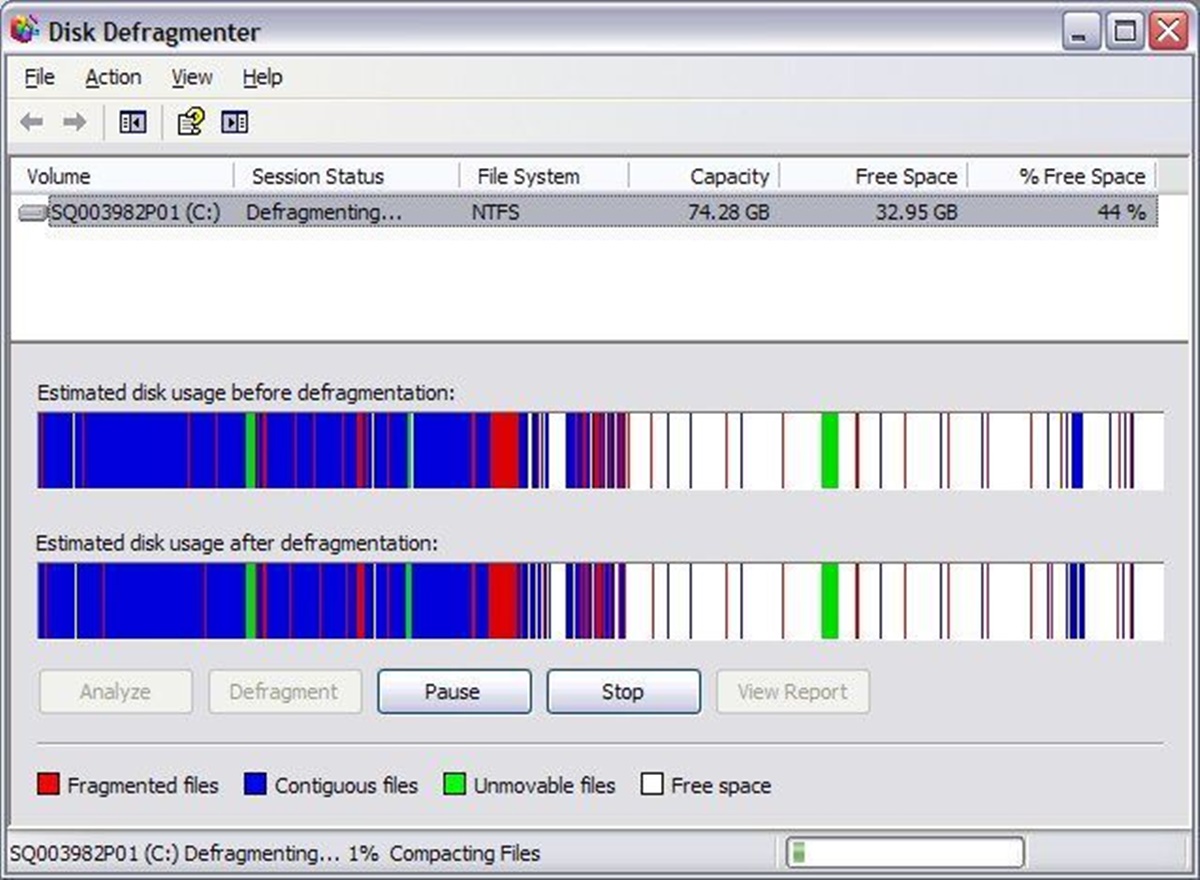
What is defragmentation?
In the world of computers, defragmentation refers to the process of reorganizing the fragmented files and scattered data on your hard drive. Over time, as you create, modify, and delete files, your computer’s storage becomes fragmented, meaning that files are no longer stored in contiguous blocks. This fragmentation results in slower access times and decreased overall performance.
When you save a file on your computer, it is stored in numerous blocks of data. Over time, as you save and delete files, gaps begin to form between these blocks, causing them to be scattered all over the hard drive. This fragmentation makes it harder for your computer to retrieve data and increases the time it takes to access files.
Defragmentation works by rearranging these fragmented files and organizing them into contiguous blocks. It essentially brings related data together, allowing your computer to access files more quickly and efficiently.
Defragmenting your computer’s hard drive can improve overall performance, reduce system crashes, and extend the lifespan of your storage device. It’s like tidying up your computer’s file system, ensuring that everything is stored in an organized and logical manner.
While modern operating systems have built-in defragmentation tools that automatically perform periodic defragmentation, it is still important to understand the benefits and significance of this process. By manually defragmenting your computer and knowing how often to do it, you can optimize your system’s performance and keep it running smoothly.
How does defragmentation work?
In order to understand how defragmentation works, it’s crucial to have a basic understanding of how data is stored on a hard drive. When you save a file, the computer allocates space on the hard drive to store that file. If the space available is not large enough to fit the entire file, the computer will split it into smaller parts and save them in non-adjacent sectors on the drive.
Over time, as you create and delete files, these gaps between the allocated space start to appear, resulting in fragmented data. This fragmentation causes the hard drive to work harder to access the scattered parts of the file, leading to slower read and write speeds.
Defragmentation works by rearranging the fragmented files and putting the scattered parts back into contiguous blocks. When you initiate the defragmentation process, the software scans the hard drive and identifies the fragmented files. It then moves them, piece by piece, to create large, contiguous sections of data.
During defragmentation, the software attempts to group related files together, such as system files or frequently accessed program files. It also organizes files based on their size, prioritizing larger files that require more read/write time. By organizing the files in this way, the computer can access them more efficiently and quickly, resulting in improved system performance.
The defragmentation process typically involves three stages:
- Analyzing: The software scans the hard drive to determine the level of fragmentation and identify the files that need to be reorganized.
- Defragmenting: Once the analysis is complete, the software begins moving the fragmented files and putting them back together, creating contiguous blocks of data.
- Consolidating: After the defragmentation process, the software consolidates the free space on the hard drive, ensuring that files have enough room to be stored in contiguous blocks in the future.
While the time required for defragmentation varies depending on factors such as the size of your hard drive and the level of fragmentation, it is recommended to schedule defragmentation during periods of low computer usage to avoid interruptions.
Overall, the goal of defragmentation is to optimize the storage of files and improve the efficiency of your computer’s hard drive, leading to faster access times and enhanced performance.
Why do you need to defrag your computer?
Defragmenting your computer’s hard drive is important for maintaining optimal system performance and improving overall efficiency. Here are several key reasons why you need to defrag your computer:
- Enhanced Speed: As files become fragmented, your computer takes longer to access and retrieve the data it needs. Defragmentation rearranges the files, placing them in contiguous blocks, allowing for faster read and write speeds. This results in improved performance and reduced waiting times when opening applications or accessing files.
- Improved File Organization: Over time, as you create, modify, and delete files, gaps and fragments occur, leading to disorganized storage. Defragmentation regroups related files and ensures that data is stored in a more organized manner. This makes it easier for the operating system to locate and access files, resulting in smoother file management and a more efficient system.
- Extended Hardware Lifespan: Fragmented files cause your hard drive to work harder, as it needs to search scattered parts of data. This continuous strain on the drive can lead to increased wear and tear, reducing its overall lifespan. By defragmenting your computer regularly, you reduce the workload on the hard drive, potentially extending its longevity.
- Decreased System Crashes: Fragmented files can increase the likelihood of system crashes and freezes. When your computer struggles to locate and access the necessary data, it can lead to instability and errors. By defragmenting your computer, you minimize the chances of experiencing system crashes and enjoy a more stable computing experience.
- Optimized Disk Space: Defragmentation not only reorganizes files but also consolidates free space on your hard drive. This consolidation ensures that future files can be stored in larger contiguous blocks, reducing fragmentation and maximizing available disk space. As a result, you can make the most efficient use of your storage capacity.
By regularly defragmenting your computer’s hard drive, you can maintain peak performance, extend the lifespan of your hardware, and enjoy a smoother, more efficient computing experience. It is a beneficial practice for any computer user, whether you use your computer for personal tasks, work, or gaming.
Factors determining the frequency of defragmentation
When it comes to determining how often you should defragment your computer, several factors come into play. While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer, considering these factors can help you establish an appropriate defragmentation schedule:
- Usage: The frequency of defragmentation can vary based on how heavily you use your computer. If you regularly create, modify, or delete large files, your hard drive is more likely to become fragmented faster. In such cases, more frequent defragmentation may be necessary to maintain optimal performance.
- Storage Capacity: The size of your hard drive and the amount of free space available also impact the need for defragmentation. Larger hard drives with ample free space generally experience less fragmentation compared to smaller drives or drives with limited free space. If you have a small capacity drive or are consistently using a significant portion of the available space, you may need to defrag more frequently.
- Computing Activities: Different computing activities can contribute to fragmentation at varying rates. For example, activities such as video editing, gaming, and running virtual machines can generate a higher number of temporary files and lead to faster fragmentation. If you engage in resource-intensive activities, it is advisable to defragment more frequently.
- Operating System and File System: The operating system and file system you use can influence the fragmentation rate. Modern operating systems, such as Windows 10 or macOS, have built-in tools that automatically defragment your drive in the background, reducing the need for manual intervention. Additionally, different file systems handle file allocation and organization differently, resulting in varying levels of fragmentation.
- Age of the Computer: Older computers often have slower hard drives, which can experience more significant fragmentation. If you are using an older computer, you may need to defragment more frequently to counteract the performance degradation caused by fragmentation.
It is important to strike a balance when determining the frequency of defragmentation. Defragmenting too frequently may cause unnecessary wear on your hard drive, while defragmenting too infrequently can lead to performance degradation. Observing the aforementioned factors and regularly monitoring your computer’s performance will help you find the optimal defragmentation schedule for your specific needs.
Recommended frequency for different types of computers
The recommended frequency for defragmentation can vary depending on the type of computer you have. While there is no exact formula that applies to all situations, considering the following guidelines can help you determine the ideal defragmentation schedule for your specific computer:
- Traditional Hard Drives: For computers with traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), it is generally recommended to defragment them every one to three months. HDDs are more prone to fragmentation due to their mechanical nature, and regular defragmentation can help maintain their performance over time.
- SSDs and Hybrid Drives: Solid State Drives (SSDs) and hybrid drives, which combine both solid-state and mechanical storage, do not require regular defragmentation. In fact, defragmenting SSDs can reduce their lifespan and does not provide performance benefits. Some operating systems have built-in optimizations specifically designed for SSDs, which automatically manage their storage efficiency. Therefore, you can avoid defragmenting SSDs and hybrid drives.
- Excessive Fragmentation: If you notice a significant decline in performance or experience frequent system crashes, it may be necessary to defragment your computer more frequently than the recommended guidelines. Excessive fragmentation can severely impact your computer’s performance, and defragmenting it more often can help alleviate these issues.
- Automatic Defragmentation: Many modern operating systems come with built-in automatic defragmentation tools that run in the background. These tools perform regular maintenance and defragmentation tasks, ensuring that your files remain organized and your computer functions optimally. If your operating system offers automatic defragmentation, you can rely on this feature and adjust the schedule or frequency based on your specific needs.
It is worth mentioning that as technology evolves, the need for manual defragmentation decreases. Newer operating systems and storage technologies are designed to handle fragmentation more efficiently, reducing the need for frequent manual intervention. However, it is always a good practice to monitor your computer’s performance and defragment it as needed to keep your system running smoothly.
Signs that your computer needs to be defragmented
While regular defragmentation is important for maintaining optimal performance, it can be helpful to know the signs that indicate your computer may be due for a defragmentation. Here are some common signs that your computer needs to be defragmented:
- Slow Performance: One of the most noticeable signs that your computer needs to be defragmented is slow performance. If your computer is taking longer to boot up, open programs, or access files, it could be due to the fragmentation of data on your hard drive. Defragmenting your computer can help consolidate the fragmented files and improve system responsiveness.
- Longer File Access Times: If you notice that it takes longer for your computer to open files or save changes to files, it could be an indication of fragmentation. Fragmented files require the hard drive to search for scattered parts of the data, leading to increased access times. Defragmenting your computer can reduce these access times and speed up file operations.
- Frequent Freezing or Crashing: Fragmented files can cause your computer to freeze or crash frequently. When the hard drive struggles to locate and retrieve the necessary data, it can lead to system instability. If you experience frequent freezes or crashes, defragmenting your computer can help resolve these issues and provide a more stable computing experience.
- Inefficient File Organization: Fragmentation can result in disorganized file storage. If you find it difficult to locate specific files or notice that files are scattered across different areas of your hard drive, it may be a sign that your computer needs defragmentation. Defragmenting your computer can help organize and consolidate the files, making them easier to find and manage.
- Increased Disk Activity: When your computer’s hard drive is fragmented, it needs to work harder to access and retrieve data. This can lead to increased disk activity, with the hard drive constantly spinning and working to locate the fragmented files. If you hear excessive noise coming from your computer’s hard drive or notice the hard drive light frequently flashing, it may be an indication that defragmentation is needed.
Recognizing these signs and addressing them promptly by defragmenting your computer can help restore optimal performance and improve your overall computing experience. It is recommended to regularly monitor your computer’s performance and consider defragmentation as a potential solution whenever you notice these signs.
The dangers of over-defragmentation
While defragmentation is beneficial for maintaining optimal performance, it is important to be aware of the potential dangers of over-defragmentation. Here are some risks associated with excessive or unnecessary defragmentation:
- Increased Wear on the Hard Drive: Every time you defragment your computer, it involves the movement of a large amount of data on your hard drive. Excessive defragmentation can cause unnecessary wear and tear on the drive, potentially shortening its lifespan. It is important to strike a balance and defragment your computer only when necessary.
- Decreased Performance: While defragmentation helps improve performance by organizing and consolidating files, overdoing it can have the opposite effect. Excessive defragmentation can lead to unnecessary file movements, resulting in increased disk activity and decreased overall system performance. It is crucial to observe the recommended frequency for defragmentation to avoid diminishing returns.
- Unnecessary Resource Consumption: Defragmentation is a resource-intensive process that requires significant CPU and hard drive usage. Over-defragmenting your computer can consume valuable system resources, causing a slowdown and affecting other tasks you may be performing simultaneously. Balancing the defragmentation process with other system activities is essential to prevent resource exhaustion.
- Potential Data Loss: Although the risk is low, there is a small possibility of data loss during the defragmentation process. The movement of large amounts of data increases the chances of encountering a hardware or software failure, which could result in data corruption or loss. It is always wise to back up your important files before undertaking any disk maintenance procedures.
- SSD Wear and Lifespan: Over-defragmenting solid-state drives (SSDs) is not only unnecessary but also detrimental. SSDs have a finite lifespan determined by the number of write cycles they endure. Defragmenting SSDs can cause more write operations, potentially reducing their overall lifespan. It is advisable to avoid defragmenting SSDs and rely on the built-in optimization features provided by the operating system.
It is crucial to defragment your computer responsibly and follow the recommended guidelines to avoid the dangers associated with over-defragmentation. Regularly monitor your computer’s performance and visually inspect the fragmented state of your hard drive before proceeding with defragmentation. By finding the right balance, you can ensure that your computer operates efficiently without risking unnecessary wear, data loss, or diminished performance.
How to defragment your computer
Defragmenting your computer is a straightforward process that can help improve performance and optimize your hard drive. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to defragment your computer:
- Check disk health: Before initiating the defragmentation process, ensure that your hard drive is in good health. Run a disk check utility to identify and resolve any disk errors or issues. This will help prevent potential data loss or corruption during the defragmentation process.
- Close unnecessary applications: Close any open programs and applications running on your computer. This will free up system resources and allow the defragmentation process to run more efficiently without interruptions.
- Open the defragmentation tool: Depending on your operating system, you can access the built-in defragmentation tool. For Windows users, go to the “Start” menu, type “defragment” in the search bar, and select “Defragment and Optimize Drives.” Mac users can open “Disk Utility” and choose the hard drive they want to defragment.
- Select the drive to defragment: In the defragmentation tool, select the hard drive you want to defragment. If you have multiple drives, prioritize the one that houses your operating system and frequently used files.
- Initiate the defragmentation process: Click on the “Optimize” or “Defragment” button to start the defragmentation process. The tool will analyze the drive, identify fragmented files, and begin organizing them into contiguous blocks. The time required will depend on the size of the drive and the level of fragmentation.
- Monitor the progress: While the defragmentation process is running, you can monitor its progress. Some tools provide a visual representation of the fragmented files being rearranged. It is important to avoid interrupting the process to ensure the best results.
- Review the results: Once the defragmentation process is complete, review the results provided by the tool. It should indicate the level of fragmentation before and after the process, allowing you to assess the effectiveness of the defragmentation.
- Restart your computer: After defragmenting your hard drive, it is recommended to restart your computer. This will allow the system to fully optimize and integrate the changes made during the defragmentation process.
It is important to note that the exact steps may vary slightly depending on your operating system and the version of the defragmentation tool you are using. Additionally, it is generally recommended to schedule defragmentation during periods of low computer usage to avoid interruptions and maximize resources.
By following these steps and defragmenting your computer regularly, you can improve performance, reduce file access times, and maintain an organized file system on your hard drive.
Alternative methods to optimize your computer’s performance
In addition to defragmentation, there are several alternative methods you can utilize to optimize your computer’s performance. These methods focus on improving overall system efficiency and can complement the benefits of defragmentation. Here are some alternative methods worth considering:
- Regular Disk Cleanup: Performing regular disk cleanup helps remove unnecessary files and frees up disk space. Use the built-in disk cleanup utility in your operating system to remove temporary files, system caches, and other clutter that accumulates over time. This can help improve performance and maintain a lean file system.
- Update Software and Drivers: Keeping your software and drivers up to date is crucial for a smooth and optimized computing experience. Outdated software and drivers can result in performance issues and vulnerabilities. Regularly check for updates and install them to ensure optimal functionality and compatibility.
- Manage Startup Programs: Take control of the programs that start automatically when you boot up your computer. Many applications set themselves to launch at startup, which can slow down the boot process and consume system resources. Review and disable unnecessary startup programs to improve startup times and free up resources.
- Remove Unwanted or Unused Programs: Over time, your computer may accumulate unused or unwanted programs and applications. These can take up valuable storage space and potentially impact performance. Regularly uninstall programs that you no longer need to free up disk space and streamline system resources.
- Upgrade Hardware: If your computer is still experiencing sluggish performance despite regular maintenance and optimization, it may be time to consider upgrading hardware components. Upgrading the RAM, hard drive, or processor can significantly enhance your computer’s speed and responsiveness. Consult with a professional or research compatible upgrades for your specific computer model.
- Scan for Malware and Viruses: Malware and viruses can cause significant performance degradation and compromise your computer’s security. Regularly scan your system with an up-to-date antivirus program to detect and remove any malicious software. Additionally, use anti-malware software to identify potential threats and ensure your computer remains protected.
- Optimize Power Settings: Adjusting power settings can help optimize your computer’s performance based on your usage patterns. For example, switching to the “High Performance” power plan can provide a performance boost but may consume more energy. Balance your power settings to match your needs and optimize performance accordingly.
- Manage Browser Extensions: Excessive browser extensions can slow down web browsing and consume system resources. Regularly review and remove unnecessary or unused browser extensions to streamline your browsing experience.
By incorporating these alternative methods into your regular computer maintenance routine, you can enhance system performance, optimize resource utilization, and ensure a smooth and efficient computing experience.
Tips to prevent fragmentation
Preventing fragmentation in the first place can help maintain optimal system performance and minimize the need for frequent defragmentation. Here are some useful tips to help prevent fragmentation on your computer:
- Regularly Clean Up Your Disk: Perform regular disk cleanup to remove unnecessary files and free up disk space. This helps minimize the chances of fragmentation by reducing the amount of temporary and unnecessary data on your hard drive.
- Avoid Near-Full Hard Drives: Keep a sufficient amount of free space on your hard drive. When a hard drive reaches near-full capacity, it becomes more susceptible to fragmentation. Aim to have at least 15-20% of your hard drive’s total space available to prevent excessive fragmentation.
- Install Programs and Store Files Wisely: Organize your files and install programs in a strategic manner. Avoid saving files and installing programs directly on your desktop or in the root directory of your hard drive. Instead, create organized folders and directories to categorize and store your data. This helps minimize fragmentation and keeps files more contiguous.
- Monitor and Manage Your Downloads: Be mindful of large file downloads, particularly if your hard drive is already near full capacity. Downloading multiple large files simultaneously can quickly fragment your hard drive. Consider scheduling downloads during periods of low computer usage to minimize the impact on fragmentation.
- Regularly Update Operating System and Software: Keeping your operating system and software up to date not only provides you with the latest features and security patches but can also include optimizations that help prevent fragmentation and improve overall file system efficiency.
- Defragment with Smart Scheduling: If you still opt to defragment your computer manually, establish a smart defragmentation schedule. Choose a time when your computer is not in heavy use, such as during overnight hours, and schedule regular defragmentation sessions based on your usage patterns.
- Use Solid-State Drives (SSDs): Consider upgrading to an SSD if you have not done so already. Unlike traditional hard drives, SSDs do not require defragmentation as their storage is not affected by file fragmentation. SSDs offer faster and more efficient storage, reducing the need for defragmentation altogether.
- Invest in Regular Hardware Maintenance: Keeping your computer hardware in good condition also plays a role in preventing fragmentation. Regularly clean your computer to remove dust and debris, ensure proper airflow, and prevent excessive heating. Overheating can lead to performance issues, which may contribute to fragmentation.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce the chances of fragmentation and maintain a more organized and efficient file system on your computer.