The Basics of Surround Sound
Surround sound is a technology that creates a multi-dimensional audio experience, immersing the listener in a three-dimensional sound environment. Unlike traditional stereo sound, which only provides audio signals from two speakers, surround sound uses multiple speakers strategically placed around the listening area. This setup allows for the realistic spatial positioning of sounds, making you feel like you’re part of the action.
The concept behind surround sound is based on the way we perceive sound in real life. When we hear a sound in our environment, our brain processes subtle audio cues such as direction, distance, and intensity to determine the source of the sound. By replicating these natural cues through a speaker system, surround sound aims to recreate a lifelike audio experience.
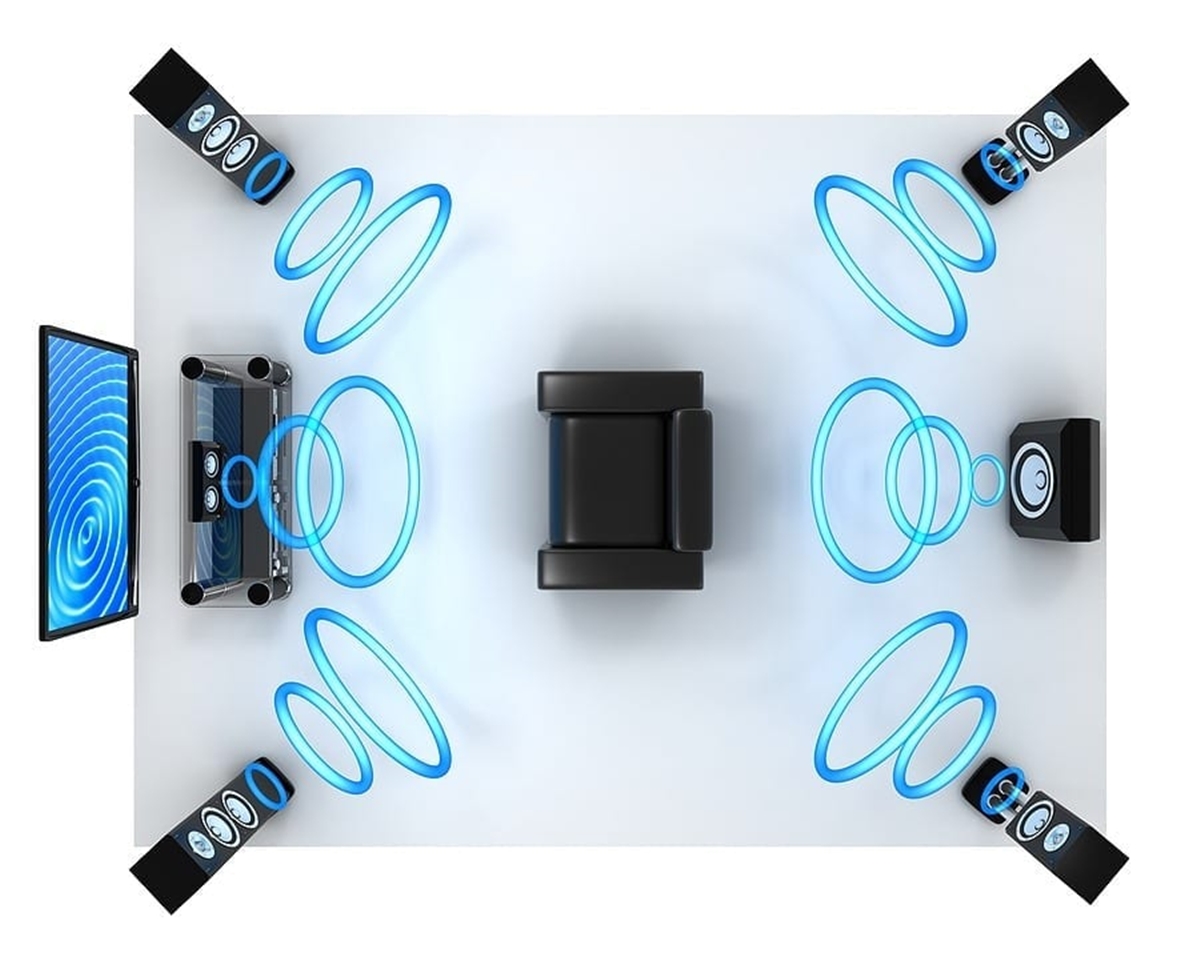
The most common surround sound setups are 5.1 and 7.1 systems. In a 5.1 system, there are five main speakers and one subwoofer. The main speakers consist of a center speaker placed below or above the display screen, two front speakers on either side of the screen, and two surround speakers placed behind the listener. The subwoofer is responsible for reproducing low-frequency sounds, adding depth and impact to the audio. A 7.1 system includes two additional surround speakers, placed alongside or slightly behind the listener.
Surround sound technology is commonly used in home theater systems, gaming setups, and movie theaters. It enhances the audio experience by providing a more realistic and immersive soundstage. For example, watching a movie with surround sound allows you to hear the dialogue coming from the center speaker, background sounds from the surround speakers, and low-frequency effects from the subwoofer.
To achieve the full potential of surround sound, audio content needs to be specially encoded in formats such as Dolby Digital or DTS. These formats encode the audio with separate channels for each speaker in the system, ensuring accurate positioning and distribution of sound. This encoded audio is then decoded and played back by the surround sound receiver, which sends the appropriate signals to each speaker.
Overall, surround sound technology revolutionizes the way we experience audio, providing a more immersive and engaging sound environment. Whether you’re watching your favorite movies, playing games, or enjoying music, surround sound adds depth, realism, and excitement to your listening experience.
How Surround Sound Works
Surround sound technology works by using multiple speakers strategically placed around the listener to create a more immersive audio experience. It relies on the principle of audio localization, which is our ability to determine the direction and distance of sound sources. By reproducing audio cues that mimic the way we hear sound in the real world, surround sound systems create a three-dimensional soundstage.
The key element in surround sound is the use of multiple speakers. The most common setup is a 5.1 system, which includes five main speakers and one subwoofer. The main speakers consist of a center speaker, two front speakers, and two surround speakers. The center speaker serves as the anchor, reproducing dialogues and other prominent sounds in a movie or TV show. The front speakers, usually placed on either side of the screen, provide a wide stereo image and handle directional effects. The surround speakers are responsible for creating an enveloping sound environment by reproducing ambient sounds and background effects.
The subwoofer, also known as the “.1” in the 5.1 setup, handles the low-frequency sounds or bass. It adds depth and impact to explosions, rumbling sounds, and music with deep bass. The subwoofer is typically placed in a central location to evenly distribute low-frequency audio throughout the room.
Surround sound systems also rely on audio codecs such as Dolby Digital and DTS. These codecs encode the audio signals into separate channels, allowing for accurate positioning of sound. For example, a surround sound-encoded movie will have separate audio tracks for the center speaker, front speakers, surround speakers, and the subwoofer. The surround sound receiver decodes these encoded audio signals and sends them to the respective speakers for playback.
The listener’s position and the room acoustics also play a significant role in how surround sound works. Ideally, the listener should be seated at the center of the room, equidistant from all the speakers, to experience the optimal soundstage. Additionally, the room’s layout, furniture, and wall surfaces can affect the way sound reflects and interacts with the environment. Proper speaker placement, room treatment, and calibration become crucial in creating an accurate and immersive surround sound experience.
Dolby Digital Surround Sound
Dolby Digital is a widely used audio coding format that is commonly associated with surround sound systems. It is known for its high-quality audio reproduction and widespread compatibility across various devices and platforms.
The Dolby Digital format utilizes a 5.1-channel configuration, consisting of five speakers and one subwoofer. The five speakers include a center speaker, two front speakers, and two surround speakers, while the subwoofer handles low-frequency sounds.
Dolby Digital employs perceptual audio coding, which compresses the audio without significant loss in sound quality. This compression allows for efficient storage and transmission of audio content while delivering a cinematic and immersive experience.
One of the key features of Dolby Digital is its ability to create a multidimensional soundstage by precisely placing sounds in space. This enhances the overall audio experience by accurately reproducing directionality, depth, and spatial positioning of different sound elements. For example, the dialogue in a movie will come from the center speaker, while special effects and background sounds will be distributed across the front, surround, and subwoofer speakers.
Furthermore, Dolby Digital supports a wide dynamic range, allowing for both subtle nuances and powerful crescendos to be reproduced faithfully. This dynamic range is especially crucial for delivering impactful and realistic sound effects in movies, games, and other multimedia content.
In addition to its use in home theater systems, Dolby Digital is also commonly used in cinemas and broadcasting. It has become the standard for encoding audio in DVDs and Blu-ray discs, ensuring a consistent and immersive audio experience for viewers.
Over the years, Dolby has introduced advancements to the Dolby Digital format. For example, Dolby Digital Plus provides even higher audio quality and supports up to 7.1 channels for an extended surround sound experience. Dolby TrueHD, on the other hand, is a lossless audio codec that offers uncompressed, studio-quality audio.
Overall, Dolby Digital has played a significant role in shaping the way we experience audio in home theaters, cinemas, and various entertainment platforms. Its ability to provide exceptional sound quality and precise audio positioning has made it a preferred choice among audio enthusiasts and movie lovers alike.
DTS Surround Sound
DTS, which stands for “Digital Theater Systems,” is another popular audio coding format widely used in surround sound systems. Similar to Dolby Digital, DTS provides high-quality audio reproduction and is known for its immersive sound experience.
DTS surround sound systems typically use a 5.1 or 7.1-channel configuration, similar to Dolby Digital. Both setups consist of a center speaker, front speakers, surround speakers, and a subwoofer. The main difference lies in the encoding and decoding process.
DTS employs a different audio encoding algorithm known as “coherent acoustics,” which utilizes a higher bitrate compared to Dolby Digital. This higher bitrate allows for less compression and, in turn, can result in potentially better audio quality.
One of the key advantages of DTS surround sound is its ability to deliver highly detailed audio reproduction, especially in the mid and high-frequency ranges. This can result in a more nuanced and accurate sound representation, allowing listeners to experience every subtle detail in the audio mix.
DTS is also known for its support of high-definition audio formats, such as DTS-HD Master Audio and DTS:X. DTS-HD Master Audio, equivalent to Dolby TrueHD, is a lossless audio codec that provides uncompressed, studio-quality audio, offering a truly immersive listening experience. DTS:X, on the other hand, is an object-based audio technology that allows sound engineers to position sounds in a three-dimensional space, providing a more realistic and lifelike audio environment.
Another significant advantage of DTS surround sound is its ability to support lower latency, making it an attractive choice for gaming enthusiasts. The low latency ensures that audio is synchronized with the on-screen action, reducing any perceived delay between visuals and sound effects.
Similar to Dolby Digital, DTS is widely used in various entertainment platforms, including home theaters, cinemas, and gaming consoles. Many Blu-ray discs and video games include DTS-encoded audio tracks, enabling users to experience high-quality surround sound.
In recent years, there have been ongoing debates among audio enthusiasts regarding the differences between Dolby Digital and DTS surround sound. Personal preferences often play a significant role, as some individuals may prefer the audio characteristics of one format over the other.
Ultimately, both Dolby Digital and DTS surround sound formats offer exceptional audio experiences, immersing listeners in a rich, multi-dimensional soundstage. The choice between them often depends on the specific requirements, equipment compatibility, and personal preferences of the user.
1 Surround Sound
5.1 surround sound is one of the most common and widely used configurations in home theater systems and entertainment setups. It refers to a speaker setup consisting of five main speakers and one subwoofer, creating a multi-channel audio experience.
The “5” in 5.1 represents the number of main speakers, and the “.1” refers to the subwoofer. The five main speakers include a center speaker, two front speakers (left and right), and two surround speakers (left and right). These speakers work in harmony to deliver an immersive audio experience with accurate sound positioning and spatial effects.
The center speaker plays a vital role in 5.1 surround sound as it is responsible for reproducing dialogues and other significant sounds in movies, TV shows, and games. Placed either above or below the display screen, the center speaker helps to anchor the audio and ensure clear and distinct dialogue reproduction.
The two front speakers are typically placed on either side of the display screen or the viewing area. They deliver stereo sound with a wide soundstage, providing clear left and right audio separation. These speakers are responsible for directional effects, such as panning sounds, music, and ambient effects.
The two surround speakers are placed behind or to the side of the listener, creating an enveloping sound environment. These speakers reproduce ambient sounds, background effects, and positional audio cues, enhancing the overall immersiveness of the audio playback.
Lastly, the subwoofer, often referred to as the “.1” in the setup, is designed to handle low-frequency sounds or bass. It adds depth and impact to explosive action scenes, rumbling sound effects, and music with deep bass notes. The subwoofer is typically placed in a central location within the setup to evenly distribute low-frequency audio throughout the room.
5.1 surround sound technology enhances the overall audio experience by creating a realistic and immersive soundstage. It allows for accurate positioning of sounds, making viewers feel like they are a part of the action happening on the screen. Whether you are watching movies, playing games, or listening to music, 5.1 surround sound delivers a more engaging and lifelike audio experience.
To enjoy the full benefits of 5.1 surround sound, it is crucial to properly set up and calibrate the speakers. This includes ensuring correct speaker placement, considering room acoustics, and fine-tuning the settings of the audio receiver or amplifier. Proper calibration ensures accurate sound distribution, balanced audio levels, and seamless integration between the speakers and subwoofer.
Overall, 5.1 surround sound is a popular choice for those seeking an immersive audio experience at home. Its incorporation of multiple speakers and a dedicated subwoofer provides a rich and dynamic sound environment, bringing movies, games, and music to life.
1 Surround Sound
7.1 surround sound takes the immersive audio experience to the next level by incorporating an additional set of surround speakers to the traditional 5.1 setup. It is designed to provide an even more immersive and lifelike soundstage for home theater enthusiasts and audio enthusiasts.
A 7.1 surround sound setup consists of seven main speakers and one subwoofer. The additional two speakers are known as “rear surround speakers” and are placed behind the listener, completing the surround sound experience.
Similar to the 5.1 setup, the seven main speakers include a center speaker, two front speakers (left and right), two surround speakers (left and right), and now, two rear surround speakers (left and right). Each of these speakers plays a specific role in creating a realistic and enveloping audio environment.
The center speaker acts as the anchor for dialogue and important sound elements, reproducing clear and distinct vocals. The front left and right speakers provide a wide stereo soundstage, creating directional effects and delivering detailed audio separation.
The two surround speakers are responsible for producing ambient sounds, background effects, and positional audio cues, enveloping the listener and enhancing the immersive experience. Placed on the sides of the listening area, these speakers help create a sense of depth and dimensionality in the soundstage.
The addition of two rear surround speakers is what sets the 7.1 setup apart. These speakers are placed behind the listener and provide an even more immersive audio experience. By including rear surround speakers, sound effects or ambient noises that are meant to come from behind the viewer can be accurately positioned, creating a more realistic and captivating audio presentation.
The subwoofer, as in the 5.1 setup, handles low-frequency sounds and adds depth to explosive action scenes, rumbling effects, and bass-heavy music. It helps create a powerful and impactful audio experience, allowing viewers to feel the intensity of the sound effects.
7.1 surround sound systems are particularly popular among avid film enthusiasts, gamers, and audio enthusiasts who seek a high-fidelity audio experience. The additional speakers provide improved accuracy in sound positioning, creating a more immersive and engaging environment.
When setting up a 7.1 surround sound system, careful consideration of speaker placement and room acoustics is essential. Proper calibration and fine-tuning of the audio receiver or amplifier ensure seamless integration between all speakers, allowing for optimal sound distribution and balance.
Overall, 7.1 surround sound brings an enhanced level of realism and immersion to home theaters and entertainment setups. By expanding the speaker configuration to include rear surround speakers, viewers can experience a more complete and immersive audio experience, making movies, games, and music come to life in a whole new way.
Difference between Dolby Digital and DTS Surround Sound
Dolby Digital and DTS are two popular audio coding formats used in surround sound systems. While they both aim to deliver immersive and high-quality audio experiences, there are some differences between the two that may influence personal preferences.
Compression and Audio Quality: One key difference between Dolby Digital and DTS lies in their compression algorithms. Dolby Digital uses perceptual audio coding, which offers efficient compression without significant loss of sound quality. On the other hand, DTS utilizes coherent acoustics coding, which typically results in higher bitrates and potentially better audio fidelity. As a result, some audio enthusiasts claim that DTS provides a more detailed and precise sound experience, especially in the mid and high-frequency ranges.
Compatibility and Availability: Dolby Digital has been a prevalent and widely supported format for many years. It is commonly used in DVDs, Blu-ray discs, and streaming platforms, making it easily accessible and compatible with various devices. DTS, while also widely used, may have slightly less availability compared to Dolby Digital, particularly in certain streaming services or older media formats. However, both formats have become more widely supported, and the difference in availability is diminishing.
Bitrate and Channel Support: Dolby Digital typically uses a lower bitrate compared to DTS. While this may result in slightly lower audio fidelity in some cases, Dolby Digital still offers excellent sound quality for most consumers. Additionally, Dolby Digital is known for its 5.1-channel surround sound, but it has expanded to support newer formats such as Dolby TrueHD, which offers even higher audio quality and support for more channels. DTS, on the other hand, often offers higher bitrates and has embraced newer technologies like DTS-HD Master Audio and DTS:X, allowing for lossless audio and object-based audio experiences with advanced speaker configurations.
Auditory Preference and Room Acoustics: Ultimately, the perceived difference between Dolby Digital and DTS may depend on the individual’s subjective auditory preferences and the specific room acoustics. Some individuals may prefer the characteristics of one format over the other, and the room itself may have unique acoustic properties that accentuate certain nuances in the sound. Personal preference and the specific playback equipment being used can greatly influence the listener’s perception of the differences between Dolby Digital and DTS.
It’s important to note that the differences between Dolby Digital and DTS are often subtle and may not be noticeable to casual listeners or those without high-end audio equipment. Both formats have their strengths and have been used to provide immersive audio experiences in movies, gaming, and other forms of entertainment for many years. Ultimately, the choice between Dolby Digital and DTS may come down to personal preference, equipment compatibility, and the availability of content in each format.
Benefits of Surround Sound
Surround sound technology offers a range of benefits that enhance the audio experience and provide a more immersive and engaging entertainment environment. Whether you’re watching movies, playing games, or listening to music, surround sound can elevate your audio enjoyment in several ways:
1. Immersive Audio Experience: Surround sound creates a multi-dimensional audio environment by using multiple speakers strategically placed around the listening area. This setup allows for accurate sound positioning and spatial effects, making you feel like you’re right in the middle of the action. It enhances the realism and immersiveness of movies, games, and other audio content, pulling you deeper into the entertainment experience.
2. Enhanced Soundstage: With surround sound, you can experience a wider and more expansive soundstage compared to traditional stereo setups. The audio is distributed between different speakers, giving a sense of depth and dimensionality. This allows for more precise audio imaging, where sound effects, dialogue, and music are placed in specific locations, replicating how we naturally perceive sound in the real world.
3. Accurate Sound Localization: Surround sound enables accurate sound localization, which means you can perceive the direction from which different sounds are coming. This is particularly beneficial in movies and games where positional audio cues play a crucial role. By accurately positioning sounds in space, surround sound technology enhances realism and helps you to fully immerse in the audio experience.
4. Enhanced Detail and Clarity: Surround sound systems provide improved audio detail and clarity, allowing you to hear subtle nuances and intricate sounds that may be missed in traditional stereo setups. In movies, this means hearing the soft rustle of leaves or the distant footsteps, adding depth and realism to the audio. In music, surround sound can reveal intricate instrument separations and spatial audio effects, enhancing the overall listening experience.
5. Impactful Low-Frequency Effects: Subwoofers are an integral part of surround sound systems, delivering low-frequency sounds or bass. Explosions, rumbling effects, and deep and powerful music notes benefit from these dedicated speakers. The subwoofer adds depth and impact to the audio, allowing you to feel the vibrations and intensify the emotional impact of the content you’re experiencing.
6. Customizability: Surround sound systems often come with various audio settings and customization options. These options allow you to fine-tune the audio output based on your personal preferences, the content being played, and the characteristics of your listening environment. By adjusting speaker levels, equalizer settings, and other parameters, you can tailor the audio experience to suit your specific preferences and optimize the sound quality to your liking.
Overall, surround sound offers a more immersive and engaging audio experience, bringing movies, games, and music to life in a way that traditional stereo systems cannot. By recreating a realistic sound environment with accurate sound positioning, enhanced detail, and impactful bass, surround sound technology allows you to fully immerse yourself in the audio content and enjoy a more captivating entertainment experience.
Surround Sound Formats
Surround sound formats are audio technologies used to encode and decode multi-channel audio for playback on surround sound systems. These formats ensure accurate sound positioning, immersive audio experiences, and compatibility across various devices and media formats.
Two of the most commonly used surround sound formats are Dolby Digital and DTS, which have become industry standards for audio encoding. They are widely supported in home theater systems, cinemas, gaming consoles, and other entertainment platforms.
Dolby Digital: Dolby Digital is a widely used audio coding format that provides high-quality audio reproduction and compatibility. It supports a range of channel configurations, including 5.1 and 7.1 surround sound setups. Dolby Digital is commonly used in DVDs, Blu-ray discs, streaming platforms, and broadcasting. It offers efficient compression with minimal loss in audio quality, enabling immersive sound experiences in movies, TV shows, and games.
DTS: DTS, which stands for “Digital Theater Systems,” is another popular audio coding format used in surround sound systems. DTS utilizes different encoding algorithms and often offers higher bitrates compared to Dolby Digital. This can result in potentially better audio fidelity, particularly in the mid and high-frequency ranges. DTS supports various channel configurations, including 5.1 and 7.1 setups. It is commonly used in DVDs, Blu-ray discs, streaming services, and gaming consoles.
In addition to Dolby Digital and DTS, there are other surround sound formats available, depending on the specific audio requirements and equipment compatibility. These formats include Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio, and DTS:X. Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio are lossless audio codecs, providing uncompressed, studio-quality audio reproduction. They are typically found in Blu-ray discs and offer heightened audio fidelity. DTS:X is an object-based audio technology that allows for precise positioning of sounds in a three-dimensional space, creating a more realistic and immersive audio experience.
When selecting a surround sound format, it is essential to consider media compatibility, the capabilities of your audio playback devices, and the availability of content encoded in the desired format. Compatibility with your chosen format ensures optimal playback and an enhanced audio experience. It’s worth noting that many modern devices and systems support multiple surround sound formats, allowing you to enjoy a wide range of content encoded in different formats.
Overall, surround sound formats play a crucial role in delivering immersive and realistic audio experiences. They enable accurate sound positioning, spatial effects, and high-quality audio reproduction, enhancing the viewing, gaming, and listening experiences for home theater enthusiasts and audio enthusiasts alike.
Choosing the Right Speakers for Surround Sound
Choosing the right speakers for your surround sound setup is crucial to achieve optimal audio performance and create a truly immersive audio experience. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting speakers for surround sound:
1. Speaker Configuration: Consider the specific speaker configuration that matches your chosen surround sound format, whether it’s 5.1 or 7.1. Make sure the speakers you choose are designed for the corresponding setup, including having the necessary channels (center, front, surround, and rear) and a subwoofer for low-frequency reproduction.
2. Speaker Types: Different types of speakers are designed to handle specific frequency ranges and deliver certain sound characteristics. Consider a combination of different speaker types, such as floor-standing or bookshelf speakers for front and surround channels, a dedicated center speaker for clear dialogue reproduction, and specialized subwoofers for impactful low-frequency effects.
3. Speaker Sensitivity and Power Handling: Pay attention to the sensitivity and power handling specifications of the speakers. Higher sensitivity ratings indicate that the speakers require less power to produce a certain volume level, which can be advantageous in achieving better audio performance. Ensure that your receiver or amplifier can properly drive the chosen speakers within their recommended power range.
4. Timbre Matching: Timbre matching refers to the consistency of sound characteristics across all speakers in your surround sound system. It is desirable to choose speakers from the same brand or series to ensure a seamless and balanced sound reproduction. Timbre matching helps maintain tonal harmony and audio continuity as sounds move across different speakers.
5. Room Size and Acoustics: Consider the size and layout of your room, as well as its acoustic properties. Larger rooms may benefit from larger speakers with more power and extended frequency range, while smaller spaces may require compact speakers that can deliver quality sound in a limited footprint. Rooms with reflective surfaces may benefit from speakers with adjustable tweeters or speaker placement options to optimize sound reflection and absorption.
6. Budget: Determine a realistic budget for your surround sound speakers. While it is important to invest in quality speakers that meet your audio needs, there are options available at various price points. Remember that speakers are a long-term investment and can significantly impact your overall audio experience, so allocate your budget wisely.
7. Auditioning and Research: Whenever possible, audition speakers before making a purchase. Visit local audio retailers, attend trade shows, or listen to demos to get a sense of how speakers sound in person. Additionally, read reviews, forums, and expert opinions to gain insight into the performance, reliability, and overall quality of the speakers you are considering.
By considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can make an informed decision when choosing speakers for your surround sound system. Remember that every setup is unique, so finding the right combination of speakers that suits your preferences, room size, and budget will yield the best audio performance and immersive entertainment experience.
Placement of Surround Sound Speakers
The proper placement of surround sound speakers is essential to achieve optimal audio performance and create an immersive soundstage. Here are some guidelines to consider when placing your surround sound speakers:
1. Center Speaker: The center speaker, responsible for dialogue and prominent sounds, should be placed either above or below the display screen. It should be positioned facing the listener at ear level for clear and accurate sound reproduction.
2. Front Speakers: The front left and right speakers should be positioned on either side of the display screen, facing the listener. Ideally, they should be placed at ear level or slightly angled towards the listening position to ensure proper stereo imaging and soundstage. Ensure that the distance between the two front speakers is equal to the distance between the listener and the display screen for optimal audio balance.
3. Surround Speakers: The surround speakers, responsible for creating a sense of envelopment and space, should be placed to the sides or slightly behind the listening position. Aim to position them a few feet above the listener’s ear level, angled towards the listener, and ideally at an equal distance from the listener as the front speakers. This placement helps to create an immersive sound experience by simulating sounds coming from the sides or rear.
4. Rear Surround Speakers (7.1 setup): In a 7.1 surround sound setup, the rear surround speakers further enhance the surround experience. They should be placed behind the listening position, equidistant from the listener and the side surround speakers. Again, positioning them slightly above the listener’s ear level and angled towards the listener helps to create a cohesive and seamless surround soundfield.
5. Subwoofer: The subwoofer, responsible for low-frequency reproduction, can be placed anywhere in the room to achieve desired bass effects. Experiment with various locations to find the spot that provides the best bass response and integration with the other speakers. Placing the subwoofer near a wall or corner can often enhance low-frequency performance due to the room’s acoustic characteristics.
6. Speaker Angles and Toe-in: To optimize sound dispersion and imaging, consider angling the front speakers and surround speakers slightly towards the listening area. This directed sound projection helps to focus the audio towards the listener. Experiment with different angles and toe-in adjustments to find the sweet spot that provides the best audio coverage and imaging for your specific room setup.
7. Room Acoustics: Remember that the acoustic characteristics of the room can affect sound quality. Incorporate acoustic treatments such as wall panels, diffusers, or bass traps to minimize sound reflections, echoes, and resonances. These treatments can help improve the clarity and balance of the surround sound system by reducing unwanted acoustic distortions.
8. Calibration and Fine-tuning: After placing the speakers, use the calibration features in your audio receiver or amplifier to adjust speaker levels, delay, and crossover settings. This step ensures proper integration and optimal performance of each speaker in the surround sound system.
By following these guidelines and considering the unique characteristics of your room, you can optimize the placement of your surround sound speakers to achieve a balanced and immersive audio experience. Experimentation and fine-tuning may be necessary to find the ideal speaker positions that best suit your specific listening environment and preferences.
Important Considerations for Setting up Surround Sound
When setting up your surround sound system, there are several important considerations to keep in mind to ensure optimal audio performance and a seamless entertainment experience. Taking these factors into account can make a significant difference in the overall audio quality and enjoyment of your surround sound setup:
1. Room Layout: Consider the layout and size of your room when placing your speakers. Take note of any obstacles, furniture, and the distance between the listener and the speakers. Room dimensions can affect sound reflections and the overall acoustic characteristics, so it’s essential to position the speakers accordingly.
2. Speaker Placement: Follow the recommended guidelines for placing your surround sound speakers, taking into consideration the specific speaker configuration (e.g., 5.1 or 7.1). Correctly positioning the speakers ensures accurate sound localization and optimal audio dispersion throughout the room.
3. Cable Management: Take the time to plan and organize your speaker cables to avoid clutter and potential tripping hazards. Conceal the cables by running them along walls or using cable management solutions to maintain a clean and tidy setup.
4. Receiver/Audio Processor Settings: Familiarize yourself with the settings and features of your audio receiver or processor. Adjust speaker levels, crossover frequencies, and other calibration settings to match the characteristics of your speakers and room environment. This calibration process ensures proper sound integration and balance.
5. Source Compatibility: Ensure that your source devices, such as media players, gaming consoles, and streaming devices, are compatible with your surround sound system. Check the supported audio formats and connections to ensure seamless integration and optimal audio playback.
6. Balanced Speaker Levels: Use a sound level meter or the built-in calibration tools in your receiver to balance the volume levels of all your speakers. Each speaker should be set to the appropriate level to achieve a cohesive and balanced surround sound experience.
7. Acoustic Treatments: Consider incorporating acoustic treatments in your room to minimize sound reflections and improve audio clarity. These treatments can include sound-absorbing panels, diffusers, bass traps, or even curtains, rugs, and furniture placement. Acoustic enhancements optimize the listening environment and help to reduce unwanted echoes and distortions.
8. Test and Adjust: Take the time to test your surround sound system with various types of audio content, such as movies, music, and games. Make incremental adjustments to the settings and speaker positions as needed to achieve the desired audio performance and immersive experience.
9. Regular Maintenance and Upkeep: Keep your surround sound system clean and free from dust or debris. Regularly inspect and clean the speakers and ensure all connections are secure. Performing routine maintenance helps to preserve audio quality and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
By considering these important factors and implementing them during the setup process, you can create a well-optimized surround sound system that delivers exceptional audio performance and a truly immersive entertainment experience.
Troubleshooting Surround Sound Issues
While surround sound systems can offer an immersive audio experience, occasional issues may arise that impact performance. Here are some common troubleshooting steps to help address and resolve potential problems:
1. Check Connections: Ensure that all audio cables, including HDMI, optical, or analog connections, are securely and properly connected to their respective ports. Loose or faulty connections can cause audio disruptions or no sound at all.
2. Verify Source Settings: Check the audio settings on your source device, such as a Blu-ray player or game console. Ensure that it is set to output audio in the appropriate surround sound format (e.g., Dolby Digital or DTS) and that the audio output is correctly configured for your specific setup.
3. Receiver Settings: Review the settings on your audio receiver or processor. Verify that the speaker configuration, channel levels, and listening modes are appropriately set. Adjustments may be needed to match your speaker setup and optimize audio performance.
4. Speaker Wiring: Double-check the speaker wiring to ensure that each speaker is connected correctly to the corresponding speaker terminals on the receiver or amplifier. Incorrect wiring can result in audio imbalances or no audio output from specific speakers.
5. Test Speaker Functionality: Use the built-in speaker test function on your receiver or amplifier to confirm that each speaker is functioning properly. This helps to identify any issues with individual speakers or their connections.
6. Subwoofer Issues: If the subwoofer is not producing sound or is not functioning as expected, check the power connection and volume level settings. Additionally, ensure that the subwoofer’s crossover and phase settings are appropriately adjusted. Adjustments may be necessary to integrate the subwoofer with the rest of the speakers in your setup.
7. Room Acoustics: Consider any room-specific issues that may affect the audio performance. Excessive sound reflections or echoes can impact clarity and balance. Acoustic treatments like sound-absorbing panels or rugs strategically placed in the room can help address these issues.
8. Firmware Updates: Ensure that your audio receiver or any other components in your setup have the latest firmware updates installed. Manufacturers frequently release updates to improve performance, address bugs, and add new features.
9. Check for Interference: Keep electronic devices like mobile phones, wireless routers, or microwave ovens away from your surround sound system. These devices can cause electromagnetic interference, leading to audio disruptions or signal degradation.
10. Seek Professional Help: If you have exhausted troubleshooting options and are still experiencing issues, contacting a professional audio technician or the customer support of your audio equipment manufacturer may be necessary. They can offer specific guidance or provide further assistance in resolving complex issues.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can identify and resolve common surround sound issues to ensure a smooth and enjoyable audio experience.
Enhancing Your Surround Sound Experience
To further enhance your surround sound experience and take full advantage of your audio setup, consider implementing the following tips and techniques:
1. Room Acoustics: Optimize your listening environment by adding acoustic treatments such as diffusers, absorbers, or bass traps. These improvements help reduce unwanted echoes, reflections, and resonance that can negatively impact audio clarity and immersion.
2. Speaker Placement and Calibration: Fine-tune the placement of your speakers to optimize sound dispersion and imaging. Use a sound level meter or the calibration features in your receiver to ensure that each speaker is balanced and properly calibrated within your room.
3. Upgrade Audio Source Quality: Invest in high-quality audio sources such as Blu-ray discs, high-resolution audio files, or streaming services that offer lossless audio formats. These sources provide better sound quality, allowing you to fully appreciate the capabilities of your surround sound system.
4. Invest in High-Quality Speaker Cables: Consider using higher-quality speaker cables that have better conductivity and insulation. Although it may not provide a drastic change in audio quality, it can minimize potential signal loss and electromagnetic interference, allowing for optimal audio performance.
5. Explore Different Listening Modes: Experiment with the various listening modes offered by your audio receiver. These modes can enhance specific audio content like movies, music, or games, altering the sound processing to match the intended audio experience.
6. Use Room Correction Systems: Consider utilizing room correction systems available in some audio receivers or external devices. These systems automatically analyze your room’s acoustics and make adjustments to optimize audio output, providing a more accurate and balanced soundstage.
7. Surround Sound Gaming Headsets: If gaming is a significant part of your audio experience, consider investing in a surround sound gaming headset. These headsets provide virtual surround sound, simulating the audio immersion of a surround sound system directly in your ears.
8. Audio Streaming Services with Spatial Audio: Take advantage of audio streaming services that offer spatial audio technologies such as Dolby Atmos Music or Sony 360 Reality Audio. These formats provide a more immersive and three-dimensional audio experience, creating a sense of audio depth and height.
9. Experiment with Room Correction Software: Consider using room correction software programs that utilize measurement tools to analyze your room’s acoustics and make precise adjustments to audio output. These software programs can help optimize sound frequencies and correct any room-related acoustic issues.
10. Regularly Update Firmware: Stay up to date with firmware updates for your audio receiver or other audio components. Manufacturers often release firmware updates that improve audio performance, add new features, or address any known issues.
By implementing these tips and techniques, you can enhance your surround sound experience, bringing your audio setup to its fullest potential and immersing yourself in a rich and captivating soundstage.
Surround Sound vs. Stereo Sound: Which is Better?
The debate between surround sound and stereo sound often arises when considering the audio setup for your entertainment system. Both options have their merits and can provide an enjoyable listening experience, but understanding the differences can help you determine which is best suited for your needs.
Stereo Sound: Stereo sound refers to a two-channel audio system, typically consisting of a left speaker and a right speaker. This setup delivers sound from a fixed position and creates a wide stereo image, allowing for a good sense of separation between left and right audio channels.
Stereo sound systems are commonly used for music listening and can provide an accurate reproduction of recorded sound. The simplicity of stereo sound makes it versatile and easy to set up, making it a popular choice for many listening environments.
Surround Sound: Surround sound, on the other hand, is a multi-channel audio setup designed to immerse the listener in a more realistic and three-dimensional sound environment. It uses multiple speakers placed strategically around the listening area to provide accurate sound positioning, depth, and spatial effects.
Surround sound systems are commonly used in home theaters and gaming setups, as well as in cinemas. They create an immersive audio experience, allowing for accurate sound localization and a more realistic representation of sound in movies, games, and other multimedia content.
Comparing the two, surround sound systems offer several advantages over stereo sound:
Immersive Experience: Surround sound systems excel in reproducing spatial audio cues, simulating sounds coming from various directions. This immerses the listener in the audio environment, enhancing the sense of realism and depth.
Accurate Sound Localization: Surround sound systems allow for precise sound placement, enabling the listener to perceive the direction from which sounds are coming. This enhances the overall audio experience, especially in movies or games where positional audio cues are crucial.
Enhanced Audio Detail: Surround sound systems provide greater audio detail by distributing sound across multiple speakers. This allows for more accurate representation of individual sound elements and subtle nuances within the audio mix.
Despite these advantages, stereo sound still has its place:
Music Fidelity: For music listening, stereo sound systems can provide an excellent audio experience. They offer accurate left-right speaker imaging and can faithfully reproduce the intricacies of stereo recordings.
Simplicity: Stereo sound systems are often simpler to set up and more accessible for casual users. They require fewer speakers and typically have less complexity in terms of audio processing and calibration.
The choice between surround sound and stereo sound ultimately depends on personal preference, intended use, and the environment in which you’ll be listening. Consider factors such as the content you consume, the available space, and your budget when making a decision.