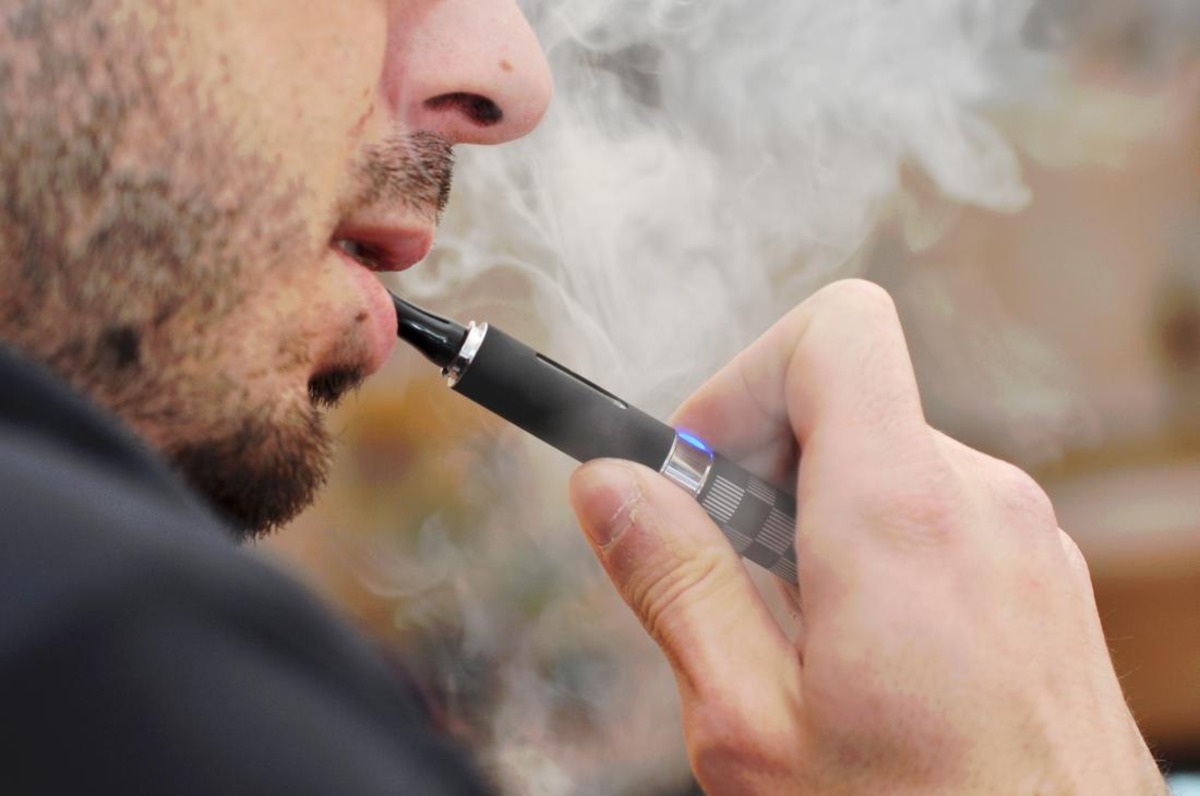
What are Electronic Cigarettes?
Electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, have gained popularity in recent years as alternatives to traditional tobacco cigarettes. These battery-operated devices are designed to simulate the experience of smoking by delivering nicotine and flavorings through an aerosol vapor. While electronic cigarettes are often marketed as a safer alternative to smoking, there is growing concern about their potential health risks.
Electronic cigarettes typically consist of three main components: a battery, an atomizer, and a cartridge or tank. The battery powers the device, while the atomizer heats up the liquid in the cartridge to produce a vapor. The user inhales this vapor, mimicking the act of smoking a traditional cigarette.
One of the reasons electronic cigarettes have gained popularity is their wide range of available flavors. From fruity to dessert-inspired flavors, users have the option to choose their preferred taste. However, it is important to note that while these flavors may be appealing, they can also mask the harmful chemicals present in the electronic cigarette aerosol.
The liquid used in electronic cigarettes, often referred to as e-liquid or vape juice, typically contains nicotine, propylene glycol (PG), vegetable glycerin (VG), and various flavorings. Nicotine, the addictive substance found in tobacco cigarettes, is also present in electronic cigarettes in varying concentrations.
While proponents suggest that electronic cigarettes are a way to satisfy nicotine cravings without the harmful effects of tobacco smoke, there are several health concerns associated with their use. Some studies have suggested that nicotine use in any form, including through electronic cigarettes, can have adverse effects on brain development, especially in adolescents.
In addition to nicotine, electronic cigarette aerosols can contain harmful chemicals such as formaldehyde, acrolein, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These chemicals can have detrimental effects when inhaled, potentially leading to respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and other health complications.
It’s important to note that electronic cigarettes are not without risks. Despite their potential as a smoking cessation aid, they are not approved by regulatory bodies as such. The long-term effects of electronic cigarette use are still being studied, and more research is needed to fully understand the impact on both users and bystanders.
How do Electronic Cigarettes Work?
Electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, work by heating a liquid solution known as e-liquid or vape juice. This liquid is usually made up of nicotine, propylene glycol (PG), vegetable glycerin (VG), and flavorings. When the user inhales, a battery-powered heating element called an atomizer heats up the e-liquid and converts it into an aerosol vapor that is then inhaled.
The process of how electronic cigarettes work can be broken down into several steps:
- Activation: When the user takes a puff or presses a button on the device, the battery is activated and supplies power to the atomizer.
- Heating: The battery powers the atomizer, which contains a small coil or heating element. As the battery heats up the coil, it reaches a high temperature.
- Vaporization: The e-liquid, which is stored in a cartridge or tank, comes into contact with the heated coil. The heat causes the e-liquid to vaporize and turn into an aerosol.
- Inhalation: The user inhales the aerosol vapor through a mouthpiece or drip tip. This vapor is then drawn into the lungs, simulating the act of smoking.
Electronic cigarettes offer users the ability to customize their vaping experience. They can choose from a wide variety of e-liquids with different nicotine strengths and flavors. Some devices even allow users to adjust the temperature or wattage of the heating element, giving them more control over the vapor production and intensity.
Various types of electronic cigarettes are available on the market, including disposable e-cigarettes, rechargeable devices, and advanced personal vaporizers. Disposable e-cigarettes are typically pre-filled with e-liquid and are discarded once the e-liquid runs out. Rechargeable devices usually consist of a rechargeable battery and a refillable cartridge or tank. Advanced personal vaporizers, also known as mods, offer more customization options and are often preferred by experienced vapers.
It’s important to note that while electronic cigarettes are often marketed as safer alternatives to traditional cigarettes, they still deliver nicotine, an addictive substance. The long-term health effects of using electronic cigarettes, especially in non-smokers and young individuals, are still being researched.
Understanding how electronic cigarettes work can help users make informed decisions and be aware of the potential risks associated with their use. It is always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice on smoking cessation and harm reduction strategies.
The Harmful Chemicals in Electronic Cigarettes
Electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, are often marketed as a safer alternative to traditional tobacco cigarettes. However, research has shown that they are not without health risks. One of the major concerns is the presence of harmful chemicals in electronic cigarette aerosols.
Here are some of the harmful chemicals commonly found in electronic cigarettes:
- Nicotine: Nicotine is an addictive substance found in tobacco cigarettes and is also present in electronic cigarettes. It can have various adverse effects on cardiovascular health and can lead to addiction.
- Formaldehyde: Formaldehyde is a known carcinogen and respiratory irritant. It is produced when the liquid in electronic cigarettes is heated to high temperatures.
- Acrolein: Acrolein is a toxic chemical that can cause irritation and damage to the respiratory system. It is formed when glycerin, an ingredient commonly found in e-liquids, is heated.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): VOCs such as benzene, toluene, and xylene are carcinogenic substances that can be present in electronic cigarette aerosols. Prolonged exposure to these compounds can have serious health consequences.
- Heavy Metals: Electronic cigarettes can release small amounts of heavy metals, including lead, cadmium, and nickel, which can be inhaled into the lungs. These metals can have toxic effects on various organs and systems in the body.
- Flavoring Chemicals: Many e-liquids contain flavorings to enhance the vaping experience. However, some flavoring chemicals, such as diacetyl and acetyl propionyl, can cause respiratory health issues when inhaled.
It’s important to note that the levels of these chemicals can vary depending on factors such as the type of electronic cigarette device, the temperature at which it is operated, and the e-liquid composition. Additionally, some studies have found that certain flavors may produce higher levels of toxic chemicals than others.
The inhalation of these harmful chemicals can have serious health implications. They can irritate the respiratory system, cause inflammation in the lungs, and contribute to the development of respiratory diseases. Additionally, long-term exposure to these chemicals may increase the risk of developing cancer, heart disease, and other chronic conditions.
To mitigate the risks associated with electronic cigarette use, it is crucial for users to be informed about the potential dangers of these chemicals. Regulatory bodies are also implementing measures to restrict the use of certain harmful substances in e-liquids and set limitations on nicotine concentrations.
It is always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support on smoking cessation and harm reduction strategies. Quitting smoking altogether remains the best way to minimize the health risks associated with nicotine addiction and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Nicotine Addiction and Health Risks
Nicotine, a highly addictive substance found in tobacco cigarettes, is also present in electronic cigarettes. The presence of nicotine in electronic cigarettes poses significant health risks and can contribute to nicotine addiction.
Here are some key points to consider regarding nicotine addiction and its associated health risks:
- Nicotine Addiction: Nicotine is highly addictive and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Regular use of nicotine-containing electronic cigarettes can result in addiction, making it challenging for individuals to quit or reduce their use.
- Cardiovascular Risks: Nicotine can have detrimental effects on cardiovascular health. It can increase heart rate, raise blood pressure, and constrict blood vessels, potentially leading to an increased risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Respiratory Problems: Inhalation of nicotine can irritate and damage the respiratory system. It can cause coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Prolonged exposure to nicotine may contribute to the development of respiratory conditions such as chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Brain Development: Nicotine use, especially during adolescence, can negatively impact brain development. It can interfere with memory, attention, and cognitive function. The adolescent brain is particularly vulnerable to the effects of nicotine, potentially leading to long-term consequences.
- Mood and Mental Health: Nicotine can affect mood and mental health. It can worsen symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress. Some individuals may use electronic cigarettes as a means to self-medicate or cope with emotional difficulties, creating a cycle of dependence.
It’s crucial to recognize that nicotine addiction and its associated health risks apply to both traditional tobacco cigarettes and electronic cigarettes. While electronic cigarettes are often marketed as a smoking cessation aid or a safer alternative to smoking, they are not without risks.
Individuals who are considering using electronic cigarettes as a means to quit smoking should consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and support. There are evidence-based smoking cessation methods available that do not involve the use of nicotine-containing products.
Ultimately, quitting nicotine altogether is the most effective way to reduce the associated health risks. Breaking free from nicotine addiction can lead to significant improvements in overall health and wellbeing.
Respiratory Problems Caused by Electronic Cigarettes
While electronic cigarettes are often promoted as a safer alternative to traditional tobacco cigarettes, there is growing evidence that they can present respiratory health risks. The inhalation of electronic cigarette aerosols can lead to various respiratory problems, ranging from mild irritation to more severe conditions.
Here are some key respiratory problems associated with electronic cigarette use:
- Irritation and Airway Sensitivity: Electronic cigarette aerosols can irritate the respiratory system, causing symptoms such as coughing, throat irritation, and excessive phlegm production. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma, may experience worsened symptoms due to exposure to electronic cigarette aerosols.
- Acute Respiratory Effects: Inhalation of electronic cigarette aerosols can lead to acute respiratory effects, such as bronchoconstriction and airway constriction. These effects can cause breathing difficulties, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Increased Risk of Respiratory Infections: The inhalation of electronic cigarette aerosols has been associated with an increased risk of respiratory infections. The chemicals and fine particles in the aerosols can impair the immune system’s ability to fight off infections, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory illnesses.
- Development of Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Long-term exposure to electronic cigarette aerosols may contribute to the development of chronic respiratory conditions. Studies have suggested potential links between electronic cigarette use and conditions such as chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Popcorn Lung: Some flavoring chemicals commonly used in e-liquids, such as diacetyl, have been associated with a condition called bronchiolitis obliterans, also known as “popcorn lung.” This irreversible lung disease damages the smallest airways in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties and decreased lung function.
It’s important to note that long-term studies on the respiratory effects of electronic cigarette use are still ongoing, and the full extent of the risks is not yet fully understood. However, the current evidence highlights concerns about the potential for respiratory harm.
Reducing exposure to electronic cigarette aerosols is crucial for protecting respiratory health. Individuals who do not currently use electronic cigarettes should refrain from starting, while current users should consider exploring alternative smoking cessation methods that do not involve inhalation of potentially harmful aerosols.
Consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and support for individuals seeking to quit smoking or reduce their use of electronic cigarettes. Prioritizing respiratory health is essential for maintaining overall wellbeing.
Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Electronic Cigarettes
Electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, have been marketed as a safer alternative to traditional tobacco cigarettes. However, recent evidence suggests that they are not without cardiovascular risks. The use of electronic cigarettes can have detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of various cardiovascular diseases.
Here are some key cardiovascular risks associated with electronic cigarette use:
- Increased Heart Rate: The nicotine present in electronic cigarettes can lead to an increase in heart rate. This increase in heart rate can strain the cardiovascular system and potentially contribute to the development of heart-related issues.
- Elevated Blood Pressure: Nicotine, when absorbed into the bloodstream, can cause a temporary increase in blood pressure. Prolonged elevation in blood pressure can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of hypertension, heart disease, and strokes.
- Arterial Stiffness and Atherosclerosis: Electronic cigarette use has been linked to arterial stiffness, a condition characterized by reduced elasticity of the arteries. Arterial stiffness is a risk factor for atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries that can narrow them and restrict blood flow, leading to cardiovascular problems.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: Exposure to electronic cigarette aerosols has been shown to impair the function of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. Endothelial dysfunction can contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease by affecting blood flow regulation and promoting inflammation and clot formation.
- Increased Risk of Heart Attacks and Strokes: The combination of nicotine and other chemicals in electronic cigarettes can increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. The effects of electronic cigarette use on blood coagulation and the development of blood clots can further contribute to these cardiovascular events.
It is crucial to recognize that electronic cigarettes are not a risk-free alternative to smoking. While they may offer some harm reduction compared to traditional cigarettes, they still carry health risks, particularly for the cardiovascular system.
It is advisable for individuals concerned about their cardiovascular health to avoid electronic cigarette use altogether. Quitting smoking altogether, including the use of electronic cigarettes, is the best way to reduce the associated cardiovascular risks.
Consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and support for individuals seeking to quit smoking or explore alternative smoking cessation methods. Prioritizing cardiovascular health through a smoke-free lifestyle is essential for long-term wellbeing.
Effects of Electronic Cigarettes on Oral Health
Electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, have gained popularity as an alternative to traditional tobacco cigarettes. However, concerns have been raised about the potential effects of electronic cigarette use on oral health. While more research is needed to fully understand the long-term impacts, several oral health risks have been associated with electronic cigarette use.
Here are some key effects of electronic cigarettes on oral health:
- Dry Mouth: The inhalation of electronic cigarette aerosols can contribute to dry mouth, a condition in which there is a reduced production of saliva. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing acids, washing away food particles, and preventing the growth of bacteria. Dry mouth can lead to an increased risk of cavities, bad breath, and oral infections.
- Decreased Immune Response: Electronic cigarette aerosols contain chemicals that can weaken the immune response in the oral cavity. This can make individuals more susceptible to oral infections, including gum disease.
- Gum Irritation and Inflammation: The chemicals in electronic cigarette aerosols can irritate the gums and promote inflammation. This can lead to gum redness, swelling, and tenderness. Long-term use may contribute to the development of gum disease, a condition that can cause tooth and bone loss if left untreated.
- Delayed Wound Healing: Electronic cigarette use has been linked to delayed wound healing in the oral cavity. This can impact the recovery process after oral surgeries, tooth extractions, or other dental procedures.
- Oral Cancer Risk: Some studies have suggested an association between electronic cigarette use and an increased risk of oral cancer. While more research is needed to understand the exact relationship, the presence of potentially harmful chemicals in electronic cigarette aerosols raises concerns about their impact on oral tissue.
It is important to note that electronic cigarettes are relatively new, and the long-term effects on oral health are still being studied. However, the current evidence suggests that electronic cigarette use can have adverse effects on oral health, similar to the risks associated with traditional tobacco cigarettes.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular dental check-ups, brushing and flossing daily, and avoiding electronic cigarette use altogether, can help mitigate the potential oral health risks. Consulting with dental professionals can provide personalized guidance and support for maintaining oral health and making informed decisions about electronic cigarette use.
Prioritizing oral health is essential for overall wellbeing, and minimizing exposure to potentially harmful substances is crucial for a healthy mouth.
Impact of Electronic Cigarettes on Lung Function
The inhalation of electronic cigarette aerosols, also known as vaping, has become increasingly popular in recent years. However, concerns have arisen regarding the potential impact of electronic cigarette use on lung function. While research is still ongoing, evidence suggests that electronic cigarettes can have detrimental effects on lung health.
Here are some key points about the impact of electronic cigarettes on lung function:
- Lung Irritation and Inflammation: Electronic cigarette aerosols can irritate and inflame the airways, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can be especially problematic for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Reduced Lung Function: Studies have indicated that electronic cigarette use is associated with a decrease in lung function measurements, such as forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC). This reduction in lung function can impair the ability to breathe effectively and can contribute to the development of respiratory diseases.
- Development of Respiratory Symptoms: Individuals who use electronic cigarettes are more likely to experience respiratory symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, and wheezing. These symptoms can be indicative of airway obstruction and inflammation.
- Lung Injury and Respiratory Distress: Cases of severe lung injury, known as e-cigarette or vaping-associated lung injury (EVALI), have been reported in individuals who use electronic cigarettes. These cases have resulted in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and, in some instances, death. The exact cause of EVALI is still under investigation, but it highlights the potential for serious lung damage caused by electronic cigarette use.
- Altered Lung Microbiome: Research has suggested that electronic cigarette use can lead to alterations in the lung microbiome, the community of bacteria and microorganisms that reside in the lungs. Imbalances in the lung microbiome can impact lung health and increase the risk of respiratory infections.
While electronic cigarettes are often marketed as a safer alternative to traditional tobacco cigarettes, it is important to recognize that they are not risk-free. The chemicals and particles present in electronic cigarette aerosols can have harmful effects on lung function and respiratory health.
Quitting smoking altogether, including the use of electronic cigarettes, is the best option for preserving lung health. For individuals seeking assistance with smoking cessation or reducing electronic cigarette use, healthcare professionals can provide guidance, support, and access to resources.
Protecting lung function is crucial for overall wellbeing, and minimizing exposure to potentially harmful substances is essential for maintaining healthy lungs.
Electronic Cigarettes and the Risk of Cancer
The use of electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, has raised concerns about the potential risk of cancer. While electronic cigarettes are often marketed as a safer alternative to traditional tobacco cigarettes, research suggests that they are not without potential risks for developing cancer.
Here are some key points regarding the relationship between electronic cigarettes and the risk of cancer:
- Chemical Exposure: Electronic cigarette aerosols contain a variety of chemicals, including potentially harmful substances such as formaldehyde, acrolein, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Prolonged exposure to these chemicals can increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Nicotine: Nicotine, a highly addictive substance found in both traditional and electronic cigarettes, is not a direct cause of cancer. However, nicotine can promote the growth and spread of cancer cells, making it easier for cancer to develop and progress.
- Genotoxicity: Some studies have suggested that electronic cigarette aerosols can cause DNA damage and mutations, which are known factors in the development of cancer. These genotoxic effects are believed to be the result of the chemicals present in electronic cigarette aerosols.
- Exposure to Carcinogens: Electronic cigarettes can expose users to carcinogens such as formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and acrolein, all of which are known to cause cancer in humans. These carcinogens are formed when the e-liquid in electronic cigarettes is heated and aerosolized.
- Long-Term Effects: While electronic cigarettes have not been in use long enough for long-term studies, it is important to note that the development of cancer can be a gradual process. Prolonged exposure to the chemicals and carcinogens in electronic cigarette aerosols may increase the risk of cancer over time.
While the exact risk of developing cancer from electronic cigarette use is still being studied, it is important for individuals to be aware of the potential risks involved. The available evidence suggests that electronic cigarettes are not risk-free when it comes to cancer development.
To protect overall health and reduce the risk of cancer, it is advisable to avoid the use of electronic cigarettes altogether, particularly for individuals who do not currently use tobacco products. Consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and support for smoking cessation and reducing the use of electronic cigarettes.
Minimizing exposure to potentially harmful substances, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and participating in regular cancer screenings are important steps in reducing the risk of cancer and maintaining overall well-being.
Secondhand Vapor and Its Dangers
Electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, are not only a concern for the individuals who use them but also for those who are exposed to the secondhand vapor. Secondhand vapor refers to the aerosol that is exhaled by electronic cigarette users and can pose potential dangers to bystanders. While more research is needed to fully understand the extent of the risks, there are several key points to consider:
- Chemical Exposure: Secondhand vapor from electronic cigarettes can contain a variety of potentially harmful chemicals, including nicotine, formaldehyde, and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Bystanders can be exposed to these substances, which can cause respiratory irritation and have short-term and long-term health effects.
- Nicotine Exposure: Secondhand vapor can also contain nicotine, an addictive substance. Non-users, especially children, pregnant women, and individuals with cardiovascular conditions, may be particularly vulnerable to the effects of nicotine exposure. Nicotine exposure can increase heart rate and blood pressure, potentially contributing to cardiovascular issues.
- Respiratory Effects: The inhalation of secondhand vapor can irritate the respiratory system and trigger respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions may experience worsened symptoms when exposed to electronic cigarette aerosols.
- Chemical Composition Variation: The composition of secondhand vapor can vary depending on factors such as the type of electronic cigarette device, the e-liquid used, and how the device is operated. Different devices and settings can produce varying levels of chemicals and different combinations of potentially harmful substances.
- Unregulated Exposure: Unlike traditional tobacco cigarettes, there are currently no standardized regulations regarding where and when electronic cigarettes can be used. This lack of regulation puts non-users at higher risk of involuntary exposure to secondhand vapor in various settings, including public spaces and enclosed environments.
It is important to be aware of the potential dangers of secondhand vapor and to consider the well-being of those around electronic cigarette users. Implementing policies to restrict electronic cigarette use in public areas and promoting awareness about the potential risks can help protect individuals from unnecessary exposure to secondhand vapor.
Further research is necessary to better understand the long-term effects of secondhand vapor exposure. However, it is prudent to take precautions and prioritize the health and safety of both electronic cigarette users and non-users by promoting smoke-free environments.
Consulting with healthcare professionals can provide additional insight on ways to minimize exposure and protect the health of both users and non-users alike.
Electronic Cigarettes and the Youth
The rise in popularity of electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, has raised concerns about their impact on the youth. Electronic cigarettes have become a prevalent trend among young individuals, posing risks and potential consequences for this vulnerable population.
Here are some key points regarding electronic cigarettes and the youth:
- Gateway to Nicotine Use: Electronic cigarettes have been found to serve as a gateway to nicotine addiction among young individuals. Experimentation with electronic cigarettes can potentially lead to the use of traditional tobacco cigarettes, putting young people at risk for long-term nicotine dependency.
- Brain Development: The adolescent brain is particularly vulnerable to the effects of nicotine. Nicotine exposure during this critical period can disrupt brain development, impacting learning, attention, and cognitive function. It may have long-lasting consequences on the developing brain, potentially leading to addiction and other mental health issues.
- Appealing Marketing Strategies: Electronic cigarette companies often use marketing strategies that target young individuals, incorporating appealing flavors, vibrant packaging, and social media influence. These tactics can make electronic cigarettes more attractive and accessible to young people, increasing their likelihood of experimenting with these products.
- Peer Pressure and Social Norms: Young individuals may feel pressured to use electronic cigarettes due to peer influence and the perception that it is a socially acceptable behavior. The normalization of electronic cigarette use among their peers can reinforce the belief that it is safe and minimize awareness of potential risks and long-term health consequences.
- Risks of Nicotine Addiction: Young individuals who experiment with electronic cigarettes are at an increased risk of developing nicotine addiction. Nicotine addiction can have serious health consequences and may persist into adulthood, affecting future choices and overall wellbeing.
It is crucial to implement effective measures to prevent the initiation of electronic cigarette use among young individuals:
- Comprehensive Education and Awareness: Providing accurate and age-appropriate information about the risks of electronic cigarettes can help young individuals make informed decisions and resist the temptation to experiment with these products.
- Stricter Regulations: Enforcing stricter age verification systems and implementing policies that restrict the marketing, sales, and availability of electronic cigarettes to minors can help reduce their accessibility and curb the use among young individuals.
- Promoting Healthy Alternatives: Encouraging young individuals to engage in healthier activities, such as sports, hobbies, and creative pursuits, can divert their attention from electronic cigarette use and provide healthier outlets for self-expression and stress relief.
- Fostering Supportive Environments: Creating environments that promote positive role models, emphasize the dangers of tobacco and nicotine use, and provide support for those seeking to quit can be instrumental in preventing and reducing electronic cigarette use among the youth.
It is essential to prioritize the health and well-being of young individuals by implementing preventative measures and providing supportive resources to help them make informed choices and lead healthy, tobacco-free lives.
Are Electronic Cigarettes a Safer Alternative to Smoking?
Electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, have been marketed as a potentially safer alternative to traditional tobacco cigarettes. While it is true that electronic cigarettes do not produce tobacco smoke, which contains numerous harmful chemicals, the question of whether they are a truly safer alternative is a complex one.
Here are some key points to consider when evaluating the safety of electronic cigarettes:
- Reduced Chemical Exposure: Electronic cigarettes do not burn tobacco like traditional cigarettes, which eliminates the combustion process that leads to the formation of many harmful chemicals. As a result, electronic cigarette aerosols generally contain fewer toxic chemicals compared to tobacco smoke.
- Presence of Nicotine: Most electronic cigarettes contain nicotine, a highly addictive substance found in tobacco. While nicotine itself is not carcinogenic, it can have adverse effects on cardiovascular health and may contribute to addiction. It is important to note that the health risks associated with nicotine use extend beyond the method of delivery.
- Potential for Harmful Chemicals: While electronic cigarette aerosols contain fewer toxic chemicals than tobacco smoke, they are not free from potentially harmful substances. The chemicals in electronic cigarette aerosols can include formaldehyde, acrolein, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which have been associated with respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Limited Long-Term Studies: Electronic cigarettes are a relatively new phenomenon, and long-term studies on their effects are still ongoing. It will take time to fully understand the potential long-term health implications of regular electronic cigarette use.
- Gateway to Smoking: Electronic cigarettes have raised concerns about serving as a gateway to traditional smoking, especially among young individuals. Experimentation with electronic cigarettes can increase the likelihood of transitioning to tobacco cigarettes, which come with well-established health risks.
- Regulatory Challenges: The fast-evolving electronic cigarette industry presents regulatory challenges, particularly in monitoring and ensuring product safety standards. Inconsistent manufacturing practices and quality control can lead to variations in product safety and reliability.
It is crucial to approach the concept of electronic cigarettes as a safer alternative with caution. While they may offer harm reduction potential for current smokers who switch completely, they are not without risks, particularly for non-smokers and young individuals. Quitting smoking altogether remains the best way to minimize health risks associated with tobacco and nicotine use.
For individuals seeking to quit smoking or reduce their use of electronic cigarettes, consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and support. They can recommend evidence-based smoking cessation methods and develop tailored plans to improve overall health and wellbeing.
Regulations and Restrictions on Electronic Cigarettes
As the popularity of electronic cigarettes, also known as e-cigarettes or vape pens, has increased, regulatory bodies have started implementing measures to address their use and potential risks. These regulations aim to protect public health, especially that of non-users and young individuals, by establishing guidelines and restrictions on electronic cigarette manufacturing, marketing, sales, and usage.
Here are some key points regarding regulations and restrictions on electronic cigarettes:
- Age Restrictions: Many countries and regions have implemented age restrictions on the sale and purchase of electronic cigarettes. These restrictions aim to prevent underage individuals from accessing and using these products, as young people are more susceptible to the negative effects of nicotine and potential addiction.
- Product Safety and Quality: Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on ensuring the safety and quality of electronic cigarette products. This includes implementing standards for manufacturing processes, ingredients, and labeling requirements. Regulations aim to minimize potential health risks associated with poorly manufactured or contaminated products.
- Marketing and Advertising: Restrictions on marketing and advertising of electronic cigarettes vary by jurisdiction. Many countries have implemented rules to prohibit or limit advertising that targets young individuals or makes unsubstantiated claims about the safety or effectiveness of electronic cigarettes as smoking cessation aids.
- Public Use and Indoor Vaping: Some jurisdictions have established restrictions on where electronic cigarettes can be used, including bans on vaping in public places and enclosed environments. These restrictions aim to protect bystanders from exposure to secondhand vapor and promote smoke-free environments.
- Flavor Bans: In response to concerns about flavored electronic cigarettes attracting young individuals, some jurisdictions have implemented flavor bans or restrictions. These measures aim to reduce the appeal of electronic cigarettes to youth by limiting the availability of enticing flavors.
- Product Packaging: Regulations also address electronic cigarette product packaging, including requirements for child-resistant packaging to prevent accidental ingestion by young children. Packaging regulations aim to enhance consumer safety and reduce the risk of unintentional exposure.
It is important to note that regulations on electronic cigarettes can vary significantly between countries and regions. As the understanding of the potential risks associated with electronic cigarettes continues to evolve, regulatory bodies may adjust their guidelines to adapt to emerging evidence and protect public health.
Ensuring compliance with regulations is crucial for electronic cigarette manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. It is equally important for individuals using electronic cigarettes to stay informed about the regulations in their specific jurisdiction to promote responsible and safe usage.
Consulting with healthcare professionals and staying updated on local regulations can provide individuals with the necessary information to make informed decisions about electronic cigarette use and ensure adherence to applicable guidelines.