How NFC Works
Near Field Communication, or NFC, is a wireless communication technology that allows devices in close proximity to establish a connection and exchange information. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a magnetic field is generated between two NFC-enabled devices when they come into close range, typically within a few centimeters.
NFC operates on a high-frequency radio wave, typically 13.56 MHz, and uses a simple and secure transmission method called Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). It enables devices to communicate by employing two main modes: active and passive.
In the active mode, both devices generate and transmit their own signals simultaneously. They exchange data back and forth by rapidly switching between being a transmitter and a receiver. This mode is commonly used for peer-to-peer communication, such as transferring files between two smartphones.
In the passive mode, one device acts as a reader while the other acts as a tag, which is a passive component that only responds to the reader’s requests. The reader device emits a radio frequency field that powers the tag, allowing it to transmit its data back to the reader. This mode is widely employed for contactless payments, where the reader is usually a payment terminal or a point-of-sale device.
NFC technology enables various types of data to be transferred securely and efficiently. It supports two basic data transfer modes: read/write and card emulation. In the read/write mode, NFC devices can read information from and write data to compatible tags or other NFC devices. This is extensively used for applications like accessing digital content, like posters or business cards, with a simple tap.
Card emulation, on the other hand, allows an NFC-enabled device to function like a contactless smart card. It can emulate the data stored on a physical card, such as a credit or debit card, allowing users to make payments or gain access to secure locations by simply tapping their device on a compatible reader.
NFC technology is not only limited to smartphones and tablets. It can be incorporated into various devices, including wearable tech, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and even IoT devices like smart home appliances. The versatility of NFC makes it a convenient and reliable technology for a wide range of applications.
To utilize NFC, devices must have their NFC feature enabled and be in close proximity to each other. Typically, this involves simply tapping the NFC-enabled devices together or holding them close to initiate communication.
That’s a brief overview of how NFC technology works. In the next section, we will explore the differences between NFC and Bluetooth, providing insight into when each technology is best suited for various applications.
NFC vs. Bluetooth
NFC and Bluetooth are both wireless technologies that enable communication between devices. However, they have distinct differences in terms of range, speed, power consumption, and use cases.
One of the key differences between NFC and Bluetooth is their range. NFC operates within a very short range, typically up to 4 centimeters, making it suitable for close-proximity interactions. On the other hand, Bluetooth has a considerably greater range, usually up to 100 meters, allowing devices to connect from a greater distance.
Another distinguishing factor is the speed at which data is transferred. NFC is known for its fast data transfer rate, with a maximum transfer rate of 424 kbps. This makes it ideal for quick exchanges of information, such as sharing contacts or small files. Bluetooth, on the other hand, offers higher data transfer rates, with the latest Bluetooth 5.2 specification providing speeds of up to 2 Mbps. This makes it more suitable for tasks that require larger file transfers or streaming audio.
Power consumption is another area where NFC and Bluetooth differ. NFC is designed to be highly energy-efficient, as it requires very little power to operate. This makes it ideal for applications where low power consumption is critical, such as contactless payments or smart wearable devices. Bluetooth, on the other hand, can consume more power due to its extended range and higher data transfer capabilities.
In terms of use cases, NFC is often used for quick and easy interactions, such as contactless payments, ticketing, and access control. It is commonly employed in situations where convenience and simplicity are essential, such as sharing content between smartphones or connecting to Bluetooth speakers with just a tap.
Bluetooth, on the other hand, is more versatile and widely used in a range of applications. It is commonly found in devices such as smartphones, laptops, speakers, headphones, and smart home devices. Bluetooth is well-suited for tasks that require continuous connectivity, like streaming audio, connecting peripherals, and controlling smart devices remotely.
Types of NFC Devices
NFC technology has become increasingly prevalent and is now incorporated into a wide range of devices. Let’s explore some of the common types of NFC-enabled devices:
- Smartphones: NFC is a standard feature in most modern smartphones. These devices allow users to make contactless payments, share files, and connect with other NFC devices. Many popular mobile operating systems, such as Android and iOS, have built-in support for NFC technology.
- Tablets: Similar to smartphones, many tablets are equipped with NFC capabilities. This allows users to engage in various NFC-based activities, such as transferring files and accessing digital content.
- Wearable Devices: NFC is increasingly integrated into wearable tech, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and smart jewelry. With NFC-enabled wearables, users can conveniently make payments, access secure locations, and exchange information with other NFC devices.
- Payment Terminals: NFC technology is commonly used in payment terminals or point-of-sale (POS) devices. These devices allow customers to make quick and secure contactless payments by simply tapping their NFC-enabled payment cards or smartphones.
- Access Control Systems: NFC is widely used in access control systems to grant entry to secured areas. NFC-enabled access cards or badges can be easily tapped on readers to authorize access privileges.
- NFC Tags: NFC tags are small, passive devices that can store information and be read by NFC-enabled devices. These tags can be programmed to trigger specific actions, such as opening a website, launching an app, or adjusting device settings. NFC tags are often used in marketing campaigns, smart posters, and smart city applications.
- Automotive Devices: NFC technology is increasingly being incorporated into automobiles for various purposes, including keyless entry, device pairing, and wireless charging.
- IoT Devices: The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem benefits from NFC technology as well. IoT devices, such as smart home appliances, medical devices, and industrial equipment, can leverage NFC to streamline connectivity and data exchange.
These are just a few examples of the diverse range of NFC-enabled devices available in the market. The continued growth and adoption of NFC technology are paving the way for innovative applications and enhancing the overall user experience.
Popular Uses of NFC Technology
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology has emerged as a versatile and convenient solution for various industries and everyday applications. Let’s explore some of the popular use cases of NFC:
- Contactless Payments: One of the most widespread applications of NFC is in contactless payments. NFC-enabled smartphones or payment cards can be used to make secure and convenient transactions by simply tapping them on payment terminals. This technology has revolutionized the way we make payments, offering speed, security, and ease of use.
- Smart Access Control: NFC plays a significant role in access control systems. NFC-enabled cards or badges can be used to grant access to secure areas, such as office buildings or hotel rooms, by simply tapping them on NFC readers. This eliminates the need for physical keys or manual authentication processes.
- Transportation Ticketing: NFC technology is widely used in transportation ticketing systems, offering a seamless and quick way for passengers to validate their tickets. Public transport cards, such as fare cards or smart cards, can be tapped on NFC readers to pay for fares and gain entry to buses, trains, or subways. This reduces the reliance on paper tickets and minimizes queues and waiting times.
- Smart Advertising and Marketing: NFC tags and smart posters are integrated into advertising and marketing campaigns. By simply tapping an NFC-enabled device on the tag or poster, users can access additional information, promotional content, or exclusive offers. This allows businesses to engage users and provide a personalized experience.
- Information Sharing and File Transfer: NFC enables quick and easy information sharing between devices. By tapping two NFC-enabled devices together, users can instantly exchange contacts, photos, videos, or other files. This eliminates the need for cumbersome manual entry or file transfer methods.
- Smart Home Connectivity: NFC technology is utilized in smart home applications. NFC-enabled devices can be used to control various smart devices, such as lights, thermostats, or speakers, by simply tapping them on compatible NFC readers or hubs. This simplifies device setup and enhances the overall smart home experience.
- Healthcare Applications: NFC is gaining traction in the healthcare industry. NFC-enabled devices, such as medical bracelets or devices worn by patients, can store vital medical information. In case of emergencies, healthcare professionals can easily access this information by tapping their NFC-enabled devices, aiding in quick and accurate medical treatment.
- Event Ticketing: NFC technology is commonly used in event ticketing systems. NFC-enabled tickets or wristbands can be used for entry validation and access to various event areas. This eliminates the risk of counterfeit tickets and enhances the overall event experience for attendees.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of applications of NFC technology. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative uses that enhance convenience and streamline everyday tasks.
NFC Security Considerations
While Near Field Communication (NFC) technology offers numerous benefits and convenience, it’s important to be aware of the security considerations associated with its use. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Data Protection: When using NFC for contactless payments or data transfer, it’s crucial to ensure the protection of sensitive information. NFC transactions rely on encryption protocols to secure data transmission and prevent unauthorized access. It’s essential to choose NFC-enabled devices and applications from trusted sources to minimize the risk of data breaches.
- Unauthorized Access: The short-range nature of NFC technology can be advantageous in terms of convenient, proximity-based interactions. However, it also means that potential attackers need to be in close physical proximity to exploit vulnerabilities. Nevertheless, it’s important to be vigilant and protect NFC-enabled devices from unauthorized access. This can be done by enabling PIN or password protection, setting up biometric authentication, or using secure NFC reader modes.
- Snooping and Eavesdropping: NFC communication can be susceptible to snooping and eavesdropping attacks. As NFC operates in close proximity, attackers with specialized equipment may try to intercept and capture NFC communication to gather sensitive information. To mitigate this risk, NFC devices and applications employ encryption techniques to ensure the confidentiality of transmitted data. Implementing secure encryption algorithms and keeping software up to date are essential in preventing unauthorized access.
- Malware and Fraudulent Tags: NFC-enabled devices can be vulnerable to malware or fraudulent tags that are designed to exploit security weaknesses. Users should exercise caution when tapping on unknown tags or connecting with unfamiliar devices. It’s crucial to only interact with trusted sources and avoid downloading content or applications from unverified platforms.
- Lost or Stolen Devices: The convenience of NFC can pose a risk if the device gets lost or stolen. If an NFC-enabled device, such as a smartphone or payment card, falls into the wrong hands, unauthorized individuals may gain access to sensitive data or conduct fraudulent transactions. Users should immediately report lost or stolen devices to their service providers to minimize the potential risk.
- Secure NFC Tags: NFC tags, which are widely used in marketing campaigns and smart city applications, need to be carefully managed to prevent tampering or misuse. Organizations should utilize tamper-proof NFC tags and regularly audit and monitor their deployment to ensure the integrity of the information being shared.
By being aware of these security considerations and implementing appropriate safeguards, users can enjoy the benefits of NFC technology while minimizing the risks associated with its use. It’s always important to stay informed about the latest security practices and stay vigilant when utilizing NFC-enabled devices and applications.
NFC Tags and How They Work
NFC (Near Field Communication) tags are small, passive devices that can store and transmit information to NFC-enabled devices. These tags contain a microchip and an antenna, allowing them to communicate with NFC devices, such as smartphones or tablets, when they come into close range. Let’s explore how NFC tags work:
Memory Capacity: NFC tags come in various memory capacities, ranging from a few kilobytes to several megabytes. The memory size determines the amount of data that can be stored on the tag. The information stored on NFC tags can include URLs, contact details, promotional offers, or commands to perform specific actions on the NFC-enabled device.
Tag Types: NFC tags are available in different types, such as the NFC Forum Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, and Type 4 tags. Each type has its own specifications, memory capacity, and functionality. The most common types are Type 1 and Type 2, which are widely used in marketing campaigns and everyday applications.
Read and Write: NFC tags can be read by NFC-enabled devices, allowing users to access the information stored on the tag. Additionally, certain types of NFC tags support read and write capabilities, enabling users to update or modify the data stored on the tag. This makes NFC tags versatile and adaptable for different applications and scenarios.
Tap and Scan: To interact with an NFC tag, users simply need to tap or scan their NFC-enabled device, such as a smartphone, against the tag. The NFC-enabled device emits a radio frequency field that powers the tag, allowing it to transmit its data back to the device. This communication happens in a matter of seconds, making it a quick and convenient way to access information or trigger actions.
Tag Encoding: NFC tags need to be encoded with the appropriate data before they can be read by NFC-enabled devices. This encoding can be done through dedicated NFC tag writer apps or by using devices that have built-in tag encoding capabilities. When encoding a tag, users can specify the type and format of the data they want to store, ensuring compatibility with the NFC-enabled devices that will interact with the tag.
Applications: NFC tags have a wide range of applications. They are commonly used in marketing and advertising to provide additional information or offers to customers. NFC tags can be embedded in smart posters, business cards, or product labels, enabling users to tap their device and instantly access digital content. They are also used in logistics and inventory management, allowing tracking and identification of products throughout the supply chain.
Authentication and Security: Some NFC tags support advanced security features, such as encryption and password protection, to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the stored data. This is particularly important when NFC tags are used for access control systems or sensitive information storage. Secure NFC tags provide an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access and tampering.
NFC tags play an integral role in enabling convenient and intuitive interactions between NFC-enabled devices and the physical world. Their versatility and ease of use make them a valuable tool in various industries and everyday applications.
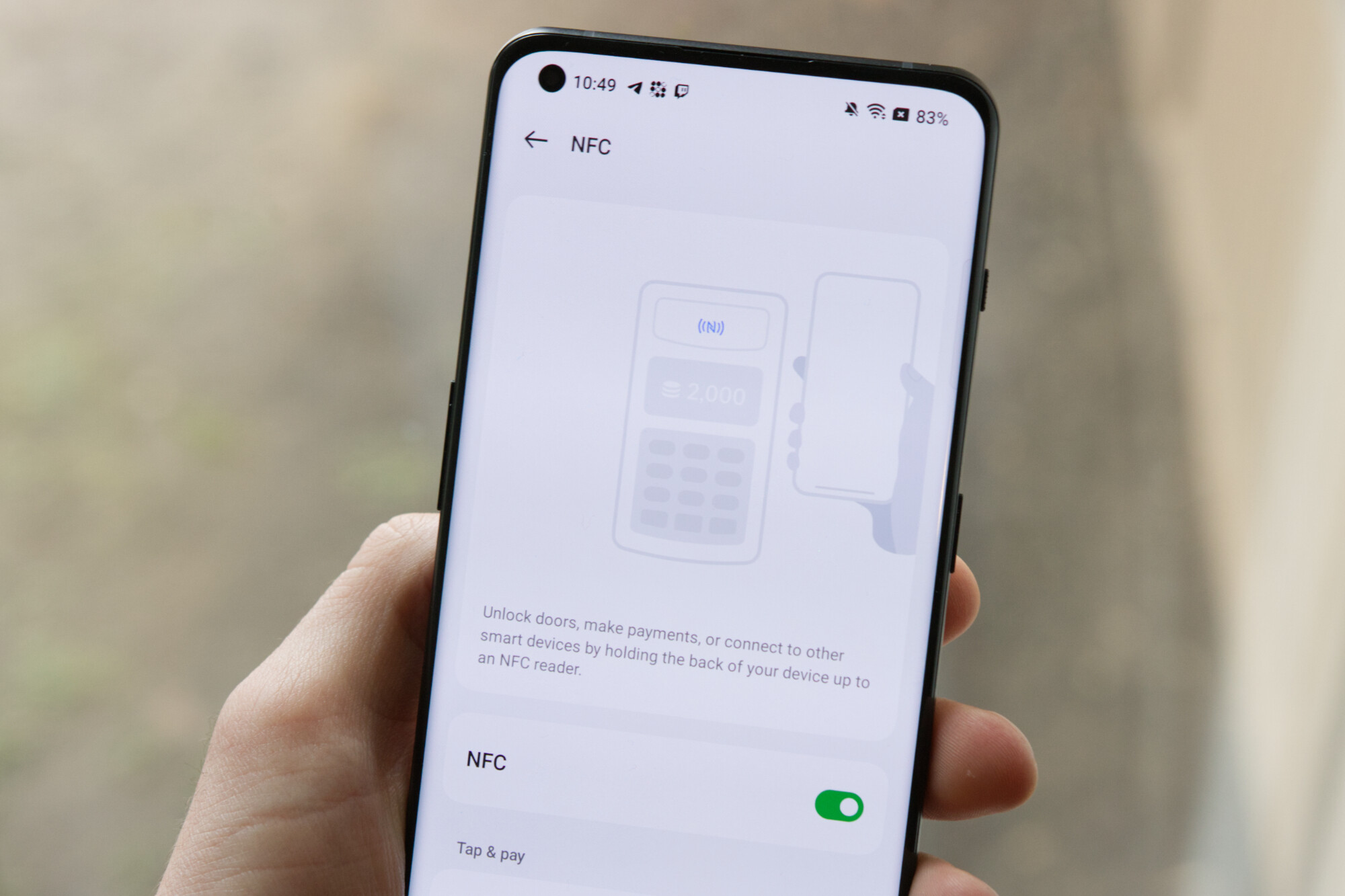
How to Set Up and Use NFC on Your Smartphone
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology is now a standard feature on many smartphones and offers a wide range of convenient applications. If you have an NFC-enabled smartphone, here’s how you can set up and use NFC:
1. Check NFC Compatibility: First, ensure that your smartphone supports NFC technology. Most modern Android and iOS devices have built-in NFC functionality. You can find this information in your device’s settings or by referring to the manufacturer’s specifications.
2. Enable NFC: Once you confirm that your smartphone supports NFC, go to the settings menu to enable the NFC feature. On Android devices, this is usually found in the “Wireless & Networks” or “Connections” section. On iPhones, NFC is automatically enabled for Apple Pay but may require additional settings for other NFC applications.
3. Tap and Go: To use NFC, simply place your smartphone within close proximity to another NFC-enabled device or tag. For example, to share contacts or files, tap your device against another NFC-enabled device and follow the prompts to establish the connection.
4. Contactless Payments: To make contactless payments using NFC, ensure that your smartphone is compatible with mobile payment services such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, or Samsung Pay. Set up your preferred payment method and add your payment card details to the digital wallet app. Then, when making a purchase, simply tap your device against the payment terminal to authorize the transaction.
5. Interacting with NFC Tags: NFC tags can trigger specific actions or provide additional information with a simple tap of your smartphone. Many apps are available that allow you to read and write data on NFC tags. For example, you can use an NFC tag to automate tasks like adjusting phone settings, launching an app, or sharing Wi-Fi credentials.
6. Security Measures: As with any technology, it’s important to take basic security precautions when using NFC. Ensure that your device has screen lock enabled, such as a PIN, password, or biometric authentication. Be cautious when interacting with unknown NFC tags or devices to avoid potential security risks.
7. Explore NFC Applications: NFC technology offers a plethora of applications beyond payments and file sharing. Explore the growing ecosystem of NFC-enabled apps and devices, such as smart home automation, loyalty programs, public transportation ticketing, and more. Keep an eye out for future updates and advancements in NFC technology to make the most of its capabilities.
Remember, NFC functionality may vary slightly depending on your smartphone brand or model. Refer to your device’s user manual or online resources for specific instructions tailored to your device.
By setting up and utilizing NFC on your smartphone, you can enjoy the convenience and versatility of this technology, whether it’s for payments, sharing information, or automating tasks with a simple tap.
Future Developments and Applications of NFC Technology
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology has come a long way since its inception. As technology advances, we can anticipate significant developments and new applications for NFC in the future. Here are some potential areas of growth:
1. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: NFC technology can seamlessly connect various IoT devices, such as smart appliances, wearables, and industrial equipment. NFC-enabled IoT devices can communicate with each other, facilitating data exchange and enabling seamless connectivity and automation in our daily lives.
2. Enhanced Security: With the growing importance of data security, NFC technology is likely to incorporate stronger security features. This includes advancements in encryption protocols, authentication methods, and tamper-proof tags to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of transmitted data.
3. Healthcare Applications: The healthcare industry can benefit from NFC technology in areas such as patient monitoring, medication management, and quick access to medical records. NFC-enabled devices and tags can securely store and transmit vital health information, improving patient care and facilitating efficient healthcare processes.
4. Smart City Solutions: NFC technology can play a vital role in smart city initiatives. From transportation ticketing and access control to interactive street signs and public services, NFC-enabled devices and tags can simplify and enhance urban living, making cities more efficient, connected, and sustainable.
5. Event Management: NFC has already transformed event ticketing, but its applications can extend to event management as well. NFC-enabled devices and tags can streamline registration, access control, exhibitor engagement, and attendee interactions, providing a seamless and integrated event experience.
6. Personalization and Contextual Interaction: NFC enables personalized and contextual interactions. By tapping an NFC tag or device, users can receive customized content, tailored recommendations, or real-time information based on their preferences, location, or other contextual factors.
7. Cross-Platform Integration: NFC technology has the potential to integrate with other wireless communication technologies, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, to provide a seamless user experience across different platforms. This could enable devices to seamlessly switch between wireless connections, ensuring continuous connectivity and enhanced usability.
8. Blockchain Integration: The combination of NFC and blockchain technology can provide enhanced security and transparency for various applications. NFC can authenticate and secure transactions, while blockchain technology can ensure a decentralized and tamper-proof record of these transactions.
As NFC technology continues to evolve, businesses and industries will find innovative ways to leverage its benefits. From improved consumer experiences to streamlined processes and enhanced security, the future of NFC holds great potential in transforming how we interact with the digital and physical worlds.