Benefits of Out-Of-Band Management
Out-of-band management (OOBM) refers to the ability to remotely monitor and manage network devices, even when the primary network connection is down or unresponsive. This alternative method provides several key benefits for businesses of all sizes. Let’s explore the advantages of implementing OOBM solutions:
- Improved Network Resilience: One of the significant benefits of out-of-band management is its ability to enhance network resilience. In the event of a network outage or failure, OOBM allows IT administrators to remotely access and troubleshoot devices, even if the primary network connection is down. This ensures that critical network components remain accessible, minimizing downtime and productivity losses.
- Faster Issue Resolution: With OOBM, IT teams can quickly identify and resolve network issues. By remotely accessing network devices, administrators can diagnose and troubleshoot problems without needing physical access to the infrastructure. This speeds up the resolution time, reducing the impact on business operations and improving overall network performance.
- Reduced On-Site Maintenance: Out-of-band management significantly reduces the need for on-site maintenance visits. IT personnel can remotely perform tasks such as firmware updates, configuration changes, and software installations without physically being present at the device’s location. This saves time, resources, and costs associated with travel, especially for organizations with multiple locations or geographically dispersed networks.
- Enhanced Security: OOBM offers an additional layer of security for network devices. By segregating the out-of-band management network from the primary network, organizations can isolate and protect critical infrastructure components from potential cyber threats. This separation helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of security breaches.
- Streamlined Compliance: Implementing out-of-band management can aid in meeting regulatory compliance requirements. Organizations in various industries, such as finance and healthcare, need to adhere to strict regulations related to network security and data protection. OOBM solutions offer the necessary controls and monitoring capabilities to meet these compliance standards.
Overall, out-of-band management provides numerous benefits that contribute to improved network resilience, faster issue resolution, reduced maintenance costs, enhanced security, and streamlined compliance. By incorporating OOBM solutions into their infrastructure, businesses can ensure uninterrupted network connectivity and efficient management of critical network devices, ultimately leading to increased productivity and customer satisfaction.
How Does Out-Of-Band Management Work?
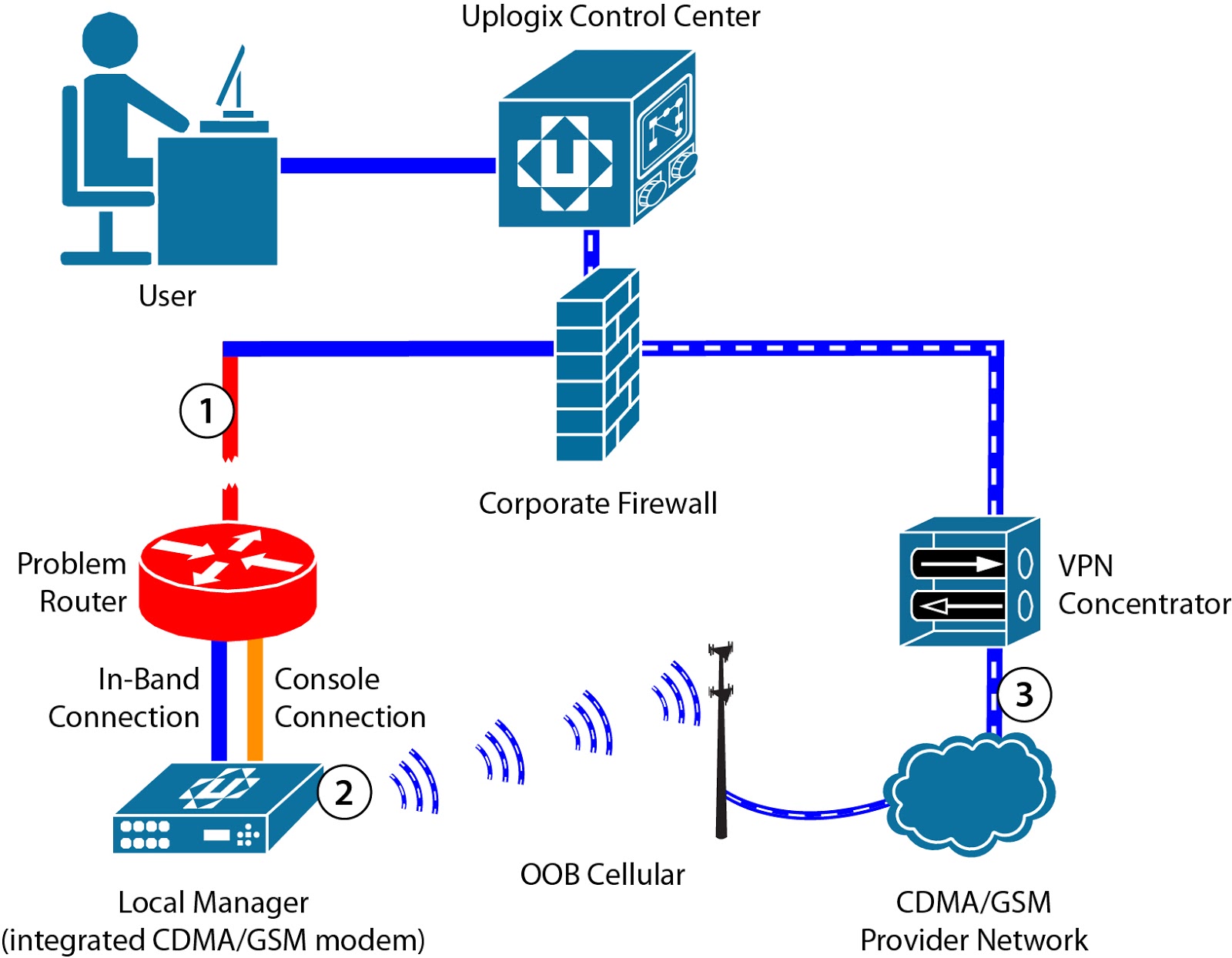
Out-of-band management (OOBM) is a method used to remotely manage and monitor network devices, even when the primary network connection is not available. It enables IT administrators to access and control network infrastructure, troubleshoot issues, and perform maintenance tasks without being physically present at the device’s location.
In simpler terms, OOBM creates a separate management channel that operates independently of the primary network connection. This secondary channel is typically established using a dedicated out-of-band management interface, such as a serial console or an Ethernet port, which enables direct access to the device’s management interface, bypassing the primary network.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how out-of-band management works:
- Secondary Management Interface: Network devices are equipped with a secondary interface that provides out-of-band management capabilities. This interface can take the form of a serial console port, Ethernet port, or a dedicated management module.
- Out-of-Band Network: Organizations establish a separate out-of-band network to facilitate communication between IT administrators and network devices. This network is isolated from the primary network and typically operates on a different subnet or VLAN.
- Remote Access: IT administrators can connect to network devices remotely using various methods. Depending on the device and infrastructure, administrators can utilize protocols such as Secure Shell (SSH), Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS), or Virtual Private Network (VPN) to establish a secure connection to the out-of-band management network.
- Device Control and Monitoring: Once connected to the out-of-band management network, administrators gain access to the device’s management interface. They can perform tasks such as configuration changes, firmware updates, and troubleshooting. Additionally, administrators can monitor device status, receive alerts, and collect performance data to ensure optimal network operations.
Out-of-band management serves as a backup method for managing network devices in situations where the primary network is unavailable. By utilizing a separate management channel, IT teams can maintain control and visibility over critical infrastructure, enabling them to address network issues promptly and efficiently.
Types of Out-Of-Band Management Methods
Out-of-band management (OOBM) utilizes various methods to establish a secondary management channel for remotely monitoring and controlling network devices. These methods provide flexibility and options for IT teams to implement the most suitable out-of-band management solution for their specific needs. Let’s explore some of the common types of OOBM methods:
- Serial Console: The serial console method involves connecting to a network device’s serial console port using a serial cable. This method allows direct access to the device’s command-line interface (CLI) for configuration and troubleshooting purposes. Serial console connections are typically used for managing networking devices such as switches, routers, and firewalls.
- Modem Dial-Up: Modem dial-up is an older but still viable out-of-band management method. It requires a modem connected to the network device’s serial console port, allowing remote access through a dial-up connection. While less commonly used nowadays, modem dial-up can be useful in situations where internet connectivity is unavailable or unreliable.
- Out-of-Band Management Port: Many modern network devices come equipped with a dedicated out-of-band management port, such as an Ethernet or console port. These ports are specifically designed to establish a separate management channel for OOBM purposes. IT administrators can connect to these ports and remotely manage the devices over the out-of-band network.
- Remote Console Servers: Remote console servers act as a central hub for managing multiple network devices through a single interface. They typically have multiple serial console ports, allowing IT administrators to connect to multiple devices simultaneously. Remote console servers consolidate and streamline out-of-band management tasks, making it easier to monitor and control network infrastructure remotely.
- Software-Based Solutions: Software-based out-of-band management solutions leverage virtualization technologies to establish remote connections to network devices. These solutions utilize virtual consoles or terminal servers to provide remote access and control over the out-of-band network. Software-based OOBM solutions are often used in cloud-based or virtualized environments.
Organizations can choose the most suitable out-of-band management method based on their infrastructure, budget, and specific requirements. It’s essential to consider factors such as the types of network devices, scalability needs, remote accessibility, and security when selecting an OOBM method.
Use Cases for Out-Of-Band Management
Out-of-band management (OOBM) offers valuable advantages and is applicable in various scenarios across different industries. Let’s explore some common use cases where OOBM solutions provide significant benefits:
- Data Centers: OOBM is crucial in data centers where uptime and uninterrupted service are paramount. With OOBM, data center administrators can remotely access and manage critical network devices, such as servers, switches, and storage systems, even during network outages. This ensures continuous operations, prompt troubleshooting, and maintenance without physical presence.
- Remote Locations: For organizations with remote branch offices or locations, OOBM is invaluable. IT teams can remotely manage networking equipment at these sites without the need for on-site visits. From configuring routers and switches to performing firmware updates, OOBM reduces travel costs and expedites issue resolution across geographically dispersed networks.
- Telecommunications: OOBM is essential in telecommunications infrastructure, where network reliability is critical. It enables remote administration of network devices such as switches, routers, and base stations. Telecommunication providers can proactively monitor, troubleshoot, and apply necessary updates to their network infrastructure, ensuring high-quality service and minimizing downtime.
- Security and Surveillance: OOBM plays a significant role in security and surveillance systems. IT administrators can remotely manage cameras, video recorders, and other security devices, ensuring smooth operations and proactive monitoring. OOBM allows for immediate troubleshooting and maintenance without disturbing critical security operations.
- Industrial Control Systems (ICS): OOBM is vital in industries that rely on industrial control systems, such as manufacturing and energy sectors. IT teams can remotely control and monitor critical components like programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs). OOBM ensures minimal disruptions, timely maintenance, and efficient troubleshooting, improving overall productivity and reducing downtime.
These are just a few examples of the many use cases for out-of-band management. Regardless of the industry or specific network infrastructure, OOBM provides the capability to remotely manage and maintain critical network devices, resulting in improved uptime, faster issue resolution, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Key Features of Out-Of-Band Management Solutions
Out-of-band management (OOBM) solutions come with a variety of key features that enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of remote network device management. These features ensure seamless monitoring, troubleshooting, and control over critical infrastructure. Let’s explore some of the essential features of OOBM solutions:
- Remote Access: The ability to remotely access network devices is a fundamental feature of OOBM solutions. This feature enables IT administrators to connect to devices over the out-of-band network, perform configuration changes, and troubleshoot issues without physical access to the equipment.
- Console Redirection: Console redirection allows IT administrators to view and interact with a device’s console output remotely. This feature is particularly useful for troubleshooting and performing tasks that require direct access to the device’s command-line interface (CLI).
- Power Management: Many OOBM solutions include power management features, enabling administrators to remotely power devices on or off. This capability is valuable in situations where a device needs to be rebooted or power-cycled to resolve issues without requiring manual intervention.
- Alerts and Notifications: OOBM solutions often come equipped with alerting and notification features. Administrators can configure the system to send alerts when specific events or issues occur. These alerts can be delivered via email, SMS, or integrated with monitoring systems, ensuring immediate attention and timely response to critical situations.
- Centralized Management: OOBM solutions with centralized management capabilities streamline the administration of multiple network devices. Administrators can access and control all devices from a single interface, simplifying configuration changes, firmware updates, and troubleshooting tasks. Centralized management enhances efficiency and reduces complexity in managing distributed networks.
- Security: Security is a crucial aspect of OOBM solutions. These solutions often include robust security features, such as secure communication protocols, encryption, authentication mechanisms, and access controls. These security measures ensure that remote access to network devices is protected from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
These key features of OOBM solutions provide organizations with the necessary tools to manage and maintain network devices efficiently. By leveraging remote access, console redirection, power management, and centralized management capabilities, businesses can minimize downtime, improve troubleshooting speed, and enhance overall network reliability.
Best Practices for Implementing Out-Of-Band Management
Implementing out-of-band management (OOBM) requires careful planning and consideration to ensure maximum effectiveness and efficiency. Here are some best practices to follow when implementing OOBM solutions:
- Identify Critical Network Devices: Begin by identifying the network devices that are crucial for the operation of your infrastructure. Focus on devices that, if they were to experience an issue, would have a significant impact on business operations. This includes routers, switches, firewalls, and servers.
- Establish Redundancy: Redundancy is essential to ensure uninterrupted access to network devices. Implement redundant OOBM connections and backup power supplies. This redundancy will help mitigate the risk of a single point of failure and increase the resilience of your OOBM infrastructure.
- Implement Secure Communication: Security is of paramount importance when implementing OOBM. Utilize secure communication protocols such as Secure Shell (SSH) or Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to protect remote access and management connections. Additionally, ensure that you regularly update security patches and employ strong authentication mechanisms.
- Centralize Management: Implement a centralized management system for your OOBM infrastructure. This will allow you to consolidate monitoring, configuration, and troubleshooting tasks into a single interface. A centralized management system simplifies administration and improves overall efficiency.
- Monitor OOBM Network: Continuously monitor the availability and performance of your OOBM network. Implement network monitoring tools to proactively detect and address any issues that may arise. Regularly reviewing logs and alerts will help you identify patterns, troubleshoot problems, and optimize your OOBM infrastructure.
- Document and Test Procedures: Document your OOBM procedures and make sure they are readily accessible to your IT team. Include detailed instructions for tasks such as remote access, console redirection, power management, and firmware updates. Regularly test these procedures through mock scenarios to ensure they are effective and efficient.
- Train IT Staff: Provide proper training to your IT personnel on how to effectively use the OOBM solutions. Ensure they understand the protocols, procedures, and best practices associated with remote access and management. Regularly conduct training sessions to keep your team up-to-date with the latest OOBM technologies and techniques.
By following these best practices, organizations can successfully implement out-of-band management solutions and maximize the benefits they provide. Implementing redundancy, prioritizing security, centralizing management, monitoring the OOBM network, documenting procedures, and training IT staff will contribute to the seamless operation and maintenance of critical network devices.
Considerations for Choosing an Out-Of-Band Management Solution
Selecting the right out-of-band management (OOBM) solution is crucial for ensuring the efficient management and monitoring of network devices. Here are key considerations to keep in mind when choosing an OOBM solution:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the OOBM solution is compatible with your existing network infrastructure. Consider factors such as device types, operating systems, and management protocols. Compatibility with your network devices and management interfaces is essential for seamless integration and effective remote management.
- Scalability: Assess the scalability of the OOBM solution in terms of both the number of devices it can support and the ability to manage a growing network. It’s important to choose a solution that can accommodate your current needs and provide room for future expansion without compromising performance or reliability.
- Remote Access Methods: Evaluate the remote access methods offered by the OOBM solution. Consider whether it supports various connection options, such as SSH, VPN, or web-based interfaces. Additionally, ensure that the solution provides secure and encrypted connections to protect sensitive data during remote access sessions.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Look for an OOBM solution that offers robust monitoring and alerting capabilities. The ability to receive real-time alerts and notifications when network devices experience issues is crucial for timely response and prompt troubleshooting. The solution should allow customizable alert settings and integration with existing monitoring systems.
- Ease of Use: Choose an OOBM solution that is user-friendly and intuitive for your IT team. The management interface should be easy to navigate, and the solution should provide clear instructions and documentation. Consider whether the solution offers features like centralized management and automation to simplify and streamline remote device management.
- Security: Security should be a top priority when choosing an OOBM solution. Look for features such as strong authentication mechanisms, encryption of data transmission, and granular access controls. Additionally, check if the solution adheres to industry-standard security protocols and undergoes regular security audits.
- Vendor Support and Reputation: Research the reputation and track record of the OOBM solution provider. Check customer reviews, testimonials, and references to gauge the level of customer satisfaction. Additionally, consider the availability and responsiveness of vendor support, as timely assistance is critical for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues.
By considering these factors, organizations can make an informed decision when choosing an out-of-band management solution that aligns with their specific needs and requirements. Compatibility, scalability, remote access methods, monitoring and alerting capabilities, ease of use, security, and vendor support are all important aspects that contribute to the effectiveness and reliability of your OOBM solution.