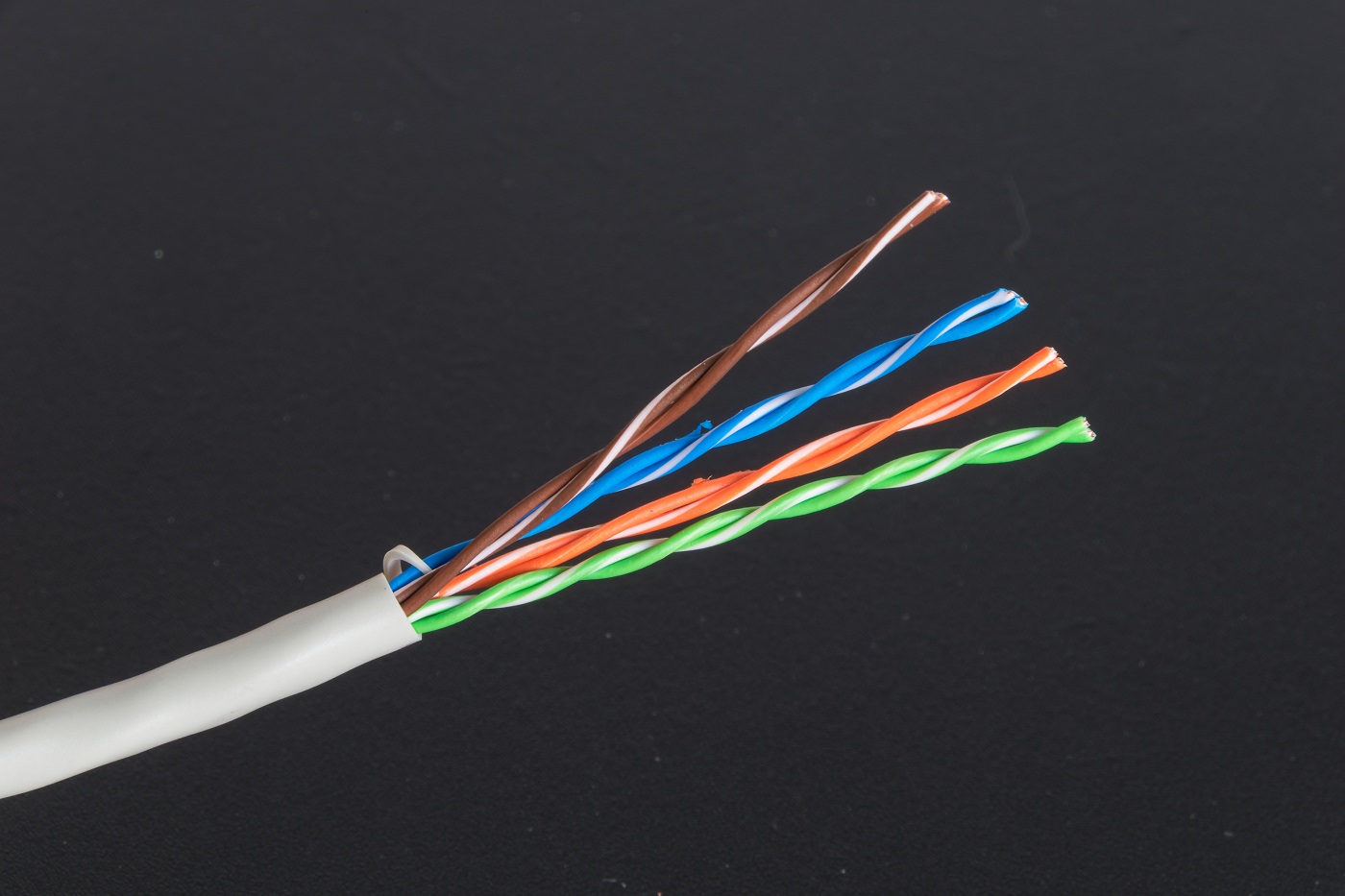
RJ45 Connector
The RJ45 connector, also known as the 8P8C (8 Position 8 Contact) connector, is one of the most widely used connectors for Ethernet networking. It is designed to terminate twisted pair cables, particularly the Category 5 (Cat 5) and Category 6 (Cat 6) cables. This versatile connector is essential for creating reliable and high-speed network connections in various applications, including home networking, office environments, data centers, and industrial settings.
Key Features and Uses
-
Versatile Compatibility: The RJ45 connector is compatible with a wide range of devices, including computers, routers, switches, and networked appliances. Its versatility makes it a popular choice for both residential and commercial networking needs.
-
Twisted Pair Termination: This connector is specifically designed to terminate twisted pair cables, which are essential for minimizing electromagnetic interference and crosstalk in network transmissions. By securely terminating the twisted pairs, the RJ45 connector helps maintain signal integrity and data reliability.
-
Ethernet Connectivity: RJ45 connectors are the standard interface for Ethernet connections, enabling seamless integration with Ethernet cables and ports. They are crucial for establishing wired network connections that support high-speed data transfer and communication.
-
Modular Design: The modular nature of the RJ45 connector allows for easy installation and replacement. It features a snap-in mechanism that facilitates quick and secure connections, making it convenient for both professional installers and end users.
Installation and Wiring
When installing RJ45 connectors, it is essential to adhere to the TIA/EIA-568 standard for wiring, which specifies the arrangement of the eight color-coded wires within the connector. Proper wiring ensures consistent connectivity and performance across network infrastructure.
Future-Proofing Networks
As networking technologies continue to advance, the RJ45 connector remains a reliable choice for current and future network infrastructure. Despite the emergence of newer connectors designed for higher data rates, such as the RJ45's successor, the RJ45 connector continues to be widely deployed and is expected to remain relevant for years to come.
In summary, the RJ45 connector plays a pivotal role in enabling dependable and high-speed network connections across diverse environments. Its compatibility, termination capabilities, and modular design make it an indispensable component for Ethernet networking, serving as a cornerstone of modern connectivity solutions.
RJ11 Connector
The RJ11 connector, also known as the 6P2C (6 Position 2 Contact) connector, is commonly used for connecting telephone and modem cables. While it shares a similar appearance to the RJ45 connector, the RJ11 connector is specifically designed for voice communication and lower-speed data transmission. Its widespread adoption in residential and small business environments has solidified its role as a standard interface for telephony applications.
Telephony and Modem Connectivity
-
Telephone Lines: RJ11 connectors are integral to connecting landline telephones to wall jacks, allowing users to establish voice communication over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). The connector’s two contacts are utilized for transmitting the tip and ring signals essential for voice transmission.
-
Modem Connections: In the context of modem connectivity, the RJ11 connector facilitates the connection between a computer’s modem and a telephone line. This enables data communication over traditional phone lines, commonly used for dial-up internet access and fax transmissions.
Wiring and Pinout
The RJ11 connector typically utilizes a 6-position configuration, accommodating the connection of up to six conductors. However, in standard telephony applications, only two contacts are utilized for the transmission of voice signals. The pinout arrangement follows a standardized wiring scheme, ensuring compatibility and consistency across different telecommunication equipment.
Distinction from RJ45
It is important to note that while the RJ11 connector resembles the RJ45 connector, they serve distinct purposes and are not interchangeable. RJ11 connectors are not designed for Ethernet networking and are not suitable for terminating twisted pair cables commonly used in Ethernet installations. Attempting to use an RJ11 connector for Ethernet connections can result in connectivity issues and signal degradation.
Applications and Relevance
Despite the prevalence of digital communication technologies, the RJ11 connector continues to be a fundamental component in telephony infrastructure, particularly in residential and small office settings. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with legacy telephone systems contribute to its enduring relevance in modern communication networks.
Modular Connector
The modular connector, often referred to as the modular plug or jack, is a type of electrical connector that allows for the interchangeability of various communication and networking interfaces. It is commonly associated with the RJ series of connectors, including the RJ45 and RJ11, and is widely used in telecommunications, data networking, and audio-visual applications. The modular connector’s versatility and standardized form factor have contributed to its widespread adoption across diverse industries.
Interchangeable Design
-
Multiple Configurations: Modular connectors are available in a variety of configurations, accommodating different numbers of contacts and positions to suit specific applications. This interchangeability allows for the seamless integration of various communication interfaces, providing flexibility in equipment connectivity.
-
Standardized Pinouts: The modular connector’s pinout arrangements adhere to industry standards, ensuring compatibility and consistency across different devices and systems. This standardization facilitates the easy replacement and interchangeability of connectors without requiring extensive rewiring or modifications.
Applications
The modular connector’s adaptability and compatibility make it suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
-
Telecommunications: Modular connectors are extensively used in telecommunication equipment, such as telephones, modems, and fax machines. They facilitate the connection of these devices to telephone lines and other communication interfaces.
-
Networking: In data networking applications, modular connectors are essential for terminating Ethernet cables and establishing wired network connections. The RJ45 modular connector, in particular, is the standard interface for Ethernet connectivity.
-
Audio-Visual Equipment: Modular connectors are employed in audio-visual equipment, including professional audio systems, intercoms, and multimedia devices. They enable the integration of audio and video signals, supporting seamless connectivity in diverse AV setups.
Installation and Termination
Modular connectors are designed for straightforward installation, typically featuring a snap-in mechanism for secure mating with compatible jacks or receptacles. Proper termination of the connector’s contacts is crucial for ensuring reliable signal transmission and connectivity, making adherence to industry-standard wiring practices essential.
Future Developments
As communication and networking technologies continue to evolve, modular connectors are expected to adapt to emerging connectivity requirements. Their proven versatility and standardized design position them as enduring components in the ever-changing landscape of communication and networking infrastructure.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Connector
The Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) connector is specifically designed to terminate shielded twisted pair cables, providing enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and signal degradation. STP cables feature an additional shielding layer, typically made of metal foil or braided shielding, that surrounds the twisted pairs of conductors. The STP connector plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of transmitted signals in environments where EMI poses a potential threat to data quality and reliability.
EMI Mitigation
-
Shielding Effectiveness: The primary function of the STP connector is to ensure the proper grounding and termination of the cable’s shielding, effectively containing and neutralizing external electromagnetic interference. This shielding effectiveness is particularly valuable in environments with high EMI sources, such as industrial facilities and areas with dense electrical equipment.
-
Signal Integrity: By minimizing the impact of EMI on the transmitted signals, STP connectors help preserve signal integrity, reducing the likelihood of data corruption and transmission errors. This is especially critical in high-speed data communication and networking applications where data accuracy and reliability are paramount.
Connector Design and Compatibility
STP connectors are engineered to accommodate the termination of shielded twisted pair cables, featuring shielding contacts that establish a secure connection with the cable’s shielding layer. The connector’s design ensures proper grounding and continuity of the shield, mitigating the risk of EMI-induced signal disturbances.
It is important to note that while STP connectors offer robust EMI protection, they are not directly interchangeable with connectors designed for unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables. The differences in connector design and termination requirements necessitate careful consideration of the cable type and connector compatibility during network installations and upgrades.
Applications and Environments
STP connectors find application in environments where EMI poses a significant risk to signal quality and network performance. Some notable applications include:
-
Industrial Settings: Manufacturing facilities, power plants, and industrial automation systems often utilize STP connectors to safeguard network communications from the detrimental effects of EMI generated by heavy machinery and electrical infrastructure.
-
High-Density Networking: Environments with dense network infrastructure, such as data centers and telecommunications facilities, benefit from the EMI protection provided by STP connectors, ensuring reliable data transmission in crowded networking environments.
-
Long-Distance Transmission: In long-distance cabling installations, where the risk of EMI interference increases with cable length, STP connectors help maintain signal integrity over extended transmission paths, contributing to stable network performance.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Connector
The Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) connector serves as a fundamental component in networking and telecommunications infrastructure, facilitating the termination of UTP cables that are widely used for Ethernet connectivity and various data transmission applications. UTP cables consist of twisted pairs of insulated copper conductors, and the UTP connector plays a pivotal role in establishing reliable and cost-effective network connections in diverse environments.
Cost-Effective Connectivity
-
Affordability: UTP connectors contribute to cost-effective networking solutions, as UTP cables are generally more economical compared to shielded alternatives. This affordability makes UTP connectors a preferred choice for a wide range of networking deployments, including residential, commercial, and educational settings.
-
Standardized Interface: The UTP connector, particularly the RJ45 variant, serves as the standard interface for Ethernet connectivity, supporting data transmission speeds ranging from traditional 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet to modern Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet standards. Its ubiquity and compatibility with Ethernet equipment make it an essential component in networking infrastructure.
Interference Resistance
While UTP cables lack the additional shielding found in STP cables, UTP connectors are designed to maintain signal integrity and resist external interference through the following mechanisms:
-
Twisted Pair Configuration: The twisted pair configuration of UTP cables helps mitigate the effects of electromagnetic interference by canceling out induced signals, resulting in improved noise immunity and reliable data transmission.
-
Quality of Installation: Proper installation and termination of UTP connectors are essential for maximizing interference resistance. Adhering to industry-standard wiring practices and ensuring secure connections are crucial for maintaining signal integrity in UTP-based networks.
Applications and Versatility
UTP connectors are integral to various networking applications and environments, including:
-
Structured Cabling Systems: UTP connectors are essential components in structured cabling systems, where they facilitate the interconnection of network devices, patch panels, and wall outlets, forming the backbone of modern network infrastructure.
-
Residential Networking: In home networking environments, UTP connectors enable the establishment of reliable wired connections for computers, media devices, and networking equipment, supporting activities such as internet access, media streaming, and online gaming.
-
Commercial and Educational Networks: UTP connectors play a vital role in supporting network connectivity in offices, schools, and other institutions, providing a versatile and scalable solution for data communication and resource sharing.
Overall, UTP connectors are essential enablers of modern networking infrastructure, offering a balance of cost-effectiveness, reliability, and compatibility for a wide range of networking applications. Their widespread adoption and proven performance make them indispensable components in the connectivity solutions that power today’s digital world.