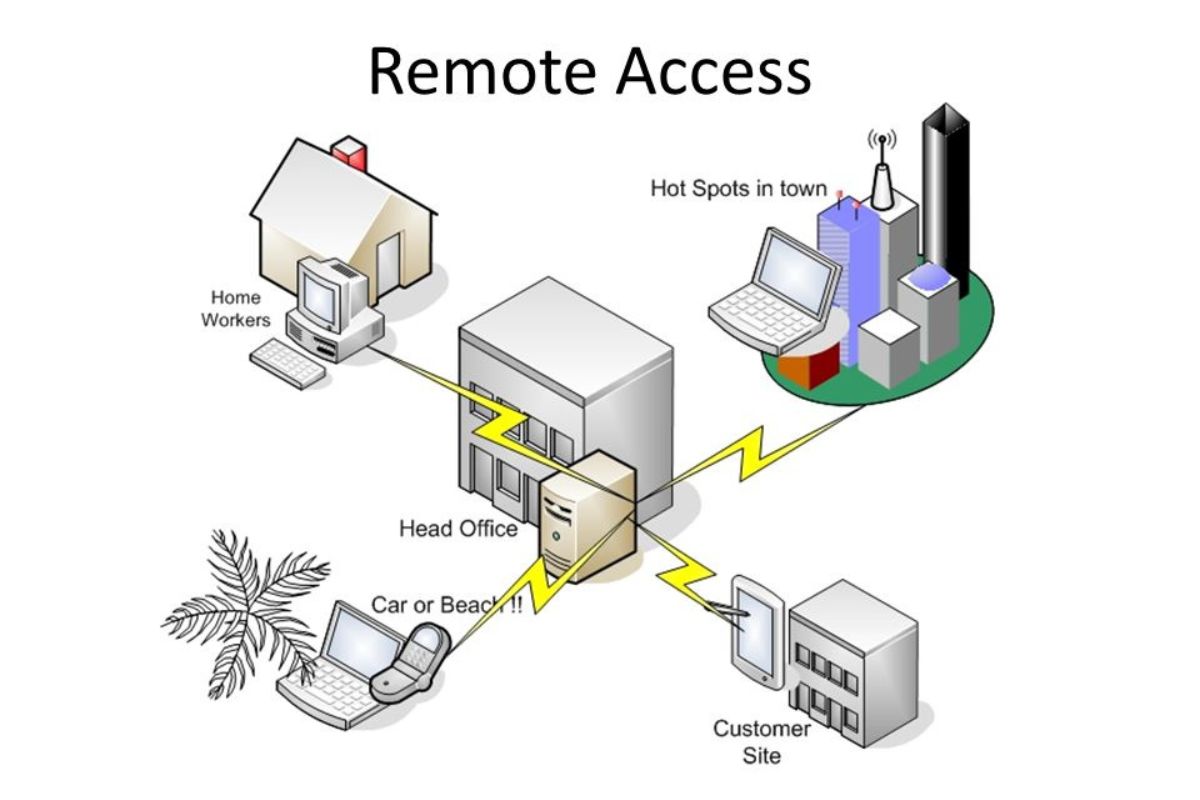
How Does Remote Access Work?
Remote access allows users to connect to a computer or a network from a location different from where the actual computer or network is physically located. Through remote access, users can access files, applications, and resources on a remote computer as if they were sitting right in front of it. This technology has revolutionized the way people work by enabling them to be productive and efficient regardless of their physical location.
Remote access works by establishing a connection between the user’s local device, such as a laptop or smartphone, and the remote device or network. This connection is typically made using the internet or a private network. Once connected, the user can interact with the remote device or network and perform various tasks as if they were physically present.
The process of remote access involves several key components. First, the user initiates a connection request from their local device to the remote device or network. This can be done using remote access software or a virtual private network (VPN) client. The connection request is then received by the remote device or network, which verifies the user’s credentials and establishes a secure connection.
Once the connection is established, the user can remotely control the desktop or interface of the remote device. This means they can see the remote screen, move the mouse, and input keyboard commands as if they were physically in front of the remote device. The user can access files, open applications, and perform tasks just as they would on their own computer.
Remote access also allows for data transfer between the local and remote devices. Files can be copied or moved back and forth, and data can be synchronized to ensure consistency. This is especially useful for collaboration and remote teamwork, as it enables seamless sharing of information and real-time updates.
Overall, remote access provides a convenient and secure way for individuals and organizations to access resources and work remotely. Whether it’s accessing work files from home, managing servers from a different location, or providing technical support to remote users, remote access has become an essential tool in today’s interconnected world.
Benefits of Using Remote Access
Remote access offers a range of benefits for both individuals and organizations. By allowing users to connect to computers and networks from anywhere, remote access has become a game-changer in the modern working landscape. Here are some of the key advantages of using remote access:
- Flexibility and Convenience: Remote access enables users to work from anywhere, whether it’s from the comfort of their homes, while traveling, or at a client’s site. This flexibility allows for a better work-life balance and eliminates the need for physical presence in traditional office spaces.
- Increased Productivity: With remote access, individuals can stay connected and work efficiently outside of normal office hours. They can tackle urgent tasks, collaborate with colleagues, and access important files or resources at any time, resulting in increased productivity and faster response times.
- Cost Savings: Remote access eliminates the need for extensive hardware and infrastructure investments. Instead of investing in multiple computers or servers, organizations can leverage remote access to centralize their resources and reduce costs associated with physical IT infrastructure.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Remote access fosters seamless collaboration among team members located in different geographic locations. It enables real-time communication, file sharing, and collaborative editing, promoting smoother workflows and efficient teamwork.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: In the event of a natural disaster or unexpected event that renders the primary workspace inaccessible, remote access ensures that essential business operations can continue without disruption. Employees can connect remotely and resume their work, minimizing downtime and maintaining business continuity.
- Access to Specialized Software and Resources: Remote access allows users to tap into specialized software or resources that may be available on a specific computer or network. This enables individuals to leverage powerful tools and applications without the need for local installation, empowering them to perform tasks efficiently.
- Improved Employee Satisfaction and Retention: Offering remote access as an option can lead to higher employee satisfaction and increased retention rates. It provides employees with the flexibility they desire, leading to better job satisfaction and a more positive work environment.
With these advantages, it’s no wonder that remote access has become an indispensable tool in modern work settings. The ability to work anytime, anywhere, with improved productivity and collaboration capabilities, makes remote access a win-win for both organizations and individuals.
Common Applications of Remote Access
Remote access is a versatile technology that finds application in various industries and scenarios. Its ability to connect users to remote computers and networks opens up a wide range of possibilities. Here are some common applications of remote access:
- Remote IT Support: IT professionals can remotely access and troubleshoot computers and servers, providing technical assistance to users from a distance. This eliminates the need for on-site visits, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Telecommuting: Remote access allows employees to work from home or any location outside the traditional office setup. They can connect to their organization’s network, access files, collaborate with colleagues, and complete tasks as if they were physically present in the office.
- Remote Training and Education: Remote access enables educators and trainers to deliver online courses and training sessions to learners located in different parts of the world. Participants can access course materials, interact with instructors, and engage in collaborative activities from their own devices.
- Data and File Access: Remote access allows users to retrieve and work with files stored on remote servers or computers. This is particularly useful for individuals who require access to important documents, images, or multimedia files while on the go.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Remote access is widely used in industries such as manufacturing, energy, and transportation, where equipment and systems need to be monitored and controlled from a central location. With remote access, operators can oversee operations, make adjustments, and troubleshoot issues without being physically present at the site.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Remote access facilitates seamless collaboration among team members, even when they are geographically dispersed. It allows for real-time communication, document sharing, and joint editing, enabling efficient teamwork and project management.
- Remote Presentations and Meetings: Remote access enables individuals to participate in virtual meetings, webinars, and presentations from any location. They can share screens, give presentations, and collaborate with participants in real-time, eliminating the need for everyone to be in the same physical space.
- Remote Healthcare: Remote access plays a crucial role in telemedicine, enabling healthcare professionals to remotely access patient records, provide consultations, and monitor conditions. It improves access to healthcare services for patients in remote areas or those unable to visit healthcare facilities.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of remote access across various industries. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for utilizing remote access are only expected to grow, making it an integral part of modern-day operations.
Types of Remote Access
Remote access can be achieved through different methods, each offering its own capabilities and features. Here are some common types of remote access:
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN establishes a secure, encrypted connection between a user’s device and a private network. It allows users to access resources on the network as if they were physically connected to it. VPNs are commonly used by organizations to enable remote access for employees while maintaining network security.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): RDP allows users to connect to a remote computer and control it as if they were sitting in front of it. This type of remote access is commonly used for technical support, accessing office computers, and managing servers.
- Web-based Access: Web-based remote access uses a browser to connect to a remote device or network. This type of access is convenient as it enables users to connect without the need for additional software installations. Web-based remote access is often used for cloud-based applications and services.
- Cloud-based Remote Access: Cloud-based remote access allows users to connect to their files and applications stored in the cloud from anywhere with an internet connection. It offers flexibility and scalability, making it popular among individuals and organizations seeking convenience and mobility.
- Mobile Remote Access: Mobile remote access enables users to connect to remote resources using smartphones or tablets. Mobile apps or web-based interfaces provide users with the ability to access files, applications, and perform tasks while on the go.
- Terminal Services: Terminal services allow multiple users to connect to a remote computer or server simultaneously. Each user has their own individual session, and they can access applications and files independently. Terminal services are often used for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solutions.
- Wireless Remote Access: Wireless remote access utilizes Wi-Fi or cellular networks to establish a connection between the user’s device and the remote network. This type of access is widely used for mobile devices and laptops, enabling connectivity in various environments.
These are just a few examples of the types of remote access available today. Each type offers its own advantages and suitability for different use cases. The choice of remote access method depends on factors such as security requirements, device compatibility, network infrastructure, and user preferences.
Security Considerations for Remote Access
While remote access brings numerous benefits, it also introduces potential security risks. It is crucial to prioritize security measures to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of the network. Here are some key security considerations for remote access:
- Authentication and Access Controls: Implement strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized users can access remote resources. Use robust access controls to limit privileges and permissions based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Encryption: Encrypt data transmissions between the local device and the remote device or network. This safeguards the confidentiality of sensitive information and prevents unauthorized access or interception.
- Secure Connections: Utilize secure protocols, such as SSL/TLS, for establishing connections and transmitting data. Avoid using unsecured public Wi-Fi networks, as they can expose sensitive information to potential eavesdroppers.
- Endpoint Security: Ensure that the local devices connecting to remote resources are equipped with up-to-date antivirus software, firewalls, and other security measures. Regularly update software and firmware to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation: Segregate the network to limit access to sensitive information. Use firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual local area networks (VLANs) to create barriers and prevent unauthorized access to critical resources.
- Audit Logs and Monitoring: Implement logging and monitoring mechanisms to track remote access activity. Regularly review logs to detect any unauthorized access attempts or suspicious behavior. This aids in identifying security incidents and initiating timely response measures.
- Data Loss Prevention: Implement data loss prevention measures to prevent the unauthorized transfer or leakage of sensitive data. Use encryption, data classification, and data backup strategies to ensure data integrity and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Employee Education: Educate employees about remote access best practices and the importance of maintaining security. Promote awareness of phishing attacks, social engineering tactics, and the need for strong password management.
By implementing these security considerations, organizations can minimize the risks associated with remote access and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data and resources. It is vital to continuously assess and update security measures to stay ahead of evolving threats in the digital landscape.
Remote Access Tools and Software
There are various remote access tools and software available that facilitate secure and efficient remote connections. These tools provide the necessary features and functionalities to enable seamless remote access. Here are some popular remote access tools and software:
- TeamViewer: TeamViewer is a widely-used remote access tool that allows users to connect to remote devices and control them from anywhere. It offers features like file transfer, chat, and remote printing, making it ideal for both personal and business use.
- AnyDesk: AnyDesk is a remote desktop software that offers high-speed connections and low latency. It supports cross-platform compatibility and provides a range of features like file transfer, session recording, and remote administration.
- Chrome Remote Desktop: Chrome Remote Desktop is a web-based remote access tool that works through the Google Chrome browser. It allows users to access their computers or provide temporary remote access to others. It is simple to set up and supports both Windows and Mac operating systems.
- Microsoft Remote Desktop: Microsoft Remote Desktop is a built-in remote access tool available in Windows operating systems. It enables users to connect to remote desktops or applications hosted on Microsoft servers. It supports both Windows and Mac platforms.
- LogMeIn: LogMeIn offers remote access solutions for individuals and businesses. It provides secure remote connections, along with features like file sharing, remote printing, and remote wake-on-LAN. LogMeIn offers different subscription plans tailored to various user needs.
- VNC (Virtual Network Computing): VNC is a remote access software that allows users to control a remote computer’s desktop environment. It is available in both free and paid versions, and it supports cross-platform connectivity.
- Remote Desktop Services (RDS): Remote Desktop Services, formerly known as Terminal Services, is a Microsoft technology that allows remote connections to Windows-based desktops and applications. It offers comprehensive features for remote access in enterprise environments.
- GoToMyPC: GoToMyPC is a remote access software that allows users to access their computers remotely from any device. It offers secure connections, multi-monitor support, and file transfer capabilities.
These tools and software provide various features and options for remote access, catering to different user requirements. When choosing a remote access tool, it is important to consider factors such as security, ease of use, platform compatibility, and the specific features needed for remote work or support.
Remote Access vs. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Remote access and virtual private networks (VPNs) are both methods used to establish connections to remote networks or devices, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Here’s a comparison of remote access and VPNs:
- Purpose: Remote access aims to provide users with the ability to connect to and control remote devices or networks as if they were physically present. It is often used for tasks like accessing files, collaborating with colleagues, or managing remote servers. On the other hand, VPNs primarily focus on establishing a secure and private connection to a remote network, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity during transmission.
- Scope: Remote access generally refers to the ability to connect to a specific device or network from a remote location. It provides direct access to resources on that remote device or network. In contrast, VPNs create a secure tunnel between the user’s device and the remote network, extending the user’s local network to the remote network. This allows users to access resources on the remote network as if they were connected locally.
- Security: Both remote access and VPNs prioritize security. Remote access implementations commonly include authentication measures, encryption, and secure protocols to protect data and prevent unauthorized access. VPNs, however, place a greater emphasis on security, as they create a secure tunnel for all data transmitted between the user’s device and the remote network, safeguarding it from potential eavesdroppers or intruders.
- Functionality: Remote access tools and software provide features that allow users to control remote devices, transfer files, collaborate with others, and perform tasks as if they were physically present at the remote location. VPNs, on the other hand, primarily serve to establish network connectivity, enabling users to access resources on a remote network securely. VPNs do not provide direct control over remote devices.
- Implementation: Remote access can be implemented using various software applications or built-in functionalities. It allows users to connect to individual devices or networks. VPNs, on the other hand, are more commonly implemented at the network level, utilizing VPN protocols and dedicated VPN servers to create secure connections for remote network access.
- Use Cases: Remote access is widely used for telecommuting, IT support, remote training, file access, and remote control of devices. VPNs are often used to establish secure connections for remote workers accessing an organization’s internal network, or for users connecting to public Wi-Fi networks to ensure the security of their data.
Challenges and Limitations of Remote Access
While remote access offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Understanding these factors is important for users and organizations considering remote access solutions. Here are some common challenges and limitations of remote access:
- Connectivity Issues: Remote access heavily relies on stable and reliable internet connections. Unstable or slow internet connections can hinder the performance and reliability of remote access, making it challenging to access resources or establish connections.
- Security Risks: Remote access introduces security risks, especially when not properly configured and secured. Without robust security measures in place, remote access connections can become vulnerable to unauthorized access, data breaches, and malware attacks.
- Compatibility Challenges: Some remote access tools and software may have compatibility limitations. Certain operating systems, devices, or network configurations may pose challenges in establishing remote access connections or accessing resources effectively.
- Performance and Latency: Depending on factors such as network speed, distance, and resource-intensive applications, remote access connections may suffer from performance issues or noticeable latency. This can impact tasks that require real-time interaction or resource-intensive processing.
- Dependency on Third-Party Infrastructure: Remote access often relies on third-party infrastructure, such as cloud-based servers or remote desktop services. Organizations need to consider the reliability, availability, and security of these third-party services when implementing remote access solutions.
- Resource Limitations: Depending on the remote access solution and network capabilities, there may be limitations on the number of simultaneous connections, bandwidth, or available system resources. These limitations can impact user experience and productivity, particularly in high-demand scenarios.
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements: Certain industries or organizations have strict regulatory and compliance requirements regarding data access, storage, and privacy. Implementing remote access solutions while adhering to these requirements can present challenges and necessitate additional security measures.
- User Training and Support: Remote access solutions often require user training and support to ensure proper usage and troubleshooting. Organizations should invest in providing adequate training and support resources to users to minimize user frustrations and maximize efficiency.
Understanding and addressing these challenges and limitations can help organizations and users make informed decisions when implementing remote access solutions. It is essential to carefully consider the specific requirements, security concerns, and user needs when deploying remote access technologies.
Best Practices for Remote Access Implementation
Implementing remote access requires careful planning and consideration of security, reliability, and user experience. By following best practices, organizations can ensure a successful remote access implementation. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Security First: Prioritize security in your remote access implementation. Use strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication, and implement encryption to protect data during transmission. Regularly update security patches and educate users about safe remote access practices.
- Choose the Right Remote Access Solution: Evaluate different remote access tools or software and select the solution that best meets your organization’s needs and security requirements. Consider factors such as user scalability, platform compatibility, performance, and ease of management.
- Establish Network Segmentation: Segment your network to limit access to sensitive resources and reduce the impact of any potential compromises. Use firewalls, VLANs, and access controls to ensure that remote access users only have access to the resources they need.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require users to go through an additional layer of verification, such as MFA, before accessing remote resources. This added security measure helps protect against unauthorized access, even if credentials are compromised.
- Monitor and Audit Access: Regularly monitor and review remote access activity logs to identify any suspicious or unauthorized attempts. Implement real-time monitoring tools to promptly detect any security incidents and take appropriate action.
- Establish Usage Policies: Create clear remote access policies and guidelines for employees to follow. Specify acceptable use, security requirements, and consequences for non-compliance. Regularly communicate and update these policies to ensure ongoing adherence.
- Provide User Training: Offer comprehensive training to remote access users to ensure they understand the security risks, best practices, and proper usage of remote access tools. Regularly educate users about phishing threats, password security, and safe browsing habits.
- Regularly Update Software and Firmware: Keep remote access software and firmware up to date on both the client and server sides. Software updates often fix security vulnerabilities and improve overall performance, ensuring the remote access environment remains secure and efficient.
- Regularly Back Up Data: Establish robust data backup procedures to ensure continuity in the event of data loss or system failures. Implement automated backups and test data restoration processes to minimize downtime and protect critical information.
- Continuously Evaluate and Improve: Regularly assess your remote access implementation to identify any potential vulnerabilities, performance issues, or areas for improvement. Stay up to date with emerging security threats and industry best practices to enhance the remote access environment.
By following these best practices, organizations can foster secure and efficient remote access environments while minimizing potential risks and ensuring a positive user experience. It is important to regularly review and update these practices as technologies and security threats evolve.