The Importance of Cellphones for the Deaf
Cellphones play a vital role in the lives of individuals with hearing impairment, providing them with greater accessibility and opportunities for communication. For deaf individuals, being able to stay connected through text messaging, video calls, and other features is essential for maintaining relationships, accessing important information, and navigating daily activities. Here, we explore the various reasons why cellphones are crucial for the deaf community.
1. Communication: Cellphones offer a range of communication options that cater to the needs of deaf individuals. Text messaging allows for quick and efficient communication, while video calls and FaceTime enable deaf individuals to communicate using sign language, enhancing their ability to express themselves naturally and effectively.
2. Emergency situations: In times of emergencies, access to a cellphone can be a lifesaver. Deaf individuals can use their cellphones to call for help, notify emergency services, and communicate their location.
3. Accessibility: Cellphones have undergone significant advancements in accessibility features, making them more inclusive for individuals with hearing impairment. Features such as TTY mode, which allows text communication over a regular phone line, and closed captioning options for videos ensure that deaf individuals can access and understand content easily.
4. Independence: Having a cellphone empowers deaf individuals to take control of their communication needs and enables them to participate fully in society. With a cellphone, they can make appointments, communicate with healthcare providers, search for employment opportunities, and navigate public transportation systems independently.
5. Social connections and support: Cellphones provide a means of maintaining connections with friends, family, and support groups within the deaf community. Social media platforms, chat applications, and online forums allow for building relationships, sharing experiences, and seeking emotional support.
6. Access to information: Cellphones enable deaf individuals to access a wealth of information in real-time. From news updates and educational resources to navigation tools and instant translation services, cellphones provide a gateway to knowledge and accessibility.
7. Employment opportunities: Cellphones play a pivotal role in accessing employment opportunities in today’s digital age. They allow deaf individuals to participate in job interviews, communicate with colleagues, and access remote work options, providing equal access to professional opportunities.
Cellphones have become an indispensable tool in the lives of individuals with hearing impairment. They break down communication barriers, promote independence, and improve accessibility for the deaf community. With ongoing technological advancements, it is crucial to ensure that cellphones and their features continue to be compatible and inclusive for the diverse needs of deaf individuals.
Understanding Hearing Aids and Their Compatibility with Cellphones
Hearing aids are essential devices that help individuals with hearing loss by amplifying sounds and improving their ability to hear. With the increasing integration of technology, hearing aids have become more advanced and compatible with various digital devices, including cellphones. In this section, we will delve into the importance of understanding hearing aids and their compatibility with cellphones.
1. Types of Hearing Aids: There are different types of hearing aids available, including behind-the-ear (BTE), in-the-ear (ITE), and completely-in-the-canal (CIC) models. Understanding the type of hearing aid you have is crucial for determining its compatibility with cellphones and other devices.
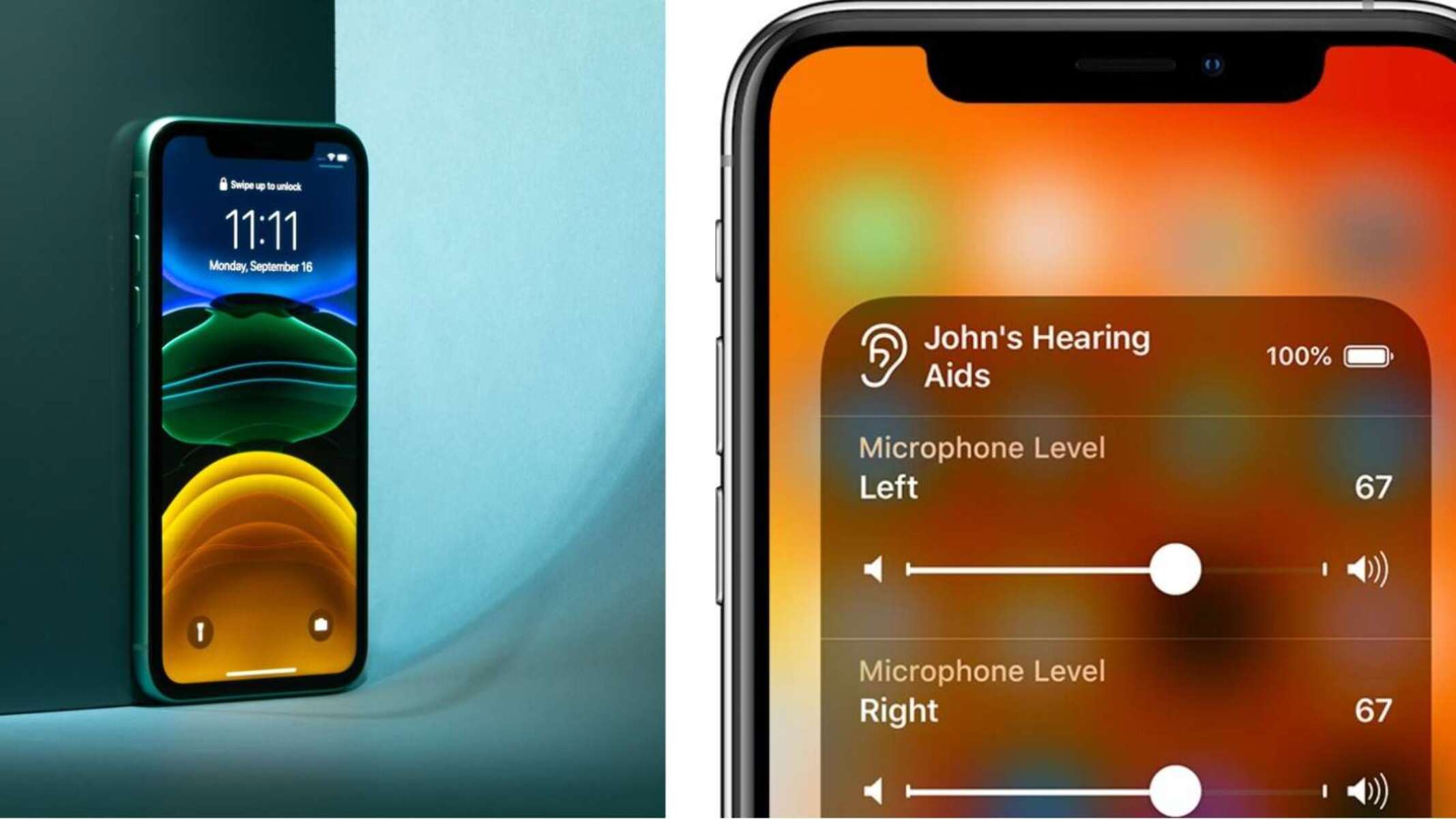
2. Telecoil Technology: Many modern hearing aids are equipped with telecoil technology, also known as T-coil. This technology allows the hearing aid to pick up magnetic signals, such as those emitted by cellphones. It enables direct audio streaming to the hearing aid, providing clearer sound quality during phone calls.
3. Bluetooth Connectivity: Some hearing aids feature Bluetooth connectivity, which allows them to connect wirelessly to cellphones and other compatible devices. This feature enables deaf individuals to stream audio from their cellphones directly to their hearing aids, enhancing the listening experience for phone calls, music, and other media.
4. Compatibility Considerations: It is important to ensure that your hearing aid is compatible with the specific cellphone model you use. Not all hearing aids are compatible with all cellphones, so it is advisable to consult with your hearing healthcare professional or refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines to verify compatibility.
5. Hearing Aid Compatibility (HAC) Ratings: Cellphones are assigned Hearing Aid Compatibility (HAC) ratings, which indicate the extent of their compatibility with hearing aids. HAC ratings are categorized as M (microphone) and T (telecoil), with higher ratings indicating better performance with hearing aids. Checking the HAC ratings of a cellphone can help you choose a device that works optimally with your hearing aid.
6. Customization Options: Many cellphones offer customization options specifically designed for hearing aid users. These options include adjustable volume controls, noise reduction settings, and compatibility with hearing aid accessories.
7. Consultation with Hearing Healthcare Professionals: If you are unsure about the compatibility of your hearing aid with cellphones, it is recommended to consult with your hearing healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on the best practices for connecting your hearing aid to a cellphone and recommend compatible devices if needed.
Understanding the capabilities and compatibility of your hearing aid with cellphones is essential for maximizing your communication experience. By utilizing telecoil technology, Bluetooth connectivity, and customization options, individuals with hearing loss can enjoy improved phone call quality and seamless integration between their hearing aids and cellphones.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cellphone for Deaf individuals
Choosing the right cellphone is crucial for individuals with hearing impairment to ensure effective communication and accessibility. With numerous options available in the market, it is important to consider specific factors that cater to the needs of deaf individuals. In this section, we will explore the key factors to consider when selecting a cellphone for deaf individuals.
1. Hearing Aid Compatibility (HAC): Look for a cellphone that is compatible with the hearing aids being used. Consider the HAC ratings, which determine the performance and compatibility of the cellphone with hearing aids. Higher ratings indicate better compatibility, ensuring clear and uninterrupted audio when using the cellphone.
2. Telecoil Support: Opt for a cellphone that supports telecoil technology, allowing for direct audio streaming to compatible hearing aids. This feature enhances the clarity and quality of phone calls, ensuring an optimal communication experience for the deaf individual.
3. Visual Alerts and Vibrations: Look for a cellphone that offers visual alerts and vibrations for incoming calls, messages, and notifications. These features provide an alternative way for a deaf individual to be notified of incoming communication events, allowing them to stay connected without relying solely on auditory cues.
4. Real-Time Text Communication: Consider a cellphone that supports real-time text communication methods, such as SMS or instant messaging apps. These features enable deaf individuals to engage in quick, written conversations that are not dependent on phone calls, providing a practical and efficient way to communicate.
5. Closed Captioning and Transcription: Check for the availability of closed captioning and transcription options on the cellphone. This feature can be particularly useful when watching videos or participating in video calls, as it provides text captions or transcriptions of the spoken content, ensuring accessibility for deaf individuals.
6. App Compatibility: Consider the availability of apps specifically designed for individuals with hearing impairment. Look for communication apps that support video calls with sign language interpretation, speech-to-text apps for converting spoken words into text, and other assistive communication apps that enhance accessibility for deaf individuals.
7. User-Friendly Interface: Choose a cellphone with a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and customize. Look for features such as adjustable font sizes, high contrast options, and intuitive menu layouts. This ensures a smooth and hassle-free user experience for individuals with hearing impairment.
8. Battery Life and Durability: Consider the battery life of the cellphone, as well as its durability. A long-lasting battery ensures uninterrupted communication throughout the day, while a durable construction withstands the rigors of daily use.
By considering these factors when choosing a cellphone, deaf individuals can find a device that meets their specific communication needs. It is important to prioritize compatibility with hearing aids, accessibility features, and ease of use to ensure seamless communication and enhanced accessibility.
Best Cellphones with Hearing Aid Compatibility
When selecting a cellphone for individuals with hearing impairment, it is important to choose a device that offers excellent compatibility with hearing aids. Here, we’ve compiled a list of some of the best cellphones available in the market that provide optimal hearing aid compatibility for deaf individuals.
1. iPhone: Apple’s iPhone has been recognized for its exceptional hearing aid compatibility. The latest iPhone models feature advanced telecoil support and Bluetooth connectivity, enabling seamless audio streaming to compatible hearing aids. Additionally, the iPhone offers closed captioning and transcription options, making it an ideal choice for deaf individuals.
2. Samsung Galaxy: The Samsung Galaxy series also offers excellent hearing aid compatibility. These Android-based smartphones support telecoil technology and feature customizable accessibility options. With their high-quality screens and user-friendly interfaces, Samsung Galaxy phones ensure a great user experience for individuals with hearing impairment.
3. Google Pixel: Google Pixel phones are known for their impressive hearing aid compatibility. With their pure Android experience, these smartphones provide a smooth and intuitive user interface. They offer robust Bluetooth connectivity and support for real-time text communication, making them an excellent choice for deaf individuals.
4. LG G Series: LG’s G Series phones have consistently provided strong compatibility with hearing aids. These smartphones feature telecoil support, along with adjustable settings for volume, sound balance, and other accessibility features. LG G Series phones cater to the needs of deaf individuals and offer a reliable and user-friendly experience.
5. Doro Smartphones: Doro smartphones are specifically designed with accessibility in mind, making them an excellent choice for individuals with hearing impairment. These devices offer amplified sound, visual call alerts, and compatibility with hearing aid telecoils. Doro smartphones prioritize ease of use and provide a simplified interface, ensuring a seamless communication experience for deaf individuals.
6. Motorola Moto G: Motorola’s Moto G series offers good hearing aid compatibility, providing clear audio during phone calls and media playback. These smartphones feature customizable accessibility settings and strong Bluetooth connectivity, making them suitable for individuals with hearing impairment.
7. OnePlus: OnePlus phones are known for their powerful performance and user-friendly interface. These smartphones support Bluetooth audio streaming and offer various customization options for accessibility. With their sleek design and reliable compatibility with hearing aids, OnePlus phones are worth considering for deaf individuals.
8. Nokia: Nokia smartphones come with a range of accessibility features, including telecoil support and closed captioning options. These phones provide a user-friendly experience and solid hearing aid compatibility, making them a reliable choice for individuals with hearing impairment.
While these cellphones offer top-notch hearing aid compatibility, it is important to check the specific model’s compatibility with your particular hearing aid. Consulting with your hearing healthcare professional or referring to the manufacturer’s guidelines will help ensure a seamless connection between your hearing aid and cellphone.
How to Connect a Hearing Aid to a Cellphone
Connecting a hearing aid to a cellphone is crucial for individuals with hearing impairment to enhance their communication experience. By utilizing the available connectivity options, deaf individuals can seamlessly stream audio from their cellphones directly to their hearing aids. Here are steps to connect a hearing aid to a cellphone:
1. Check Hearing Aid Compatibility: Ensure that both your hearing aid and cellphone are compatible with each other. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or consult your hearing healthcare professional to verify compatibility and determine which connectivity options are available.
2. Enable Bluetooth: On your cellphone, navigate to the settings and enable Bluetooth. This allows your cellphone to search for and connect to nearby Bluetooth devices, including your hearing aid.
3. Turn on Hearing Aid’s Bluetooth: Activate the Bluetooth feature on your hearing aid. Consult the user manual or follow the instructions provided by the hearing aid manufacturer to enable Bluetooth connectivity. This step may require adjustments specific to your hearing aid model.
4. Pairing Process: On your cellphone, search for available Bluetooth devices. Once your hearing aid appears in the list, select it to start the pairing process. Follow any prompts or requests for permissions to successfully connect your hearing aid to the cellphone.
5. Adjust Hearing Aid Settings: Depending on the hearing aid model, you may need to adjust the settings on both your hearing aid and cellphone to optimize the audio streaming experience. This may include adjusting volume levels, sound balance, or other personalized settings specific to your hearing aid and hearing preferences.
6. Test the Connection: Place a phone call or play media on your cellphone to test the connection between your hearing aid and cellphone. Ensure that the sound is being streamed correctly to your hearing aid and adjust settings as necessary to achieve the desired audio quality.
7. Explore Additional Features: Once your hearing aid is successfully connected to your cellphone, explore any additional features or accessibility settings offered by your cellphone. This may include closed captioning options, visual alerts, or other customization options specific to deaf individuals.
8. Regular Maintenance: It is important to regularly clean and maintain your hearing aid and cellphone to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Follow the guidelines provided by the respective manufacturers for cleaning and care instructions.
By following these steps, individuals with hearing impairment can successfully connect their hearing aids to their cellphones. Connecting a hearing aid to a cellphone opens up a world of improved communication and accessibility, allowing deaf individuals to stay connected and engaged with the world around them.
Apps and Features for Assistive Communication on Cellphones
Cellphones offer a wide range of apps and features that are specifically designed to assist individuals with hearing impairment in their communication needs. These apps and features leverage technology to enhance accessibility and promote effective communication for deaf individuals. Here, we will explore some of the key apps and features available on cellphones for assistive communication.
1. Video Calling Apps: Video calling apps, such as FaceTime (iOS) and Google Duo (Android), facilitate real-time communication through video calls. Deaf individuals can use sign language to communicate with others, allowing for more natural and effective interaction.
2. Speech-to-Text Apps: Speech-to-text apps, like Live Transcribe (Android) and Ava (iOS), convert spoken words into text in real-time. These apps enable deaf individuals to read what is being said during conversations, enhancing their understanding and participation in group settings.
3. Relay Services: Relay services, such as the Video Relay Service (VRS) or Text Relay Service (TRS), provide a means of communication between deaf individuals and hearing individuals. These services act as intermediaries, converting sign language or text messages into spoken language and vice versa, allowing for effective communication across language barriers.
4. Closed Captioning: Many video streaming apps, like YouTube and Netflix, provide closed captioning options. These features display text captions alongside video content, ensuring accessibility and enjoyment for deaf individuals. Additionally, some cellphones offer built-in closed captioning settings for phone calls and other audio content.
5. TTY Mode: TTY (Teletypewriter) mode is an accessibility feature available on some cellphones. It allows deaf individuals to communicate using text over a regular phone line. TTY mode enables real-time text-based conversations and is compatible with devices equipped with TTY technology.
6. Hearing Aid Compatibility: Cellphones with strong hearing aid compatibility (HAC) offer features that enhance communication for deaf individuals. These features include direct connectivity through telecoils, Bluetooth audio streaming, and customizable settings for sound balance and volume control.
7. Vibrations and Visual Alerts: Cellphones provide options for vibrations and visual alerts, ensuring that deaf individuals are notified of incoming calls, messages, and notifications. These features provide alternative ways to catch attention and allows for communication without relying solely on auditory cues.
8. Communication Apps: There are various communication apps designed specifically for deaf individuals. These apps offer features such as video calls with sign language interpretation, group chats, and instant messaging, providing convenient and accessible ways to stay connected with friends, family, and the deaf community.
By utilizing these apps and features on their cellphones, deaf individuals can effectively communicate, access information, and participate in various social and professional activities. These assistive communication tools contribute to breaking down barriers and promoting inclusivity for individuals with hearing impairment in the digital age.
Assistive Technology and Accessories for Cellphones and Hearing Aids
Cellphones and hearing aids can be enhanced with a range of assistive technology and accessories that further improve the communication experience for individuals with hearing impairment. These technologies bridge the gap between cellphones and hearing aids, providing additional functionality and accessibility. Let’s explore some of the assistive technology and accessories available for cellphones and hearing aids:
1. Bluetooth Transmitters and Receivers: Bluetooth transmitters and receivers enable wireless connectivity between cellphones and hearing aids. These devices can be plugged into the audio source, such as a TV or computer, and stream audio directly to compatible hearing aids, eliminating the need for additional cables or adapters.
2. Remote Microphones: Remote microphones are small devices that capture audio and transmit it wirelessly to the hearing aids. These microphones can be placed near a speaker or worn by a conversation partner, allowing for clearer and direct audio input to the hearing aids, especially in noisy environments.
3. Inductive Neckloops: Inductive neckloops provide a convenient way to connect hearing aids to cellphones or audio devices. These loops transmit audio signals wirelessly to compatible hearing aids through telecoil technology. By wearing the neckloop, individuals can stream audio directly to their hearing aids without the need for separate headphones or earbuds.
4. Vibrating Alarm Clocks and Alerts: Vibrating alarm clocks and alerts are designed to notify individuals with hearing impairment through vibrations. These devices can be connected to a cellphone or placed under a pillow, ensuring that important notifications, alarms, or incoming calls are felt and not missed.
5. Hearing Aid Apps: Many hearing aid manufacturers offer companion apps that allow users to control and adjust settings on their hearing aids using their cellphones. These apps provide convenience in adjusting volume, sound balance, and other personalized settings, ensuring a customized experience for the user.
6. Captioned Telephones: Captioned telephones feature a built-in screen that displays text captions of the conversation in real-time. These devices enable deaf individuals to read the conversation while using their cellphones for communication, ensuring accurate understanding and enhancing phone conversations.
7. Alerting Systems: Alerting systems are designed to notify individuals with hearing impairment of various events, such as doorbells, fire alarms, or phone calls. These systems utilize flashing lights, vibrations, or even send notifications to cellphones to ensure that deaf individuals are aware of important events happening around them.
8. Hearing Aid Compatibility (HAC) Accessories: Numerous accessories are available to enhance the compatibility of cellphones with hearing aids. These include hands-free kits, Bluetooth streamers, and telecoil loops that enable direct audio streaming, clearer phone conversations, and improved accessibility for individuals with hearing aids.
By utilizing assistive technology and accessories, individuals with hearing impairment can further enhance their communication experience and accessibility with cellphones and hearing aids. These technologies expand the capabilities of these devices, making them more inclusive and ensuring effective communication for deaf individuals in various settings.
Tips for Making Cellphone Usage Easier for the Deaf
For individuals with hearing impairment, using a cellphone effectively can significantly enhance communication and accessibility. Here are some useful tips to make cellphone usage easier for the deaf:
1. Customize Accessibility Settings: Take advantage of the accessibility settings on your cellphone. Adjust the font size, display settings, and color contrasts to improve visibility and readability. Customize vibration patterns and LED notifications to easily distinguish between different alerts.
2. Enable Visual and Vibrating Alerts: Activate visual and vibrating alerts for calls, messages, and notifications. This ensures that you do not miss important communications, providing alternative cues instead of relying solely on auditory signals.
3. Utilize TTY Mode: If your cellphone and hearing aid support Tele Typewriter (TTY) mode, consider using it for text-based communication with other TTY devices. TTY mode allows for real-time text conversations, providing a reliable means to communicate without relying on voice calls.
4. Use Communication Apps: Explore communication apps specifically designed for deaf individuals. These apps offer features like video calls with sign language interpretation, instant messaging, and group chats, facilitating effective and inclusive communication.
5. Keep Your Hearing Aid and Cellphone Clean: Regularly clean and maintain both your hearing aid and cellphone to ensure optimal performance. Clean the microphone and speakers of your cellphone as well as the earmold or receiver of your hearing aid to prevent any build-up that could affect sound quality.
6. Utilize Speech-to-Text Apps: Access speech-to-text apps on your cellphone to convert spoken words into written text in real-time. This can assist in understanding conversations or listening to media content, providing a clear visual representation of the spoken words.
7. Seek Professional Assistance: Consult with a hearing healthcare professional to optimize the settings on your cellphone and hearing aid. They can help you adjust volume levels, sound balance, and recommend specific apps or accessories to enhance your communication experience.
8. Stay Informed About Assistive Technology: Keep up-to-date with the latest advancements in assistive technology for individuals with hearing impairment. This includes new features and apps that can improve cellphone usage and communication accessibility.
9. Experiment with Different Apps and Features: Explore various apps and features on your cellphone to find what works best for you. Experiment with different settings, communication apps, and assistive technology to discover the combination that enhances your communication experience.
10. Educate Others About Your Communication Needs: Inform friends, family, and coworkers about your communication needs and how they can best communicate with you. Encourage them to use text-based messages or to face you directly during conversations so that you can understand and lip-read more easily.
By implementing these tips, individuals with hearing impairment can maximize the benefits of cellphone usage and improve their communication experience. The key is to customize settings, utilize assistive technology, and stay informed about available options that cater specifically to the needs of the deaf community.
Latest Advancements in Cellphone Technology for the Deaf Community
Cellphone technology has made significant advancements in recent years, especially when it comes to catering to the needs of the deaf community. These advancements have led to improved accessibility, enhanced communication features, and better integration between cellphones and hearing aids. Let’s explore some of the latest advancements in cellphone technology that have benefited individuals with hearing impairment:
1. Real-Time Speech-to-Text: Cellphones now offer advanced speech recognition technology that can convert spoken words into real-time text. This feature is particularly useful for individuals with hearing impairment as it allows them to read the conversation in real-time, improving understanding and participation in conversations.
2. Voice-to-Sign Language Translation: Some smartphones have started incorporating voice-to-sign language translation capabilities. This advancement enables individuals with hearing impairment to have spoken words translated into sign language in real-time, making communication easier and more accessible.
3. Automatic Captioning: Cellphones are now equipped with automatic captioning features that can generate real-time captions for phone calls, video calls, and video content. This technology ensures that deaf individuals can follow the conversation or media content more easily, improving accessibility and inclusivity.
4. Haptic Feedback for Sound: Haptic feedback, which uses vibrations to simulate tactile sensations, has been utilized in cellphones to create a sensory experience for sound. This advancement allows deaf individuals to perceive sounds through vibrations, providing an alternative way to experience and interpret audio information.
5. Accessibility Enhancements: Cellphone manufacturers have focused on improving accessibility features specifically designed for individuals with hearing impairment. This includes customizable vibration patterns, LED light notifications, visual alerts for incoming calls, and improved compatibility with hearing aids.
6. Enhanced Connectivity: Cellphones now offer better connectivity options for hearing aids, such as direct audio streaming via telecoil or Bluetooth technology. This advancement provides seamless integration between hearing aids and cellphones, enhancing the audio listening experience for phone calls, media, and other sound-related activities.
7. Assistive Communication Apps: There is a growing range of communication apps available specifically for individuals with hearing impairment. These apps offer features like video calls with sign language interpretation, speech-to-text conversion, and real-time captioning, promoting effective communication and inclusivity.
8. Noise Cancellation Technology: Cellphones now come with advanced noise cancellation technology that helps eliminate background noise during phone calls and video calls. This feature ensures clearer and more focused communication for individuals with hearing impairment, improving their ability to understand and engage in conversations.
These latest advancements in cellphone technology have significantly improved accessibility and communication for individuals with hearing impairment. From speech-to-text features and sign language translation to enhanced connectivity and improved accessibility settings, cellphones are playing a crucial role in empowering the deaf community and breaking down communication barriers.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Deaf Individuals Using Cellphones
While cellphones have greatly improved accessibility and communication for individuals with hearing impairment, there are still some common challenges that deaf individuals may face when using these devices. Understanding these challenges and identifying suitable solutions can help overcome barriers and enhance the overall communication experience. Let’s explore some of the most common challenges faced by deaf individuals when using cellphones, along with potential solutions:
1. Limited Audio Accessibility: Deaf individuals cannot rely on auditory cues to receive phone calls or listen to media content. Solution: Utilize customizable visual and vibrating alerts on the cellphone to receive notifications for incoming calls and messages. Consider using applications that provide real-time captions or subtitles for media content.
2. Difficulty in Phone Conversations: Traditional phone conversations can be challenging for deaf individuals. Solution: Use alternative modes of communication such as video calls, instant messaging, or text-based applications that facilitate real-time text conversations. Consider using speech-to-text apps that convert spoken words into written text for better understanding during phone calls.
3. Poor Sound Quality: Cellphone speakers may not provide optimal sound quality, making it difficult for deaf individuals to hear clearly. Solution: Use headphones or external speakers to improve sound quality during phone calls or when listening to media. Consider pairing the cellphone with hearing aids or assistive listening devices that can enhance audio clarity.
4. Language Barriers: Deaf individuals communicating with hearing individuals who do not know sign language may face communication barriers. Solution: Utilize video relay services or communication apps that offer sign language interpretation. Consider using communication apps that provide auto-translation capabilities to bridge language gaps.
5. Phone Accessibility: Some cellphones may not have user-friendly interfaces or accessibility features that cater to the needs of deaf individuals. Solution: Choose cellphones with customizable accessibility features such as adjustable font sizes, high contrast options, and vibration patterns. Explore third-party applications that provide additional accessibility features and customization options.
6. Compatibility Issues: Ensuring compatibility between cellphones and hearing aids can be challenging. Solution: Check the hearing aid compatibility (HAC) ratings of the cellphone and consult with a hearing healthcare professional to verify compatibility. Consider utilizing Bluetooth connectivity or telecoil technology to establish a direct connection between the cellphone and hearing aids for better audio streaming.
7. Limited Battery Life: Cellphones with short battery life can be inconvenient for deaf individuals who rely heavily on their devices for communication. Solution: Select cellphones with longer battery life or consider using portable charging solutions to ensure continuous access to communication and accessibility features.
8. Accessibility of Applications: Some applications may lack accessibility features, making it challenging for deaf individuals to fully utilize their functionalities. Solution: Choose applications specifically designed for individuals with hearing impairment, ensuring they offer features like real-time captioning, sign language interpretation, or customized communication options.
By recognizing and addressing these common challenges, deaf individuals can overcome communication barriers and make the most of their cellphones. It is important to explore available solutions, utilize assistive technology, and stay informed about accessibility features to enhance communication and accessibility in the digital era.