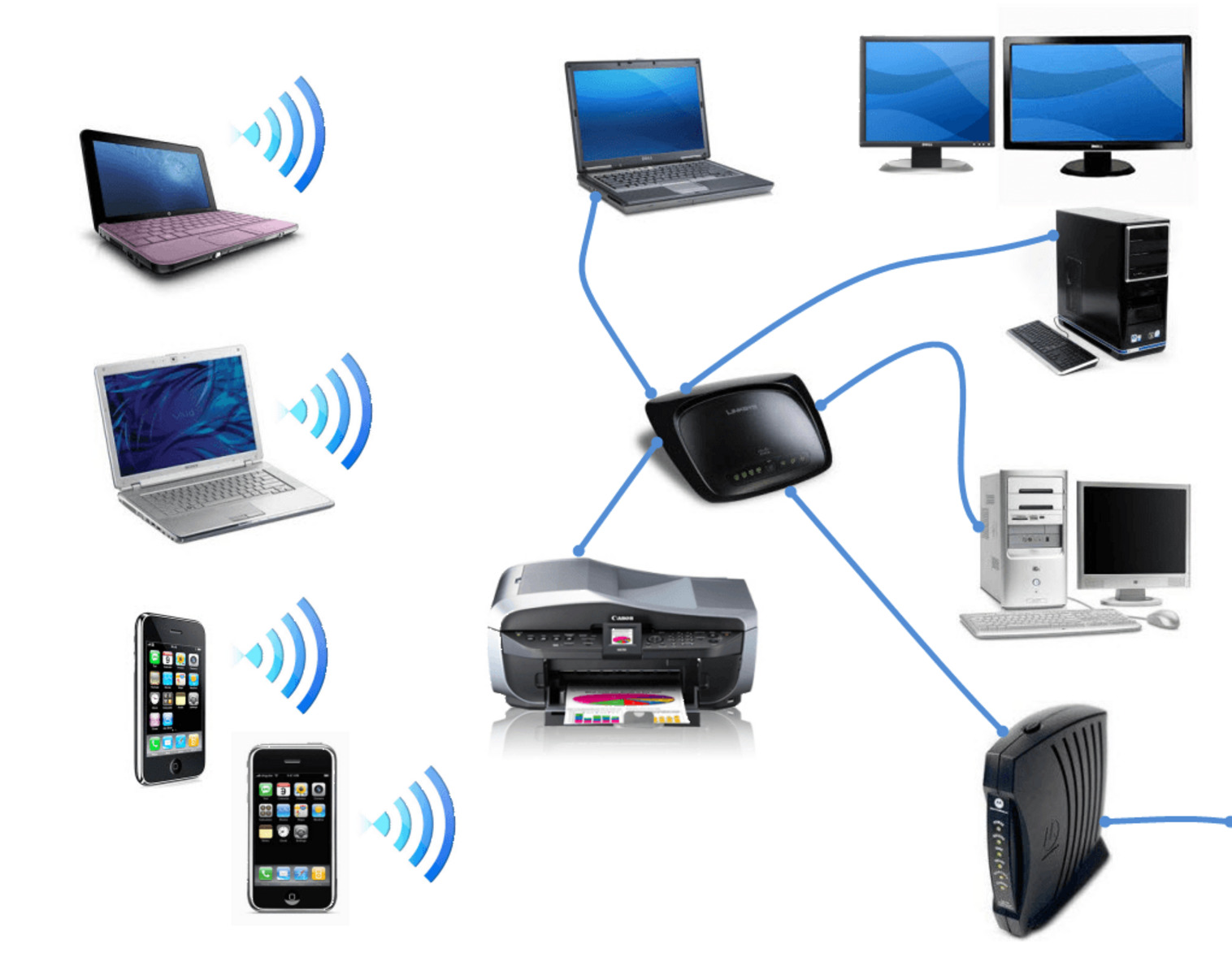
Common Issues with Home Computer Networks
A home computer network is an essential part of our daily lives, providing us with seamless connectivity and access to the digital world. However, like any technological system, home networks can encounter various challenges that can disrupt their performance and reliability. In this section, we will explore some of the most common issues that homeowners face with their computer networks and how to troubleshoot them.
One prevalent issue with home computer networks is a slow or unstable internet connection. This can be frustrating, especially when you are trying to stream your favorite show or complete an important online task. One possible cause of this problem is outdated network equipment, such as routers or modems. Ensure that your equipment supports the latest Wi-Fi standards to maximize speed and stability.
Another issue is poor network coverage. Sudden drops in signal strength or dead zones can hinder your ability to connect to the network from certain areas of your home. This can be caused by physical barriers like walls or interference from other devices. Placing your router in a central location and away from obstructions can help improve coverage. You can also use range extenders or mesh Wi-Fi systems to expand the reach of your network.
Security is a crucial concern for home networks. Without proper protection, your network and connected devices may be vulnerable to cyber threats. Weak or default passwords, outdated firmware, and unsecured Wi-Fi networks are some of the common security risks. Make sure to set strong passwords, update your firmware regularly, and enable encryption on your Wi-Fi network to safeguard your data.
Home networks can also experience connectivity issues due to conflicts between devices. Incompatible network settings, software conflicts, or IP address conflicts can lead to connection drops or limited access. Double-check your network settings, update your device drivers, and ensure that each device on your network has a unique IP address to prevent conflicts.
Lastly, network congestion can be a source of frustration, especially in homes with multiple connected devices. Bandwidth-heavy activities like streaming, gaming, or file sharing can strain your network, causing slow speeds and latency. Consider upgrading your internet plan, implementing Quality of Service (QoS) settings, or scheduling usage times to manage network congestion effectively.
Troubleshooting Wired Home Networks
Wired home networks offer reliable and stable connections, but occasionally, issues may arise that disrupt the network’s functionality. In this section, we will discuss some common troubleshooting steps to help you identify and resolve problems with your wired home network.
The first step in troubleshooting a wired home network is to check the physical connections. Ensure that all cables are securely plugged in at both ends, and there are no loose connections or damaged cables. Sometimes, a simple reconnecting of cables can resolve connectivity issues.
If you are experiencing connectivity problems with a specific device, try connecting it to a different port on your router or switch. This can help determine whether the issue lies with the device’s network interface or the specific port on the networking equipment.
Next, verify the network settings on your devices. Ensure that they are configured to obtain IP addresses automatically through DHCP, unless you have specific requirements for static IP addresses. Incorrect network settings can cause connection problems or conflicts with other devices on the network.
If all physical connections and settings are correct, but you still have connectivity issues, it may be helpful to power cycle your networking equipment. Start by turning off your modem, router, and any connected switches. Wait for a few minutes, then turn them back on in the following order: modem, router, and switch. This can often resolve temporary network issues or conflicts.
If you are still experiencing problems with your wired network, you may need to update the firmware on your router or switch. Manufacturers periodically release firmware updates to fix bugs and improve performance. Visit the manufacturer’s website to check for any available firmware updates for your networking devices and follow their instructions for updating the firmware.
In some cases, network issues may be caused by interference from other electronic devices. Electrical devices like cordless phones, microwave ovens, or even fluorescent lights can introduce electrical noise that interferes with your network signal. Try moving your networking equipment away from these devices or using shielded Ethernet cables to minimize interference.
Ultimately, if you have exhausted all troubleshooting steps and are still unable to resolve the issue, it may be helpful to consult with a professional network technician who can diagnose and fix more complex network problems.
Troubleshooting Wireless Home Networks
Wireless home networks have become increasingly popular due to their convenience and flexibility. However, they can encounter issues that affect the wireless signal and connectivity. In this section, we will discuss common troubleshooting steps to help you identify and resolve problems with your wireless home network.
The first step in troubleshooting a wireless home network is to check the signal strength. Weak signal strength can lead to slow or intermittent connections. Position your Wi-Fi router in a central location within your home, away from obstacles like walls or large objects that can interfere with the signal. If needed, consider using a Wi-Fi range extender to amplify the signal and expand the coverage area.
Interference is another common issue in wireless networks. Other electronic devices, such as microwaves, cordless phones, or even neighboring Wi-Fi networks, can interfere with your signal and degrade performance. Switch your router to a less congested channel or use the 5 GHz band, which is typically less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band. Additionally, moving your router away from these devices can help minimize interference.
Ensure that your Wi-Fi router is running the latest firmware version. Manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities and improve performance. Visit the manufacturer’s website to check for firmware updates for your specific router model and follow the instructions provided to update the firmware.
Password protect your Wi-Fi network to prevent unauthorized access. If you suspect that someone may be accessing your network without permission, change your Wi-Fi password immediately. Additionally, enable network encryption, such as WPA2, to protect your data from being intercepted.
If you are experiencing connection drops or slow speeds, restart your router and modem. Sometimes, this simple step can resolve temporary network issues. Power off both devices, wait for a few minutes, and then power them back on. Give them a few moments to establish a connection before checking your Wi-Fi network’s performance.
Another troubleshooting step is to update the Wi-Fi drivers on your devices. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause connection problems. Visit the manufacturer’s website of your computer or device to download and install the latest Wi-Fi drivers specific to your operating system.
If none of the above steps resolve your wireless network issues, it may be helpful to perform a factory reset on your router. This will restore it to its default settings, giving you a clean slate to set up your network again. Keep in mind that performing a factory reset will erase any custom settings you have made, so make sure to backup any important configurations beforehand.
If you continue to experience issues with your wireless network, contacting your internet service provider or seeking assistance from a professional network technician can help diagnose and resolve more complex problems.
Securing Your Home Network
Securing your home network is crucial to protect your personal information, devices, and privacy. With the increasing number of connected devices in our homes, it is essential to implement strong security measures. In this section, we will discuss key steps to secure your home network and keep it safe from potential threats.
The first and most fundamental step in securing your home network is to change the default administrator password on your router. Default passwords are well-known and easily accessible to hackers. Set a strong and unique password that combines uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Enabling network encryption is the next essential step. Use Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) encryption, which is the most secure option available for home networks. This encryption standard ensures that data transmitted between your devices and the router is encrypted, making it difficult for unauthorized users to access your network.
Regularly updating your router’s firmware is crucial for security. Manufacturers release firmware updates to fix vulnerabilities and improve overall network performance. Check the manufacturer’s website for any available firmware updates specific to your router model, and follow their instructions to install them.
It is also important to disable remote management on your router. Remote management allows anyone on the internet to access and control your router’s settings. By disabling this feature, you prevent unauthorized users from tampering with your network configuration.
Another layer of protection is to enable firewall features on your router. Firewalls act as a barrier between your home network and the internet, blocking potential threats. Most routers come with built-in firewall features that you can enable within the router’s settings.
Segmenting your network can further enhance security. Create separate Wi-Fi networks, such as a guest network and a private network, with different passwords. This helps ensure that guests do not have access to your main network, protecting your sensitive information.
Implementing strong and unique passwords for all your connected devices is also crucial. Many smart devices have default passwords that are easy to guess. Change these passwords to complex combinations to prevent unauthorized access to your devices.
Regularly checking for and updating security patches on your devices is another important step. Manufacturers release patches to fix vulnerabilities that hackers may exploit. Set up automatic updates on your devices to ensure that you are always running the latest security software.
Lastly, consider using a virtual private network (VPN) when accessing your home network remotely. A VPN creates an encrypted connection between your device and your home network, ensuring that your data is protected while transmitting over the internet.
By following these steps and implementing strong security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your home network from potential threats.
Setting Up a Wired Home Network
A wired home network provides a stable and reliable internet connection, making it an excellent choice for households with heavy internet usage or if you require consistent connectivity for gaming, streaming, or working from home. In this section, we will guide you through the process of setting up a wired home network.
The first step in setting up a wired home network is to determine the location for your network equipment. Choose a central location in your home, preferably near the main area where you will be connecting devices. This location should have easy access to a power outlet and your internet service provider’s modem.
Next, connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on your modem. This port is usually labeled as “Internet” or “WAN.” Then, connect the other end of the cable to the Ethernet port on your router. This connection will allow your router to receive the internet signal from the modem.
If you have multiple devices that require a wired connection, connect an Ethernet cable from each device to one of the Ethernet ports on the router. These ports are typically labeled as “LAN.” You may use additional equipment such as switches or hubs to expand the number of available ports if needed.
To ensure optimal performance, use high-quality Ethernet cables. Cat6 or Cat6a cables are recommended for Gigabit Ethernet connections, offering faster speeds and better performance than older cables.
Once all the physical connections are in place, power on your modem and then your router. Give the devices a few moments to boot up and establish a connection.
Access your router’s configuration settings using a web browser by entering its default IP address in the address bar. This IP address can usually be found in the router’s manual or on the manufacturer’s website. From the configuration settings, you can set up a network name (SSID) and secure your network with a strong password.
If you have devices that require a wired connection in different areas of your home, you may need to run Ethernet cables through walls, ceilings, or floors. If you are not confident in doing this yourself, it is advisable to consult a professional technician to ensure proper cable routing and installation.
Lastly, test your wired home network by connecting devices to the Ethernet ports on the router. Check if the devices are receiving an internet connection and ensure that the network is stable. Troubleshoot any connectivity issues, such as checking for loose cables or incorrect network settings.
Setting up a wired home network provides a reliable and high-speed internet connection for your home. With the proper planning and equipment, you can enjoy seamless connectivity across all your devices.
Setting Up a Wireless Home Network
A wireless home network offers the convenience of connecting devices without the need for cables, allowing you to enjoy internet access from any corner of your home. Whether you’re streaming movies or working remotely, setting up a wireless home network is relatively straightforward. In this section, we will guide you through the process of setting up a wireless home network.
The first step in setting up a wireless home network is to acquire a wireless router. Look for a router that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), for optimal performance and compatibility with newer devices.
Find a central location in your home to place the router. This will help ensure maximum coverage and a strong signal throughout your residence. Keep the router away from walls, large objects, and dense areas to minimize signal interference.
Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on your modem, and the other end to the WAN or Internet port on your router. This connection will allow your router to receive the internet signal from the modem.
Connect the router to a power outlet and turn it on. Wait for the router to boot up and establish a connection with the modem. Most routers have indicator lights that will show when they are ready to proceed.
On your computer or mobile device, open the Wi-Fi settings and look for available networks. Locate your router’s network name (SSID), which is typically labeled on the router itself, and click or tap to connect.
Enter the network password if prompted. By default, many routers come with a pre-set password that is usually printed on a label attached to the router. For security purposes, it is recommended to change this default password to a unique, strong password.
Once connected, you can access the router’s configuration settings through a web browser by entering the default IP address in the address bar. From there, you can customize your network settings, including renaming your network, enabling encryption (WPA2 is recommended), and adjusting other preferences as desired.
Consider creating a separate guest network for visitors to use. This network will restrict access to your main network and keep your personal devices and data secure. Most routers offer an option to set up a guest network within the configuration settings.
After configuring the router settings, test the wireless connection on your devices by connecting to the network. Ensure that all connected devices are receiving a stable internet connection and adjust the router’s placement if necessary to optimize signal strength.
If you have devices that require a wired connection, such as desktop computers or gaming consoles, you can connect them to the available LAN ports on your router using Ethernet cables.
With your wireless home network successfully set up, you can now enjoy the convenience of connecting multiple devices wirelessly and accessing the internet from anywhere in your home.
Choosing the Right Network Equipment
Choosing the right network equipment is essential for setting up a reliable and high-performance home network. With a wide variety of options available on the market, it is important to consider your specific needs and requirements. In this section, we will discuss key factors to consider when selecting network equipment for your home.
The first consideration is the type of network you want to set up. Determine whether you want a wired network, wireless network, or a combination of both (hybrid). Wired networks provide a stable and consistent connection, while wireless networks offer flexibility and convenience. Consider your internet usage, the number of devices you have, and the coverage area to make an informed decision.
When it comes to routers, look for models that support the latest Wi-Fi standards. The most current standard is Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), which offers faster speeds, better performance, and improved device capacity. However, if your devices do not support Wi-Fi 6, consider a router that supports the previous standard, Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac), for compatibility.
For wired connections, ensure that the router has enough Ethernet ports to accommodate your devices. Consider the number of wired devices you have, such as desktops, gaming consoles, or smart TVs, and choose a router that offers sufficient ports. Additionally, look for routers that have Gigabit Ethernet ports for faster wired connections.
In terms of network security, prioritize routers that offer robust security features. Look for routers that support WPA2 or WPA3 encryption standards, as these provide better protection for your data. Advanced security features like guest network access, VPN support, and built-in firewalls can also enhance the security of your home network.
Consider the size of your home and the coverage area required. If you have a larger home or multiple floors, opting for a router with strong signal strength and good range is important. Some routers come with beamforming technology, which can focus the Wi-Fi signal towards connected devices, improving overall coverage.
Another essential aspect is the performance and speed of the router. Look for routers with multiple antennas and high data transfer rates to ensure faster and more reliable internet connections. Consider the internet speed provided by your service provider and choose a router capable of handling that speed without bottlenecking.
Research and read reviews about different router models to gather insights into their performance, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Look for brands with a good reputation and positive feedback from users. Consider reaching out to technical support or customer service to assess their responsiveness and helpfulness in case you encounter any issues.
Finally, keep your budget in mind. Set a budget range and explore options within that range. Remember that investing in quality network equipment can offer better long-term performance and durability, so strike a balance between price and quality.
By considering these factors when choosing your network equipment, you can ensure that you set up a home network that meets your specific requirements and provides reliable and high-speed internet connectivity for all your devices.
Extending the Range of Your Wireless Network
Having a strong and reliable Wi-Fi signal throughout your home is crucial for seamless connectivity. However, certain factors such as the layout of your home or physical barriers can limit the range of your wireless network. Fortunately, there are several methods you can employ to extend the range of your wireless network and ensure a reliable signal in every corner of your home. In this section, we will explore some effective ways to extend the range of your wireless network.
The simplest and most immediate way to extend the range of your wireless network is by repositioning your router. Place your router in a central location, away from walls and obstructions. It is recommended to position it at an elevated level to allow the signal to spread further. Avoid placing it in basements or corners of the house where the signal may be obstructed.
If repositioning the router does not provide sufficient coverage, consider using a Wi-Fi range extender or repeater. These devices receive the existing Wi-Fi signal and amplify it, extending the coverage area. Place the range extender in an area where the signal from the router is still strong, and it can rebroadcast the signal to areas with weak coverage.
Alternatively, you can opt for a mesh Wi-Fi system. A mesh system consists of multiple nodes that work together to create a seamless Wi-Fi network. These nodes can be strategically distributed throughout your home to provide uniform coverage. Mesh Wi-Fi systems often come with a dedicated backhaul channel, ensuring fast and reliable connections throughout your home.
If you have a large home or face multiple obstructions, you might consider using powerline adapters with built-in Wi-Fi. Powerline adapters use the existing electrical wiring in your home to transmit the internet signal. By connecting a powerline adapter to your router and plugging another adapter with Wi-Fi capabilities in a different area of your home, you can extend the network’s coverage without relying on Wi-Fi signal transmission alone.
Another option to extend your wireless network is by using directional antennas. Instead of relying on the router’s built-in omni-directional antennas, you can replace them with high-gain directional antennas. These antennas transmit the Wi-Fi signal in a specific direction, allowing you to focus the signal towards areas that need better coverage.
Consider updating your router to a newer model with advanced features to extend range and improve performance. Newer routers often have enhanced signal strength, better coverage, and improved capabilities for handling multiple devices simultaneously. Make sure to check the compatibility and specifications of the new router with your internet service provider.
Finally, remember to optimize your network settings. Use the 5 GHz frequency band if your devices support it, as it typically provides faster speeds and less interference compared to the 2.4 GHz band. Additionally, choose the appropriate Wi-Fi channel to reduce interference from neighboring networks, and regularly update your router’s firmware to ensure optimal performance.
By utilizing these techniques and selecting the most suitable method for your home, you can effectively extend the range of your wireless network and enjoy reliable Wi-Fi coverage in every part of your residence.
Managing Multiple Devices on Your Home Network
In today’s connected world, managing multiple devices on your home network is essential to ensure a smooth and efficient online experience. From smartphones and tablets to laptops, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and smart home devices, the number of devices connected to your network can quickly grow. In this section, we will discuss effective strategies for managing and optimizing your home network when dealing with multiple devices.
The first step in managing multiple devices is to ensure that your router can handle the increased load. Make sure you have a router with sufficient processing power and memory to accommodate multiple devices simultaneously. Routers with multiple antennas and MU-MIMO (Multiple-User Multiple Input, Multiple Output) technology can handle concurrent connections more efficiently.
Another crucial aspect of managing multiple devices is to assign priority to certain devices or activities. Most routers offer Quality of Service (QoS) settings that allow you to prioritize specific devices or applications, ensuring they receive sufficient bandwidth during times of high network congestion. This can be especially useful for devices or activities that require low latency, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
Consider segmenting your network by creating separate Wi-Fi networks for different types of devices. For example, you can create one network for smartphones and tablets and another network for smart TVs and gaming devices. This allows you to manage and monitor the devices more effectively and reduce potential interference or conflicts between them.
Regularly monitoring and managing your network is important to ensure optimal performance. Use network monitoring tools or apps provided by your router manufacturer to keep track of connected devices, monitor bandwidth usage, and identify any potential issues or suspicious activities. This will help you take proactive steps to troubleshoot or optimize your network when necessary.
Keep your devices and router firmware up to date. Manufacturers release updates that contain bug fixes, security patches, and performance improvements. Regularly check for firmware updates for both your devices and router and apply them as necessary to ensure stability and security.
Utilize parental control features to manage and control the internet access of devices used by children. Many routers offer parental control options that allow you to set time limits, block certain websites, and monitor online activities. These features help promote a safe and healthy online environment for younger users.
Consider using a network-attached storage (NAS) device to centralize and manage data storage across your devices. NAS devices provide additional storage capacity that can be accessed by all devices on your network, allowing for easy file sharing, media streaming, and backups.
If your network experiences congestion or limitations, upgrading your internet plan may be necessary. Contact your internet service provider to explore faster options that can accommodate the increased bandwidth requirements of multiple devices.
Finally, educate yourself and your family members about proper network usage and security practices. Encourage everyone to use strong and unique passwords, avoid suspicious websites and downloads, and be cautious when sharing personal information online. Good cyber hygiene can go a long way in maintaining a secure and efficient home network.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage multiple devices on your home network, ensure optimal performance, and maintain a reliable and secure online experience for everyone in your household.
Optimizing Your Home Network’s Performance
Optimizing the performance of your home network is crucial to ensure fast and reliable internet connectivity. Slow speeds, buffering, and lag can be frustrating, especially when engaging in bandwidth-intensive activities like streaming, online gaming, or video conferencing. In this section, we will discuss effective strategies for optimizing your home network’s performance to enhance your online experience.
The first step in optimizing your home network is to conduct a speed test to determine your current internet speed. Use reputable online speed testing tools to measure your upload and download speeds. This will give you a baseline to compare against when making improvements.
Place your Wi-Fi router in a central location within your home to maximize coverage and signal strength. Keep it away from physical barriers like walls and objects that can obstruct the signal. Elevating the router to a higher position can also help improve coverage.
Regularly update your router’s firmware to the latest version provided by the manufacturer. Firmware updates often include bug fixes, security patches, and performance improvements. Check the manufacturer’s website periodically for any available updates and follow the instructions to install them.
Optimize your Wi-Fi settings by choosing the appropriate wireless channel. Interference from neighboring Wi-Fi networks can degrade the performance of your network. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer tool to identify congested channels and switch to a less crowded channel for better performance.
Secure your Wi-Fi network to prevent unauthorized access and bandwidth theft. Use a strong password and enable encryption, such as WPA2 or WPA3, to protect your network. Limit the number of devices that can connect to your network by using MAC address filtering or guest network features.
Consider upgrading your router or modem if you are using outdated equipment. Newer models often offer better performance, improved signal strength, and advanced features that can enhance your network’s capabilities.
Reduce the number of devices connected to your network when they are not in use. Some devices and applications may consume network resources even when idle, causing unnecessary network congestion. Disconnect or disable devices that are not actively being used to free up bandwidth.
Configure Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router to prioritize specific devices or applications. This ensures that critical activities like video streaming or online gaming receive the necessary bandwidth to operate smoothly, even during periods of high network activity.
Consider using wired connections for devices that require a stable and high-bandwidth connection. Ethernet cables provide a more reliable and faster connection compared to Wi-Fi. Connect devices like gaming consoles, smart TVs, or desktop computers directly to your router using Ethernet cables.
Optimize the placement of wireless devices within your home to maximize signal strength. Avoid placing devices that can cause electromagnetic interference, such as cordless phones or microwaves, near your router or other crucial networking equipment.
Monitor your network bandwidth usage to identify any devices or applications that may be consuming excessive bandwidth. This can help you identify any potential network congestion issues or activities that may affect performance.
If you are experiencing persistent performance issues, it may be helpful to contact your internet service provider (ISP) to ensure that you are subscribed to an appropriate internet plan. Your ISP can provide insights into any potential network issues or offer recommendations for improving your service.
By implementing these optimization strategies, you can significantly improve the performance of your home network, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable online experience for all your internet activities.