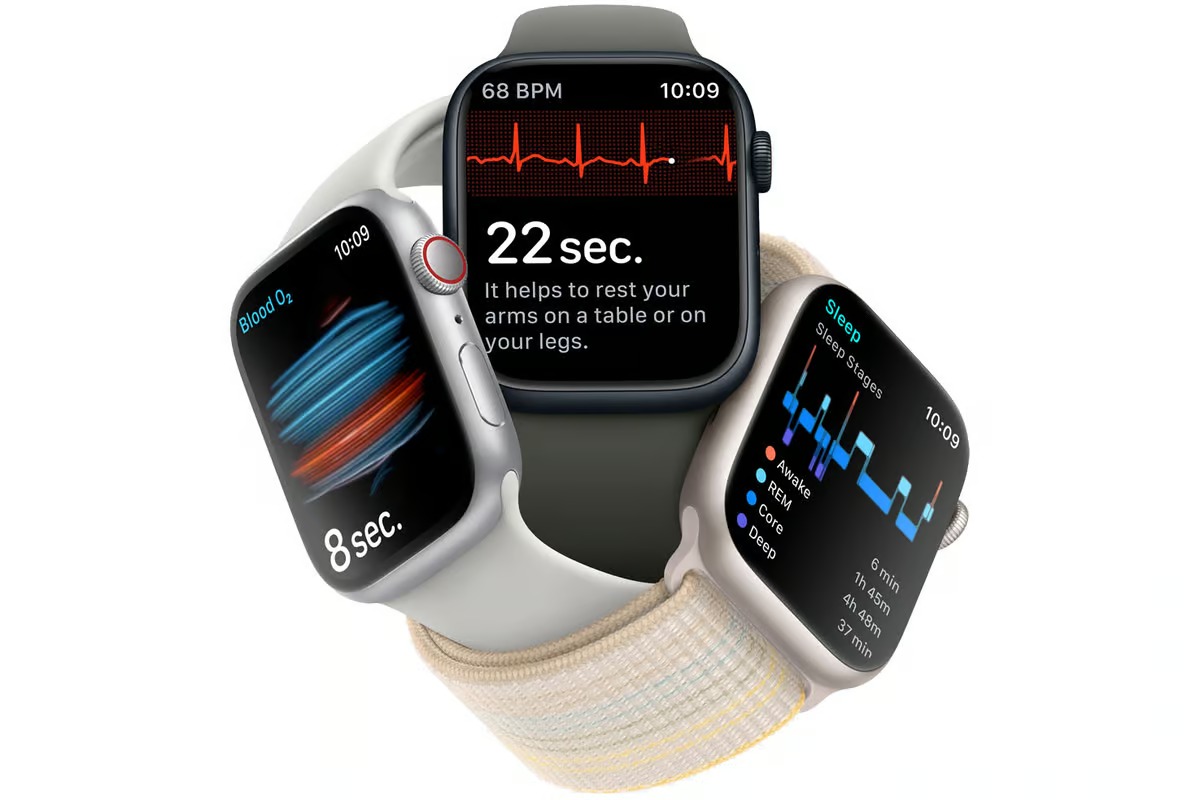
What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic tool used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. This non-invasive procedure is commonly performed in medical settings to assess the heart's rhythm and detect any irregularities. ECG technology records the electrical impulses generated by the heart as it beats, producing a visual representation of the heart's activity.
Understanding ECG Readings
An ECG reading typically consists of multiple waveforms and intervals, each providing valuable information about the heart's function. The P wave represents the atrial depolarization, while the QRS complex signifies ventricular depolarization. The T wave indicates ventricular repolarization. By analyzing these components, healthcare professionals can identify abnormalities such as arrhythmias, ischemia, and other cardiac conditions.
Diagnostic Significance
ECG technology plays a crucial role in diagnosing various cardiac conditions, including atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and myocardial infarction. The ability to detect these conditions early can significantly impact patient outcomes by enabling timely intervention and treatment.
Importance of ECG in Preventive Healthcare
In addition to diagnosing existing cardiac issues, ECGs are also valuable in preventive healthcare. They can help identify individuals at risk of developing heart conditions, allowing for proactive measures to be taken to mitigate potential health risks.
Accessibility and Advancements
Traditionally, ECGs were confined to clinical settings and required specialized equipment operated by trained professionals. However, technological advancements have led to the integration of ECG capabilities into wearable devices, such as smartwatches, making this diagnostic tool more accessible to a broader population.
Significance of ECG in Smartwatches
The incorporation of ECG technology in smartwatches has revolutionized personal health monitoring. Individuals can now conveniently perform ECG recordings on the go, empowering them to monitor their heart health proactively.
In summary, ECG technology provides valuable insights into the heart's electrical activity, aiding in the diagnosis of cardiac conditions and contributing to preventive healthcare. Its integration into smartwatches marks a significant advancement in personal health monitoring, offering users the convenience of conducting ECG recordings anytime, anywhere.
How does ECG technology work in smartwatches?
ECG technology in smartwatches operates through the use of built-in sensors that detect the electrical signals produced by the heart. When a user initiates an ECG recording on their smartwatch, the sensors make contact with the user’s skin, typically through the back of the device or the sides of the watch case. This contact enables the sensors to capture the electrical impulses generated by the heart’s activity.
Data Acquisition and Processing
Upon contact with the skin, the sensors in the smartwatch begin to record the electrical signals, which are then processed by the device’s internal algorithms. These algorithms analyze the signals to identify the various components of the ECG, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Once the analysis is complete, the smartwatch generates a visual representation of the ECG waveform, which can be viewed on the device’s display or through a companion app on a paired smartphone.
User Interaction and Interpretation
During the ECG recording process, the smartwatch may prompt the user to remain still and refrain from talking to ensure the accuracy of the reading. Once the recording is finished, the user can review the ECG waveform and, in some cases, add notes or symptoms associated with the recording. Some smartwatches also offer features that enable users to share the ECG data with healthcare professionals for further analysis and interpretation.
Regulatory Compliance and Accuracy
Smartwatches equipped with ECG technology are often subjected to rigorous testing and validation to ensure that the ECG readings meet established standards for accuracy and reliability. Regulatory bodies may require smartwatch manufacturers to demonstrate the device’s ability to consistently produce accurate ECG recordings, thereby providing users and healthcare professionals with confidence in the data’s clinical relevance.
Integration with Health Ecosystem
Many smartwatches with ECG capabilities are designed to integrate seamlessly with broader health ecosystems, allowing users to consolidate their ECG data with other health metrics, such as heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns. This integration enables users to gain comprehensive insights into their overall well-being and facilitates the correlation of ECG findings with other health-related data.
ECG technology in smartwatches leverages sophisticated sensors and algorithms to capture, process, and present the heart’s electrical activity in a user-friendly format. The integration of ECG capabilities into smartwatches has empowered individuals to take a proactive approach to monitoring their heart health, thereby contributing to a more informed and engaged healthcare experience.
Benefits of ECG Technology in Smartwatches
The integration of ECG technology in smartwatches offers a myriad of benefits that contribute to enhanced personal health monitoring and early detection of potential cardiac issues. These benefits extend to users, healthcare professionals, and the broader healthcare ecosystem.
1. Proactive Heart Health Monitoring
Smartwatches equipped with ECG technology empower users to proactively monitor their heart health by enabling on-demand ECG recordings. This capability allows individuals to capture and review their heart’s electrical activity, facilitating the early identification of irregularities or arrhythmias. By fostering a proactive approach to heart health, ECG-enabled smartwatches encourage users to prioritize preventive care and seek timely medical attention if necessary.
2. Timely Detection of Arrhythmias
The ability to perform ECG recordings using smartwatches facilitates the timely detection of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation. Early identification of these irregular heart rhythms can prompt users to seek medical evaluation and intervention, potentially preventing adverse cardiac events and improving long-term health outcomes.
3. Enhanced User Engagement
ECG technology in smartwatches promotes user engagement with their health by providing tangible data regarding their heart’s electrical activity. The visual representation of ECG waveforms on the smartwatch display or companion app fosters a deeper understanding of one’s cardiac health, encouraging users to take an active role in monitoring and managing their well-being.
4. Facilitation of Remote Healthcare
Smartwatches with ECG capabilities facilitate remote healthcare by enabling users to share ECG recordings with healthcare professionals for review and interpretation. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals in remote or underserved areas, as well as those with limited mobility, as it allows for the seamless transmission of critical health data for remote consultation and diagnosis.
5. Comprehensive Health Insights
Integration of ECG data with other health metrics, such as heart rate and activity levels, within the smartwatch ecosystem provides users with comprehensive insights into their overall health. The correlation of ECG findings with other health-related data enhances the contextual understanding of cardiac health and its relationship to lifestyle factors, facilitating informed decision-making and behavior modification.
The incorporation of ECG technology in smartwatches yields multifaceted benefits, ranging from proactive health monitoring and early arrhythmia detection to enhanced user engagement and the facilitation of remote healthcare. These benefits collectively contribute to a more informed, empowered, and proactive approach to personal health management.
Limitations and Considerations of ECG Technology in Smartwatches
While ECG technology in smartwatches offers significant advantages in personal health monitoring, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations and considerations associated with this technology to ensure informed usage and interpretation of ECG data.
1. Accuracy and Interpretation
Smartwatch ECG recordings may be susceptible to motion artifacts and signal interference, potentially impacting the accuracy of the readings. Users must be mindful of maintaining stillness during ECG recordings to minimize these artifacts. Additionally, the interpretation of ECG waveforms requires a level of expertise that users and healthcare professionals should consider when assessing the data.
2. Regulatory Approval and Clinical Validation
Not all smartwatches with ECG capabilities have received regulatory approval or undergone extensive clinical validation. Users should verify that the ECG feature on their smartwatch complies with relevant regulatory standards and has been validated for accuracy and reliability to ensure the clinical relevance of the recorded ECG data.
3. User Education and Awareness
Effective utilization of ECG technology in smartwatches necessitates user education and awareness regarding the limitations and proper use of the ECG feature. Users should familiarize themselves with the recommended practices for obtaining accurate ECG recordings and understand the significance of the data in the context of their overall health.
4. Diagnostic Limitations
While ECG recordings from smartwatches can provide valuable insights, they are not intended to replace comprehensive diagnostic evaluations performed by healthcare professionals. Users should view smartwatch ECG data as a supplementary tool for personal health monitoring and seek professional medical assessment for any concerning findings or symptoms.
5. User Population Considerations
Specific user populations, such as individuals with certain medical conditions or cardiac devices, may have unique considerations when using ECG technology in smartwatches. It is essential for users with underlying health conditions or medical implants to consult with healthcare providers to determine the appropriateness of using ECG-enabled smartwatches and interpreting the obtained ECG data.
6. Privacy and Data Security
Given the sensitive nature of health data, users should prioritize the privacy and security features of smartwatches with ECG capabilities. It is crucial to assess the data protection measures implemented by smartwatch manufacturers to safeguard ECG recordings and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
Understanding the limitations and considerations of ECG technology in smartwatches is integral to responsible and informed utilization of this feature. By acknowledging these factors, users can maximize the benefits of ECG-enabled smartwatches while maintaining a discerning approach to interpreting and acting upon the obtained ECG data.
Comparison of ECG Technology in Different Smartwatches
The integration of ECG technology in smartwatches has become increasingly prevalent, with various manufacturers incorporating this feature into their wearable devices. A comparison of ECG capabilities across different smartwatches reveals distinct attributes and functionalities that cater to diverse user preferences and healthcare needs.
1. Sensor Placement and Contact Method
Smartwatches differ in the placement of ECG sensors and the method of user contact required for ECG recordings. While some devices feature sensors on the back of the watch case that make contact with the user’s wrist, others utilize sensors on the watch bezel or sides, offering flexibility in sensor placement and user interaction.
2. ECG Interpretation and Visualization
The interpretation and visualization of ECG waveforms vary among smartwatches, with some devices providing real-time waveform display on the watch screen during ECG recordings, while others rely on companion apps for detailed waveform analysis and storage. Additionally, the comprehensiveness of ECG data presentation, including heart rate variability and rhythm analysis, may differ across smartwatch models.
3. Integration with Health Platforms
Different smartwatches offer varying degrees of integration with broader health platforms and ecosystems. Some devices seamlessly sync ECG data with comprehensive health metrics, enabling users to consolidate and analyze their ECG recordings alongside other health-related information, such as activity levels and sleep patterns.
4. Regulatory Approvals and Clinical Validation
The regulatory approvals and clinical validation processes for smartwatch ECG features may vary among manufacturers. Certain smartwatches have obtained clearances from regulatory bodies and undergone extensive clinical testing to validate the accuracy and clinical relevance of their ECG capabilities, providing users and healthcare professionals with added confidence in the obtained ECG data.
5. User Interface and Experience
The user interface and experience associated with ECG technology in smartwatches exhibit diversity in terms of usability, data accessibility, and user guidance during ECG recordings. Factors such as user prompts, data organization, and ease of sharing ECG recordings with healthcare providers contribute to the overall user experience across different smartwatch models.
6. Data Privacy and Security Measures
Smartwatches prioritize data privacy and security through varying measures, such as encryption protocols, user consent mechanisms, and data storage practices. The implementation of robust privacy features ensures the protection of sensitive ECG data and compliance with data protection regulations.
Comparing ECG technology in different smartwatches unveils a spectrum of features and functionalities that cater to diverse user needs and preferences. Understanding the nuances of ECG capabilities across various smartwatch models empowers users to make informed decisions when selecting a device that aligns with their personal health monitoring and wellness objectives.
The Future of ECG Technology in Smartwatches
The evolution of ECG technology in smartwatches is poised to drive significant advancements in personal health monitoring and contribute to the broader landscape of digital healthcare. Anticipated developments and innovations in this domain hold promise for transforming the way individuals engage with their cardiac health and interact with healthcare systems.
1. Enhanced Sensor Capabilities
Future iterations of smartwatch ECG sensors are expected to exhibit enhanced capabilities, including improved signal processing, higher sampling rates, and advanced noise reduction algorithms. These advancements aim to elevate the accuracy and reliability of ECG recordings, enabling users to obtain more precise insights into their heart’s electrical activity.
2. Artificial Intelligence Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into smartwatch ECG technology holds potential for automated arrhythmia detection, personalized health insights, and predictive analytics. AI-driven ECG analysis could enable smartwatches to detect subtle cardiac irregularities and provide actionable recommendations based on individual health profiles.
3. Expanded Health Monitoring Capabilities
Beyond ECG monitoring, future smartwatches are likely to incorporate a broader array of health monitoring features, such as continuous blood pressure measurement, blood oxygen saturation monitoring, and electrodermal activity assessment. This holistic approach to health tracking aims to provide users with comprehensive physiological data for a more thorough understanding of their well-being.
4. Telehealth Integration and Data Sharing
Smartwatches with ECG capabilities are anticipated to strengthen their integration with telehealth platforms, allowing users to seamlessly share ECG data with healthcare providers for remote consultations and diagnostics. This integration is expected to streamline the exchange of critical health information, enabling more efficient and accessible healthcare delivery.
5. Regulatory Advancements and Standardization
The future of ECG technology in smartwatches involves continued collaboration with regulatory authorities to establish standardized guidelines for ECG feature implementation and validation. Clear regulatory frameworks and industry standards are crucial for ensuring the clinical relevance and reliability of smartwatch ECG capabilities, fostering trust among users and healthcare professionals.
6. Personalized Health Insights and Behavioral Interventions
Smartwatches equipped with ECG technology are poised to offer personalized health insights and behavioral interventions based on individual ECG data and holistic health metrics. This tailored approach to health management aims to empower users to make informed lifestyle choices and proactive health decisions guided by their unique physiological indicators.
The future of ECG technology in smartwatches holds immense potential to revolutionize personal health monitoring, preventive care, and the integration of digital health solutions into everyday life. As these advancements unfold, smartwatches are expected to play an increasingly pivotal role in empowering individuals to prioritize and optimize their cardiac health.