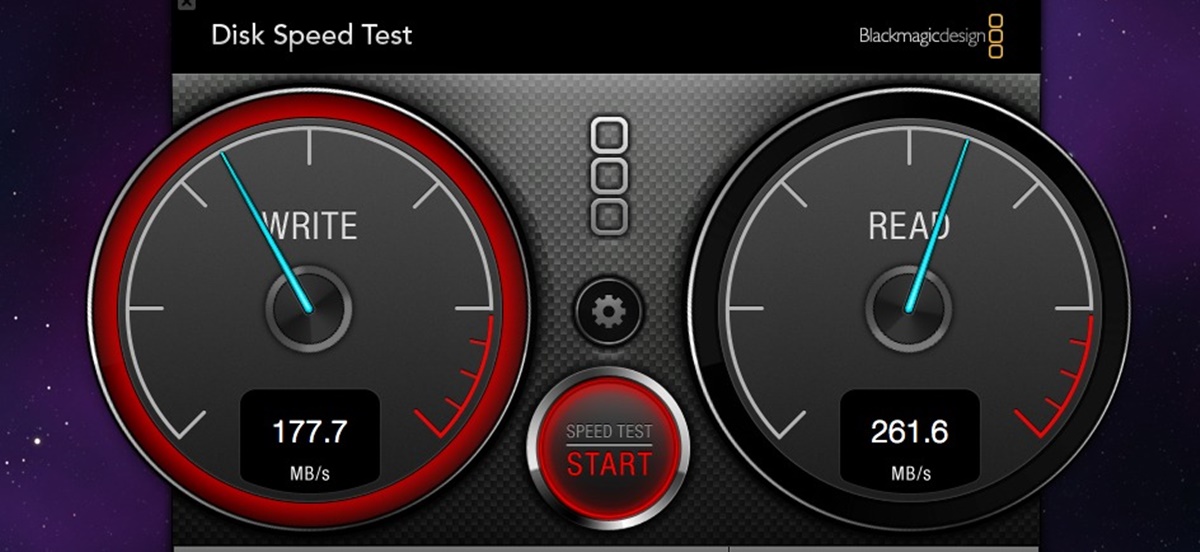
Understanding Read Speeds
Read speed refers to how quickly data can be retrieved from a storage device, such as a hard drive or solid-state drive (SSD). It is an important factor to consider when choosing a storage device, especially if you frequently work with large files or perform tasks that require fast data access.
There are several factors that can affect the read speed of a storage device:
- Hardware: The quality and capabilities of the storage device itself play a significant role in determining its read speed. Faster and more advanced drives typically offer higher read speeds.
- Interface: The interface used to connect the storage device to your computer can also impact read speed. Common interfaces include SATA, USB, and Thunderbolt, each with their own maximum transfer rates.
- File System: The file system used on the storage device can affect read speed. Some file systems are more efficient at reading data quickly, especially when dealing with large files.
- Fragmentation: Fragmentation occurs when files are scattered across different areas of a storage device, leading to slower read speeds. Regularly defragmenting your drive can help improve read performance.
- Cache: Many storage devices, particularly SSDs, feature a built-in cache that can improve read speeds. The cache stores frequently accessed data for quick retrieval.
When it comes to measuring read speed, there are a few common metrics used:
- Sequential Read Speed: This measures how quickly data can be read in a continuous, sequential manner. It is typically expressed in megabytes per second (MB/s) and is relevant for tasks such as copying large files or streaming media.
- Random Read Speed: This tests how fast the drive can access data that is scattered randomly across its storage. It is especially important for tasks that involve accessing multiple small files, like opening applications or running databases.
- Access Time: Access time measures the time it takes for the drive to locate and retrieve the requested data. It is usually measured in milliseconds (ms) and can be crucial for tasks that require quick response times.
To test the read speed of a storage device, you can use benchmarking software or specialized tools. These programs will perform various read operations on the drive and provide detailed reports of the results.
When interpreting read speed test results, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your tasks. If you work with large media files, prioritize sequential read speed. On the other hand, if you deal with numerous small files, focus on random read speed and access time.
Ultimately, understanding read speeds and how they impact your workflow can help you choose the right storage device for your needs. By considering the factors affecting read speed and evaluating the appropriate metrics, you can ensure optimal performance and efficiency when accessing and retrieving data.
Factors Affecting Read Speeds
The read speed of a storage device can be influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions when selecting a data storage device. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Hardware: The hardware components of a storage device, such as the type of drive (hard disk drive or solid-state drive) and the quality of the components, can significantly impact the read speed. SSDs, for example, typically provide faster read speeds compared to traditional hard drives due to their flash memory technology.
- Interface: The interface used to connect the storage device to your computer can affect read speeds. Different interfaces, such as SATA, USB, or Thunderbolt, have varying maximum data transfer rates. Choosing a storage device with a compatible and high-speed interface can optimize read performance.
- File System: The file system used on the storage device can impact read speeds, especially when dealing with large files. Some file systems, such as NTFS and exFAT, are more efficient at handling and retrieving data quickly.
- Fragmentation: Fragmentation occurs when files are scattered across different areas of a storage device. This can lead to slower read speeds as the drive needs to search for and retrieve multiple fragments of a file. Regularly defragmenting the drive can help optimize read performance.
- Cache: Many storage devices, particularly SSDs, feature a built-in cache that can improve read speeds. The cache temporarily stores frequently accessed data, allowing for quicker retrieval. A larger cache size can enhance read performance.
It’s important to note that these factors can interact with one another and contribute to the overall read speed of a storage device. For example, a high-speed interface paired with an SSD and an efficient file system can result in significantly faster read speeds compared to a slower interface with a traditional hard drive and a less optimized file system.
When considering the factors influencing read speeds, it’s crucial to align the storage device’s capabilities with your specific needs. If you frequently work with large files or demanding applications, investing in a storage device that excels in read speed can greatly enhance your productivity and efficiency.
Furthermore, it’s worth noting that the read speed is just one aspect to consider when evaluating a storage device. Other factors like storage capacity, durability, and cost should also be taken into account to ensure that the chosen device meets all your requirements.
By understanding the factors that affect read speeds, you can make informed decisions and choose a storage device that offers the optimal performance for your specific use cases. Whether you’re a professional in need of high-speed data access or a casual user looking for a seamless experience, selecting the right storage device can significantly enhance your overall computing experience.
Common Read Speed Measurements
When it comes to measuring read speed, there are several common metrics that are used to quantify the performance of a storage device. These measurements help you understand how quickly data can be read from the device and assist in comparing different devices. Here are some of the most common read speed measurements:
- Sequential Read Speed: This measurement assesses how quickly a storage device can read data in a continuous, sequential manner. It is usually expressed in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s). Sequential read speed is particularly relevant for tasks that involve copying or transferring large files. For example, if you frequently work with high-definition video editing, a storage device with a higher sequential read speed would allow for faster data transfer during the editing process.
- Random Read Speed: Random read speed measures how fast a storage device can access and retrieve randomly scattered data across its storage. It is especially important for tasks that involve accessing multiple small files, such as opening applications or running databases. Random read speed is typically expressed in input/output operations per second (IOPS). A higher random read speed indicates that the storage device can quickly access and retrieve small files, leading to improved responsiveness and faster data access in everyday computing tasks.
- Access Time: Access time measures the time it takes for the storage device to locate and retrieve the requested data. It is usually measured in milliseconds (ms). A lower access time indicates that the device can quickly locate and retrieve data, resulting in faster overall read performance. Access time is particularly crucial for tasks that require quick response times, such as loading applications or accessing files in real-time situations like gaming or video editing.
When comparing different storage devices, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your tasks. Sequential read speed is more relevant for tasks that involve large file transfers, while random read speed and access time are important for tasks that involve frequent access to small files or require quick response times. It’s worth noting that different use cases may prioritize different read speed measurements.
It’s important to remember that the advertised read speed specifications provided by manufacturers may not always reflect the real-world performance. Factors such as hardware, interface, file system, and cache size can also influence the actual read speed of a storage device. Therefore, relying solely on the advertised read speed numbers may not provide an accurate representation of the device’s performance.
When making a decision about which storage device to choose based on read speed measurements, it is recommended to consider benchmark tests and real-world reviews that assess the actual performance of the device under various conditions and workloads. These tests can provide a more accurate and reliable indication of the read speed performance you can expect from a particular storage device.
How to Test Read Speeds
Testing the read speed of a storage device is essential to determine its performance and suitability for specific tasks. There are various methods and tools available that can help you accurately measure the read speed of your storage device. Here are some common approaches:
- Benchmarking Software: Benchmarking software is designed specifically to test the performance of storage devices. These programs often provide comprehensive read speed tests along with other performance metrics. Popular benchmarking tools include CrystalDiskMark, ATTO Disk Benchmark, and HD Tune. These tools perform a series of read operations on the storage device and provide detailed reports of the read speeds achieved.
- Transfer Speed Tests: Transfer speed tests involve transferring large files from one location to another on a storage device. This method provides a practical and real-world performance evaluation. You can measure the time taken to transfer a large file and calculate the average read speed. However, this method may not accurately capture random read speeds or access time.
- File Copy Tests: Another method to test read speeds is by copying a large file from the storage device to your computer. You can monitor the transfer speed during the copy process, which will give you an indication of the read speed. However, keep in mind that this method involves factors such as file fragmentation and system performance that can affect the results.
- Specialized Tools: Some storage device manufacturers provide their proprietary tools for testing read speeds. These tools often offer specific features tailored to the manufacturer’s devices and can provide accurate readings of the read speed. Check the manufacturer’s website or support resources to see if such tools are available for your storage device.
Regardless of the method you choose, it is important to conduct multiple tests and average the results to get a more accurate representation of the read speed. Also, ensure that no other resource-intensive processes are running in the background, as they can impact the test results.
When performing read speed tests, it is crucial to consider the specific workload and use cases that you will be utilizing the storage device for. Different tasks require different types of read speeds. For example, if you work extensively with large media files, sequential read speed is more critical. On the other hand, if you often deal with small files or databases, random read speed and access time become more relevant.
By testing the read speeds of your storage device, you can gain valuable insights into its performance and make an informed decision regarding its suitability for your specific needs. Keep in mind that read speed is just one aspect of storage device performance, and it should be considered alongside other factors such as capacity, durability, and cost when making a purchasing decision.
Interpreting Read Speed Test Results
Once you have conducted read speed tests on your storage device using benchmarking software or other methods, it’s important to properly interpret the test results to assess the performance of the device. Here are some key considerations when interpreting read speed test results:
- Comparing Read Speeds: Compare the measured read speeds of different storage devices or different configurations of the same device. This comparison will help you determine which device or configuration offers better read performance. Look for higher sequential read speeds for tasks that involve large file transfers, and higher random read speeds for tasks that involve accessing multiple small files.
- Real-World Performance: Keep in mind that read speeds measured in synthetic benchmarks may not always directly translate to real-world performance. Various factors, such as the operating system, file system, and other software running on the computer, can impact actual read speeds. Consider real-world scenarios and workloads similar to your intended usage to get a better understanding of how the device will perform in practical situations.
- Consider Task Requirements: Consider the specific tasks and workload for which you require the storage device. Determine whether the measured read speeds align with the requirements of those tasks. For example, if you frequently work with large media files, ensure that the sequential read speed meets the demands of fast file transfers and playback. If you primarily deal with small files or databases, focus on random read speed and access time.
- Consistency: Look for consistent performance across multiple tests. Inconsistent results could indicate issues with the storage device or other factors affecting performance. Conducting multiple tests and averaging the results can help provide a more accurate representation of the device’s read speed performance.
- Consider Other Factors: Remember that read speed is just one aspect of a storage device’s performance. Consider other factors such as storage capacity, durability, reliability, and cost alongside read speed when determining the overall suitability of a device for your needs.
It’s important to note that test results and interpretations can vary depending on the specific hardware, software, and testing methods used. Therefore, it’s advisable to consult multiple sources, reviews, and expert opinions to obtain a comprehensive understanding of a storage device’s read speed performance.
Keep in mind that read speed is not the sole determinant of performance and user experience. The responsiveness and efficiency of your overall system also depend on factors such as CPU, RAM, and software optimization. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider the storage device’s read speed in conjunction with other components of your system to achieve the desired performance and productivity.
By properly interpreting read speed test results and considering the specific requirements of your tasks, you can make informed decisions when selecting a storage device that offers optimal read performance for your needs.
Understanding Write Speeds
Write speed refers to the rate at which data can be written or saved to a storage device, such as a hard drive or solid-state drive (SSD). It is an important factor to consider when choosing a storage device, especially if you frequently work with large files or perform tasks that involve extensive data writing.
Several factors can affect the write speed of a storage device:
- Hardware: The quality and capabilities of the storage device itself play a significant role in determining its write speed. Faster and more advanced drives typically offer higher write speeds.
- Interface: The interface used to connect the storage device to your computer can also impact write speed. Different interfaces, such as SATA, USB, and Thunderbolt, have varying maximum transfer rates that can affect the write speed of the device.
- File System: The file system used on the storage device can affect write speed. Some file systems are more efficient at writing data quickly and handling large file transfers.
- Cache: Many storage devices, especially SSDs, have a built-in cache that helps improve write speeds. The cache temporarily stores data before it is written to the main storage, allowing for faster write performance.
- Sequential vs. Random Writes: Just like with read speeds, the type of write operations can impact write speed. Sequential writes, where data is written in a continuous, uninterrupted manner, typically achieve higher speeds. On the other hand, random writes, which involve writing data in scattered locations, might result in slower speeds.
When it comes to measuring write speed, similar metrics are used as with read speeds:
- Sequential Write Speed: This measures how quickly data can be written in a continuous, sequential manner. It is usually expressed in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s). Sequential write speed is relevant for tasks that involve writing large files or performing continuous data transfers.
- Random Write Speed: Similar to random read speed, random write speed measures how fast the drive can write data in scattered locations. It is often expressed in input/output operations per second (IOPS) and is important for tasks involving writing multiple small files or performing random data writes.
Testing the write speed of a storage device can be done using benchmarking software or specialized tools. These tests involve writing data to the device and measuring the time it takes to complete the write operation.
When interpreting write speed results, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your tasks. If you frequently work with large file transfers or perform continuous data writes, focusing on devices with higher sequential write speeds can significantly improve your workflow. On the other hand, if you primarily deal with random writes or multiple small file writes, considering devices with higher random write speeds can be beneficial.
Remember that write speed is just one factor to consider when choosing a storage device. Other factors such as storage capacity, cost, and durability should also be taken into account to ensure that the chosen device meets all your requirements.
Factors Affecting Write Speeds
Write speed is influenced by various factors that determine how quickly data can be written or saved to a storage device. Understanding these factors is essential when evaluating the performance and suitability of a storage device for specific tasks. Here are some key factors that can affect write speeds:
- Hardware: The hardware components of a storage device play a significant role in determining its write speed. Factors such as the type of drive (hard disk drive or solid-state drive), the quality of components, and the presence of a cache can impact the overall write performance. Faster and more advanced drives generally offer higher write speeds.
- Interface: The interface used to connect the storage device to your computer can affect write speeds. Different interfaces, such as SATA, USB, or Thunderbolt, have varying maximum data transfer rates. Choosing a storage device with a compatible and high-speed interface can optimize write performance.
- File System: The file system used on the storage device can impact write speeds, especially when dealing with large files. Certain file systems, such as NTFS or exFAT, are more efficient at writing data quickly and handling large file transfers, resulting in improved write performance.
- Cache: Many storage devices, particularly SSDs, come equipped with a built-in cache. The cache temporarily stores data before it is written to the main storage, improving write speeds by allowing for fast data input. The size and efficiency of the cache can affect the overall write performance of the device.
- Sequential vs. Random Writes: The type of write operations can impact write speeds. Sequential writes, where data is written in a continuous, uninterrupted manner, typically achieve higher speeds. In contrast, random writes, which involve writing data in scattered locations, may result in slower speeds due to additional time taken for accessing different parts of the storage device.
In addition to these factors, it’s important to consider the specific workload and use cases that you will be utilizing the storage device for. Different tasks may have different write speed requirements. For example, if you frequently work with large files or perform continuous data transfers, a storage device with higher sequential write speeds may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you primarily deal with random writes or multiple small file writes, devices with higher random write speeds are desirable.
It’s worth noting that the advertised write speed specifications provided by manufacturers may not always reflect real-world performance. Other factors like hardware compatibility, interface limitations, and system configurations can also impact the actual write speeds. Therefore, it’s important to consider real-world tests and reviews that assess the performance of the storage device under various conditions and workloads.
By understanding the factors that affect write speeds, you can make informed decisions when selecting a storage device that offers optimal performance for your specific needs. Considering these factors alongside other elements such as storage capacity, cost, and reliability will help you choose a storage device that meets your requirements and enhances your productivity.
Common Write Speed Measurements
When evaluating the performance of a storage device’s write speed, there are several common metrics used to quantify its capabilities in writing data. These measurements help you understand how quickly data can be written or saved to the device. Here are some of the most common write speed measurements:
- Sequential Write Speed: This measurement assesses how quickly a storage device can write data in a continuous, sequential manner. It is typically expressed in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s). Sequential write speed is particularly relevant for tasks that involve writing or transferring large files, such as video editing or file backups. A higher sequential write speed allows for faster data transfer and more efficient handling of large amounts of data.
- Random Write Speed: Random write speed measures how fast a storage device can write data in scattered or random locations across its storage. It is often expressed in input/output operations per second (IOPS) and is crucial for tasks involving writing multiple small files or performing random data writes. A higher random write speed indicates better performance for tasks that involve frequent data writing and updating, such as running databases or operating system installations.
- Latency: Latency measures the time it takes for a storage device to respond and begin writing data after receiving the write command. It is typically measured in milliseconds (ms). Low latency is desirable since it indicates a minimal delay between issuing the write command and initiating the write process. Low-latency storage devices are particularly important for tasks that require quick response times, such as real-time data processing or high-performance gaming.
When comparing different storage devices or evaluating the performance of a specific device, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your tasks. Sequential write speed is more relevant for tasks that involve writing large files or transferring data in a continuous manner. Random write speed and latency are important for tasks that involve writing multiple small files or require quick response times.
It’s important to note that the advertised write speed specifications provided by manufacturers might not always reflect real-world performance. Other factors, such as hardware compatibility, system configurations, and the specific workload being executed, can impact the actual write speeds achieved. Therefore, it’s recommended to rely on real-world tests, independent reviews, and expert recommendations to obtain a more accurate assessment of a storage device’s write speed performance.
Keep in mind that write speed is just one aspect of a storage device’s overall performance. Factors like storage capacity, data reliability, durability, and cost are equally important considerations when selecting a storage device that best suits your needs.
By understanding common write speed measurements and how they align with your specific requirements, you can make informed decisions when choosing a storage device that offers optimal write performance for your desired tasks.
How to Test Write Speeds
Testing the write speed of a storage device is crucial to assess its performance and determine its suitability for specific tasks that involve extensive data writing. Here are a few methods and tools that can help you accurately measure the write speed of your storage device:
- Benchmarking Software: Utilize benchmarking software explicitly designed to test the performance of storage devices. These tools, such as CrystalDiskMark, ATTO Disk Benchmark, or HD Tune, provide specialized write speed tests along with other performance metrics. These programs perform a series of write operations on the storage device and provide detailed reports of the write speeds achieved.
- Transfer Speed Tests: Conduct transfer speed tests by copying a large file from your computer to the storage device. Monitor the transfer speed during the process to gauge the write speed. This method provides a practical and real-world evaluation of the write performance. However, factors such as file fragmentation, system resources, and background processes can affect the results.
- File Copy Tests: Another approach to test write speeds is by copying a large file from one location to another on the storage device. Measure the time taken to complete the copy process, and calculate the average write speed based on the file size. Keep in mind that this method can be influenced by factors such as file fragmentation and system performance, which may impact the accuracy of the results.
- Manufacturer-Specific Tools: Some storage device manufacturers provide proprietary tools for testing write speeds. These tools are specifically designed for their devices and offer customized features and insights into the write performance. Check the manufacturer’s website or support resources to see if there are any available tools for your storage device.
When conducting write speed tests, it is recommended to perform multiple tests and average the results to obtain a more accurate measurement. Ensure that no other resource-intensive processes are running in the background during the tests, as they can affect the performance and skew the results.
Consider the specific workload and use cases for which you require the storage device when performing write speed tests. Different tasks have varying requirements for write speed. For example, if you frequently work with large files and perform extensive data writing, prioritize devices with higher sequential write speeds. On the other hand, if you mainly deal with random writes or multiple small file writes, focus on devices with higher random write speeds.
Remember that write speed is just one aspect of a storage device’s overall performance. Consider other factors such as storage capacity, durability, reliability, and cost alongside write speed when selecting a storage device that meets your requirements.
By accurately testing the write speeds of your storage device and considering the specific demands of your tasks, you can make informed decisions and choose a storage device that offers optimal write performance for your needs.
Interpreting Write Speed Test Results
Interpreting the results of write speed tests is crucial for understanding the performance of a storage device and determining its suitability for specific tasks. Here are some key considerations when interpreting write speed test results:
- Comparing Write Speeds: Compare the measured write speeds of different storage devices or different configurations of the same device. This comparison helps identify which device or configuration offers better write performance. Look for higher sequential write speeds for tasks that involve writing large files or performing continuous data transfers. Higher random write speeds are desirable for tasks that involve writing multiple small files or performing random data writes.
- Real-World Performance: Remember that write speeds measured in synthetic benchmarks may not always directly translate to real-world performance. Various factors, such as the operating system, file system, and other software running on the computer, can impact actual write speeds. Consider real-world scenarios and workloads similar to your intended usage to get a better understanding of how the device will perform in practical situations.
- Consider Task Requirements: Consider the specific tasks and workload for which you require the storage device. Determine whether the measured write speeds align with the requirements of those tasks. For example, if you frequently work with large file transfers or perform continuous data writes, ensure that the write speeds meet the demands of fast data transfer and writing efficiency. If you primarily deal with random writes or multiple small file writes, focus on devices with higher random write speeds.
- Consistency and Reliability: Look for consistent performance across multiple write speed tests. Consistent results indicate a reliable and predictable performance of the storage device. However, also consider stability and reliability of write speeds under sustained workloads to ensure consistent performance over time.
- Consider Other Factors: Keep in mind that write speed is not the sole determinant of performance and usability. Consider other factors, such as storage capacity, durability, reliability, and cost, alongside write speed when evaluating the overall suitability of a storage device for your specific needs.
It’s important to note that write speed test results can be influenced by various factors, including hardware compatibility, system configurations, and the specific workload being executed. Therefore, it is advisable to rely on real-world tests, independent reviews, and expert recommendations to obtain a more accurate assessment of a storage device’s write speed performance.
By properly interpreting write speed test results and considering the specific requirements of your tasks, you can make informed decisions when selecting a storage device that offers optimal write performance for your desired workloads.
Choosing the Right Data Storage Device Based on Read and Write Speeds
When selecting a data storage device, understanding the read and write speeds is crucial to ensure optimal performance for your specific needs. Choosing the right device based on these speeds can significantly enhance your productivity and efficiency. Here are some key considerations when making a decision:
- Task Requirements: Consider the specific tasks and workloads that you will be performing. If you frequently work with large media files, rapid sequential read and write speeds are essential for quick file transfers and smooth playback. On the other hand, if you primarily deal with small files or perform random read and write operations, prioritizing devices with high random read and write speeds is crucial for improved responsiveness and efficient data handling.
- Balancing Read and Write Speeds: Determine whether your tasks require a stronger emphasis on read or write speeds. Some applications and workflows may require higher read speeds to quickly access and retrieve data, while others may be more write-intensive, necessitating faster write speeds. Understanding this balance will help you choose a storage device that best suits your workload requirements.
- Consider Real-World Scenarios: Keep in mind that the advertised read and write speeds provided by manufacturers may not always reflect real-world performance. In addition to considering the specifications, rely on benchmarks, tests, and user reviews to obtain more accurate information on the actual performance of a storage device under practical conditions similar to your intended usage.
- Other Factors: While read and write speeds are important, consider other factors like storage capacity, durability, reliability, and cost when selecting a data storage device. The storage device should meet all your requirements and align with your budget.
- Future-Proofing: Anticipate your future needs and growth when choosing a storage device. Consider whether the read and write speeds are sufficient for your current tasks and potential future workloads. Investing in a storage device with higher speeds and ample capacity can provide room for scalability as your data needs evolve.
Remember that read and write speeds are not the only factors that influence the overall performance and user experience. The responsiveness of your system also relies on factors like CPU performance, RAM capacity, and software efficiency. It’s important to consider these aspects in conjunction with the read and write speeds of the storage device to achieve the desired performance and productivity.
By carefully evaluating the read and write speeds in relation to the specific demands of your tasks, considering real-world benchmarks, and looking at other important factors, you can choose a data storage device that delivers optimal performance and efficiency for your workflow.