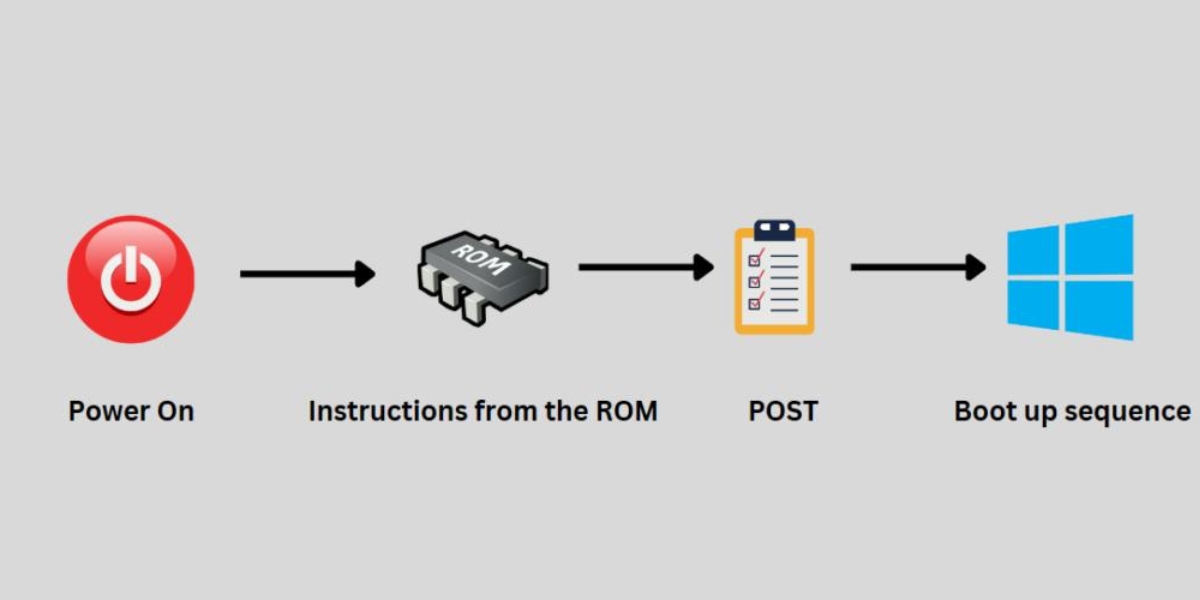
What is a POST Code?
A POST code, also known as a Power On Self Test code, is a series of diagnostic codes that are generated by a computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) during the boot process. These codes provide valuable information about the health and functionality of the computer’s hardware components.
When a computer is turned on, the BIOS initiates a series of tests to ensure that all the hardware components are working properly. This process is known as the Power On Self Test (POST). During the POST, if any issues or errors are detected, the BIOS will generate a unique POST code to indicate the specific problem.
POST codes are typically displayed as a series of numbers or alphanumeric characters on a POST code display. This display is usually located on the motherboard or on an additional card installed in the computer. It allows users or technicians to quickly identify any potential hardware issues.
These codes are designed to be deciphered by the manufacturer or experienced technicians, as they provide a detailed analysis of the computer’s current state. Each POST code is associated with a specific hardware component or system operation, allowing users to pinpoint the source of the problem more efficiently.
POST codes can vary between different computer models and manufacturers, as they are specific to the BIOS firmware used. However, most POST codes follow a similar pattern, with common codes related to CPU, RAM, video card, or storage device errors.
Overall, a POST code serves as a powerful troubleshooting tool for diagnosing hardware issues, allowing users to quickly identify and address any problems that may be preventing the computer from booting or operating optimally.
Why are POST Codes Important?
POST codes are an essential component of computer troubleshooting and diagnostics. They provide valuable information about the state of a system’s hardware during the boot process. Here are some reasons why POST codes are important:
- Quick Identification of Hardware Issues: POST codes allow users and technicians to quickly identify hardware problems. By referring to the POST code display, they can determine the specific component or system operation that is causing the issue. This saves time and helps in addressing the problem more efficiently.
- Streamlined Troubleshooting: POST codes streamline the troubleshooting process by providing a specific error code. Instead of having to go through guesswork or trial and error, users can refer to the code and consult manufacturer documentation or online resources to find the appropriate solution. This eliminates unnecessary troubleshooting steps and reduces downtime.
- Easy Communication with Technical Support: When encountering a hardware problem, having access to the POST code can be immensely helpful when contacting technical support. By sharing the code, support agents can quickly understand the issue and provide targeted assistance. This expedites the support process and increases the likelihood of a prompt resolution.
- Enhanced System Stability: By providing early detection of hardware issues, POST codes contribute to system stability. Timely identification and resolution of problems can prevent further damage and keep the system running smoothly. This is particularly crucial for critical systems where downtime can have serious consequences.
- Cost-Efficient Repairs: POST codes facilitate more accurate and targeted repairs, minimizing the need for costly trial and error hardware replacements. This saves money and ensures that the defective component is correctly identified and replaced, preventing unnecessary expenses.
Overall, POST codes play a vital role in diagnosing hardware issues, expediting troubleshooting, and maintaining system stability. They are a valuable tool for both users and technicians in identifying and addressing hardware problems effectively.
How Does a POST Code Work?
A POST code works by providing diagnostic information about the status of a computer’s hardware components during the boot process. Here’s a breakdown of how a POST code works:
- The boot process initiates when the computer is powered on, and the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) takes control.
- The BIOS performs a Power On Self Test (POST) to check the integrity and functionality of the essential hardware components, such as the CPU, memory, graphics card, and storage devices.
- During the POST, if the BIOS detects any errors or issues with the hardware, it generates a specific error code.
- The error code is displayed on a POST code display, which can be in the form of a numerical or alphanumeric panel on the motherboard or an additional card installed in the computer.
- Each POST code is associated with a particular hardware component or system operation. The code provides a detailed analysis of the problem, allowing users or technicians to pinpoint the source of the issue.
- Users or technicians can refer to the computer’s documentation or the manufacturer’s reference guide to interpret the meaning of the POST code. This enables them to understand which hardware component or system operation is causing the problem.
- Based on the identified issue, appropriate troubleshooting steps can be taken to resolve the problem. This may involve reseating components, replacing faulty hardware, updating BIOS firmware, or tweaking settings in the BIOS configuration.
- Once the issue is resolved, the system can continue with the boot process, or if multiple errors are detected, additional POST codes may be displayed to indicate subsequent errors.
The POST code system is designed to be comprehensive and detailed, allowing for efficient troubleshooting and resolution of hardware issues. It provides an invaluable diagnostic tool that aids users and technicians in identifying and addressing problems during the boot process.
Common POST Codes and Their Meanings
POST codes are unique error codes that indicate specific hardware issues encountered during the boot process. While the exact POST codes can vary depending on the computer model and BIOS firmware, here are some common POST codes and their meanings:
- POST Code 00: This code typically indicates a successful POST, meaning that the computer has passed all diagnostic tests and is ready for the operating system to load.
- POST Code 01: This code suggests a CPU-related issue, such as a faulty CPU or incorrect CPU settings. It may require checking the CPU installation, reseating it, or verifying the BIOS settings.
- POST Code 10: This code could indicate a RAM (Random Access Memory) problem, such as incompatible or defective memory modules. Reseating the RAM or testing with different modules may be necessary.
- POST Code 25: This code is commonly associated with a problem related to the graphics card or display output. It may require checking the graphics card connection, verifying driver compatibility, or replacing the card if necessary.
- POST Code 30: This code is often associated with a storage device issue, such as a faulty hard drive or connectivity problem. Verifying the connection, ensuring the drive is correctly recognized in the BIOS, or replacing the drive may be necessary.
- POST Code 50: This code could indicate an issue with the motherboard or its components. It may require inspecting the motherboard for physical damage, checking power supply connections, or consulting technical support for further assistance.
- POST Code 99: This code suggests a miscellaneous issue, such as an unknown error or multiple errors. It may require resetting the BIOS settings, reseating hardware components, or seeking professional assistance for further diagnosis.
It is important to consult the computer’s documentation, manufacturer’s reference guide, or online resources specific to your system to determine the meaning of other POST codes that may be encountered. This will help in identifying the exact hardware issues and undertaking appropriate troubleshooting steps.
Remember that POST codes can vary between different computer models and manufacturers, so it is essential to refer to the appropriate documentation for accurate interpretation and resolution of the encountered errors.
How to Troubleshoot POST Code Errors
Encountering a POST code error can be frustrating, but there are steps you can take to troubleshoot and resolve the issue. Here are some tips to help you troubleshoot POST code errors:
- Refer to the Documentation: Consult the computer’s documentation or the manufacturer’s reference guide to understand the meaning of the specific POST code. This will provide insights into the hardware component or system operation that is causing the error.
- Reseat Components: Ensure that all hardware components, such as the CPU, RAM modules, graphics card, and storage devices, are properly seated in their respective slots. Sometimes, loose connections can cause POST code errors.
- Check Hardware Compatibility: Verify that all the hardware components in your system are compatible with each other and with the BIOS firmware version. Incompatible hardware can trigger errors. Consult the manufacturer’s website for compatibility information.
- Update BIOS Firmware: Visit the manufacturer’s website and check for any available BIOS updates. Updating the BIOS firmware can often resolve compatibility issues and improve system stability. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for BIOS updates carefully.
- Disconnect Unnecessary Components: Remove any unnecessary peripherals connected to your system, such as external drives or expansion cards. Sometimes, conflicts between devices can cause POST code errors.
- Perform Memory Tests: Use software tools, such as MemTest86, to check the integrity of your RAM modules. Faulty or incompatible RAM can cause POST code errors. Replace or reconfigure the RAM if necessary.
- Verify Power Supply: Ensure that your power supply is functioning properly and supplying enough power to all components. Faulty power supply units can lead to hardware errors. Consider testing with a different power supply if available.
- Consult Technical Support: If you have tried the above steps and are still unable to resolve the POST code error, it may be necessary to contact technical support. Provide them with the specific POST code and a description of the steps you have taken so far. They may be able to provide further guidance or recommend additional troubleshooting steps.
Remember, POST code errors can indicate a wide range of issues, from minor hardware glitches to more severe component failures. It’s essential to approach troubleshooting systematically and seek professional assistance if needed.
Benefits of Using a POST Code Display
A POST code display is a valuable addition to any computer system, providing several benefits for users and technicians. Here are some advantages of using a POST code display:
- Quick Fault Identification: The primary benefit of a POST code display is its ability to quickly identify hardware faults. The display shows specific error codes that correspond to different hardware components or system operations. This allows users or technicians to pinpoint the source of the problem and take appropriate action promptly.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: With a POST code display, troubleshooting becomes more efficient. Instead of relying on vague error messages or guesswork, the display provides precise error codes. Users can refer to the computer’s documentation or the manufacturer’s reference guide to interpret the codes accurately. This streamlines troubleshooting and eliminates unnecessary steps.
- Minimized Downtime: By quickly identifying hardware faults, a POST code display helps minimize system downtime. Users can promptly address the specific issue causing the error code, speeding up the troubleshooting and repair process. Shorter downtime leads to increased productivity and reduces disruptions to workflow.
- Accurate Diagnosis: POST code displays enable more accurate diagnosis of hardware problems. The codes provide detailed information about the component or operation causing the error. This allows users or technicians to identify the root cause of the issue, preventing misdiagnosis and ensuring the correct solution is implemented.
- Assistance for Technical Support: When seeking assistance from technical support, having access to POST codes can greatly aid in the troubleshooting process. By sharing the error codes with support agents, they can better understand the problem and provide targeted guidance or solutions. This expedites the support process and increases the likelihood of a swift resolution.
- Learning and Education: POST code displays also serve as a valuable learning tool. They provide insights into the computer’s internal processes, helping users develop a better understanding of how hardware components interact and influence system functionality. This knowledge can be beneficial for future troubleshooting or upgrades.
Overall, a POST code display enhances the diagnostic capabilities of a computer system, enabling efficient troubleshooting, accurate identification of hardware faults, and reduced downtime. It is a valuable tool for both users and technicians in maintaining and optimizing the performance of computer hardware.
Alternatives to a POST Code Display
While a POST code display is a convenient and efficient way to diagnose hardware issues during the boot process, there are alternative methods that can be used to troubleshoot computer problems. Here are some alternatives to a POST code display:
- Diagnostic LEDs: Some motherboards feature diagnostic LEDs that indicate the status of various hardware components during the boot process. These LEDs light up or flash to indicate the specific component or operation experiencing the error. They provide a visual indication similar to a POST code display but in a different format.
- Beep Codes: Another alternative is the use of audio beep codes. These beep codes are generated by the motherboard’s BIOS and are emitted through the system speaker. Each beep sequence corresponds to a specific error or hardware issue. Users can consult the computer’s documentation or manufacturer’s reference guide to interpret the beep codes correctly.
- Error Messages on Screen: Sometimes, instead of using dedicated displays or audio alerts, error messages are displayed directly on the computer screen. These messages provide information about the encountered issue, allowing users to take appropriate action. It is important to note that this method requires a functional display and may not be accessible in cases where the display is not working properly.
- Software Diagnostics: Diagnostic software tools can be used to identify hardware issues without relying on physical displays. These tools run tests on various hardware components and generate reports or error logs that users or technicians can analyze. Software diagnostics can provide a comprehensive analysis of the entire system and help pinpoint specific hardware problems.
- Integrated Hardware Monitoring: Some modern motherboards include integrated hardware monitoring features that provide real-time information about the system’s temperature, voltage, and fan speed. Monitoring software can be used to track these parameters and identify any abnormalities that could indicate hardware issues.
- External Diagnostic Devices: In certain cases, external diagnostic devices or tools can be used to diagnose hardware problems. These devices connect to the computer and provide detailed diagnostic information about specific components or system operations. They often require specialized knowledge or expertise to interpret the data accurately.
Each alternative method has its own advantages and limitations, and their availability may depend on the specific computer model or hardware configuration. It is important to familiarize yourself with the available options for diagnosing hardware issues and choose the most suitable method based on your needs and resources.