Benefits of Encryption
Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. It converts data into an unreadable format, thereby ensuring the privacy and integrity of the data. Whether you’re a business owner or an individual, understanding the benefits of encryption is essential in today’s digital age.
One of the primary benefits of encryption is data protection. By encrypting your data, you can prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing and understanding the information, even if they manage to intercept it. This is particularly important for sensitive data such as financial records, personal identification information, and confidential business data.
Encryption also helps in maintaining the integrity of data. It ensures that the information remains unchanged during transmission and storage. Tampering with encrypted data will render it useless and alert the intended recipient of any unauthorized modifications.
Another advantage of encryption is that it helps establish trust. Whether it’s sending confidential documents to clients or protecting customer data, encryption provides reassurance that the information is secure. This can enhance your reputation and build trust with your customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Furthermore, encryption is an essential part of regulatory compliance. Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, have strict regulations regarding data protection. Implementing encryption measures ensures that your organization meets these requirements and avoids potential legal and financial consequences.
Encryption also acts as a deterrent to hackers and cybercriminals. When they encounter encrypted data, they are less likely to invest their time and effort into decrypting it. Instead, they will move on to easier targets, protecting you and your data from potential security breaches.
Lastly, encryption can provide peace of mind. Knowing that your sensitive information is protected by strong encryption algorithms can alleviate fears of identity theft, data leaks, or cyber attacks. It allows you to focus on your business or personal matters without constantly worrying about the security of your data.
What is a Private Encryption Key?
A private encryption key, also known as a secret key or symmetric key, is a piece of data used in symmetric encryption algorithms. It is a crucial component in the process of encrypting and decrypting sensitive information.
Unlike asymmetric encryption, which uses two separate keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption – symmetric encryption relies on a single key, known as the private encryption key. This key is shared between the sender and recipient of the encrypted data.
The private encryption key is used to transform plain text into cipher text during the encryption process. It applies a mathematical algorithm to scramble the original data, making it unreadable to anyone without the corresponding key. This ensures that only authorized parties with the correct private key can access and decrypt the information.
The private encryption key should be kept confidential and securely managed. If the key falls into the wrong hands, it can compromise the security of the encrypted data. Therefore, it is crucial to protect the privacy of the private encryption key to maintain the integrity of the encrypted information.
Private encryption keys are typically generated using random number generators or password-based key derivation functions. Random number generators create a truly random key, while password-based key derivation functions derive a key from a user’s password or passphrase.
The length and complexity of the private encryption key are important factors in its strength. The longer the key, the more secure it is against brute force attacks. A strong private encryption key should be complex enough to resist various cryptographic attacks and ensure the confidentiality of the encrypted data.
How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption is a process that transforms plain text into cipher text, rendering the information unreadable to unauthorized individuals. It involves the use of mathematical algorithms and a secret key to encrypt and decrypt data securely.
The encryption process starts with the plain text, which is the original message or data that needs to be protected. This plain text is combined with the private encryption key, and a cryptographic algorithm is applied to scramble the data.
The algorithm transforms the plain text into cipher text, which is the encrypted form of the data. The resulting cipher text is a series of jumbled characters that cannot be understood without the corresponding private encryption key.
To decrypt the cipher text, the recipient requires the same private encryption key used to encrypt the data. By applying the decryption algorithm and using the private key, the cipher text is transformed back into plain text, allowing the recipient to read the original message.
Encryption algorithms come in different forms, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption. In symmetric encryption, the same private key is used for both encryption and decryption. The sender and recipient must share this key in a secure manner.
Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, uses two separate keys – a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption. The public key can be freely shared, allowing anyone to encrypt data, while only the recipient with the corresponding private key can decrypt it.
Encryption algorithms are designed with various complexities and strengths to provide different levels of security. Some commonly used encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), and RSA.
Modern encryption techniques also incorporate additional security measures, such as hashing and digital signatures, to ensure data integrity and authenticity. Hashing involves transforming data into a fixed-length string of characters, while digital signatures use public and private keys to verify the integrity and origin of a message.
Overall, encryption is a crucial tool in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. By understanding how encryption works, individuals and organizations can implement effective security measures to keep their data safe and secure.
Importance of Private Encryption Key in Online Backup
Online backup services have become increasingly popular for individuals and businesses to securely store their data in remote servers. While these services offer convenience and accessibility, the importance of a private encryption key in online backup cannot be overstated.
A private encryption key is essential in ensuring the confidentiality and privacy of the data stored in online backup services. It serves as an additional layer of protection beyond the security measures provided by the backup provider. With a private encryption key, the user has full control over the encryption and decryption of their data, making it inaccessible to anyone without the key.
By encrypting data before it is uploaded to the online backup server, the user maintains complete ownership of their information. Even if the backup server or the backup provider’s security measures are compromised, the encrypted data remains safe and unreadable without the private encryption key.
Online backup services often offer different encryption options, including client-side encryption and server-side encryption. With client-side encryption, the data is encrypted on the user’s device before being transmitted to the backup server. This ensures that the data is protected from the moment it leaves the user’s device. The private encryption key used for encryption is known only to the user, adding an extra layer of security.
In contrast, server-side encryption means that the data is encrypted on the backup provider’s server. While this offers convenience, it also means that the backup provider has access to the encryption key. To truly maintain privacy and security, using client-side encryption with a private encryption key is crucial.
Having a private encryption key also protects against unauthorized access to data by employees or third parties. In some cases, backup providers may have access to users’ data for administrative or support purposes. However, with client-side encryption and a private encryption key, the user can be confident that their data remains confidential, even in such scenarios.
It is important to note that with the importance of the private encryption key comes the responsibility of managing and protecting it. Users must ensure that the key is securely stored and not shared with unauthorized individuals. Losing the private encryption key can result in permanent data loss, as the encrypted data will be inaccessible without the key.
How to Generate a Private Encryption Key
Generating a private encryption key is a crucial step in ensuring the security and privacy of your data. It is important to follow best practices to create a strong and reliable key that can withstand potential attacks. Here are the steps to generate a private encryption key:
- Determine the encryption algorithm: Before generating a private encryption key, you need to decide which encryption algorithm you will be using. Commonly used symmetric encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Data Encryption Standard (DES). Research and choose an algorithm that suits your security requirements.
- Choose a random key length: The length of the key will determine its strength. Longer keys generally provide better security. Check the documentation or recommendations for the chosen encryption algorithm to determine the recommended key length.
- Use a secure key generation method: To generate a private encryption key, it is crucial to use a secure key generation method. The key should be created using a random number generator (RNG) or password-based key derivation function (PBKDF). Ensure that the RNG used is of high quality and provides truly random numbers to avoid predictability.
- Ensure key uniqueness: It is essential to generate a unique key for each encryption process. Reusing the same key for multiple purposes can compromise the security of the encrypted data. Generating a new key for each encryption task ensures that even if one key is compromised, the others remain secure.
- Securely store the key: After generating the private encryption key, it is crucial to securely store it. Store the key in a secure location, such as an encrypted storage device or a password-protected file. Avoid storing the key in plain text or easily accessible locations.
- Create backups: To prevent potential data loss, it is recommended to create backups of your private encryption key. Store these backups in separate secure locations to ensure that you can recover the key if it is lost or inaccessible.
Generating a private encryption key is a critical step in maintaining the security and privacy of your data. By following these steps and best practices, you can create a strong and reliable key that protects your sensitive information.
Storing and Protecting the Private Encryption Key
Once you have generated a private encryption key, it is crucial to store and protect it properly to maintain the security and integrity of your encrypted data. Here are some important considerations for storing and protecting your private encryption key:
- Use secure storage: Store your private encryption key in a secure location. Consider using hardware-based solutions such as Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) or smart cards, which provide additional physical protection for your key.
- Implement strong access controls: Ensure that only authorized individuals have access to the private encryption key. Implement access controls such as strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, or biometric authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Separate storage from the encrypted data: It is best practice to store the private encryption key separately from the encrypted data. If the encrypted data is compromised, having the key stored separately adds an extra layer of protection.
- Consider key escrow: Key escrow involves entrusting a third party with a backup copy of your private encryption key. This can be helpful in case of key loss or when key recovery is necessary.
- Regularly update and rotate the key: As an additional security measure, consider updating and rotating your private encryption key periodically. This practice ensures that if the key is compromised, it becomes invalid after a certain period.
- Encrypt the private encryption key itself: To further enhance security, consider encrypting the private encryption key itself. This adds an extra layer of protection, as even if the storage location is compromised, the key will be encrypted and useless to unauthorized individuals.
- Regularly audit and monitor access: Implement logging and monitoring mechanisms to track access to the private encryption key. Regularly review the logs to detect any suspicious or unauthorized activities.
Remember that the security of your private encryption key is crucial to protect your sensitive information. By following these best practices and implementing robust security measures, you can ensure that your private encryption key remains secure and that your encrypted data remains safe from unauthorized access.
Using the Private Encryption Key for Online Backup
When utilizing online backup services, integrating the private encryption key is a vital step in maximizing the security and privacy of your data. Here’s how you can effectively use the private encryption key for online backup:
- Select a backup service that supports client-side encryption: Utilize an online backup service that offers client-side encryption, ensuring that your data is encrypted on your device before being transmitted to the backup server.
- Generate a strong private encryption key: Follow best practices for generating a strong private encryption key, as outlined in the previous section. Ensure that the key is sufficiently long and complex to provide robust security.
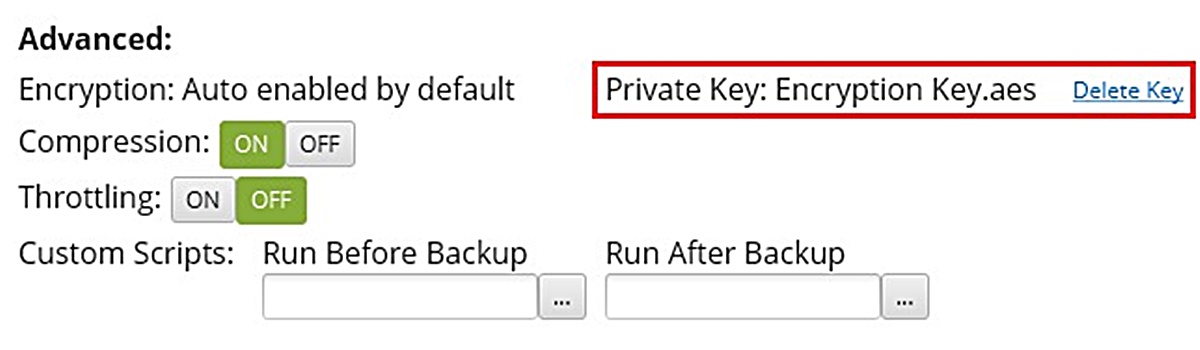
- Enable encryption within the backup software: Depending on the backup service you choose, you may need to enable encryption functionality within the backup software. This allows you to specify your private encryption key for encrypting your data before it is sent to the backup server.
- Securely store the private encryption key: Store your private encryption key in a secure location, separate from your backed-up data. Consider using encrypted storage or password-protected files to protect the key from unauthorized access.
- Ensure key availability: Maintain access to your private encryption key at all times. Losing the key may result in permanent data loss, as the encrypted files will be unreadable without it. Create backup copies of the key and securely store them in different locations.
- Regularly test the restore process: To ensure the effectiveness of your private encryption key, periodically test the restore process. Verify that you can successfully decrypt and restore your data using the private encryption key.
- Implement additional security measures: Alongside using the private encryption key, consider implementing other security measures for added protection. This may include strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates for your backup software.
- Regularly review and update your encryption key: As an extra security measure, review and update your private encryption key periodically. By rotating the encryption key, you minimize the risk of compromised data if the key is ever compromised.
By employing the private encryption key for online backup, you retain control over the encryption and decryption processes. This allows you to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of your data, even when stored on external servers.
Best Practices for Managing Private Encryption Keys
Effectively managing private encryption keys is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of your encrypted data. Follow these best practices to ensure proper management of your private encryption keys:
- Create a Key Management Policy: Establish a comprehensive key management policy that outlines the processes and procedures for generating, using, storing, and protecting private encryption keys. This policy should address key creation, rotation, storage, and access control.
- Use Strong and Unique Keys: Generate strong and unique private encryption keys for each encryption task. Ensure that the keys are sufficiently complex and random to resist attacks.
- Implement Secure Key Storage: Store private encryption keys in secure locations using appropriate encryption and access controls. Use hardware-based solutions or secure key vaults that offer protection against physical and unauthorized access.
- Establish Key Ownership: Clearly define who owns and has responsibility for managing the private encryption keys within your organization. Assign roles and responsibilities to ensure accountability and proper handling of the keys.
- Implement Key Rotation: Regularly rotate the private encryption keys to mitigate the risk of key compromise. This helps minimize the window of opportunity for attackers and ensures that older keys become invalid.
- Securely Distribute and Share Keys: If necessary, securely distribute and share private encryption keys with authorized individuals or systems. Use secure channels for key distribution and employ mechanisms such as key exchange protocols or secure key escrow.
- Encrypt Key Backups: Encrypt backup copies of private encryption keys to protect them in case of loss or compromise. Use strong encryption methods and securely store the backup copies in separate locations.
- Regularly Audit and Monitor Key Usage: Implement logging and monitoring mechanisms to track and audit key usage. Regularly review logs to identify any suspicious activities or unauthorized attempts to access the keys.
- Plan for Key Recovery: Establish a key recovery plan to ensure access to encrypted data if key loss or unavailability occurs. This may involve secure backup copies, key escrow, or alternate key recovery mechanisms.
- Train Personnel on Key Management: Provide training and awareness programs to personnel involved in key management. Ensure they understand the importance of key security, proper key handling procedures, and potential risks associated with key mismanagement.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can effectively manage their private encryption keys, mitigate risks, and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their encrypted data.