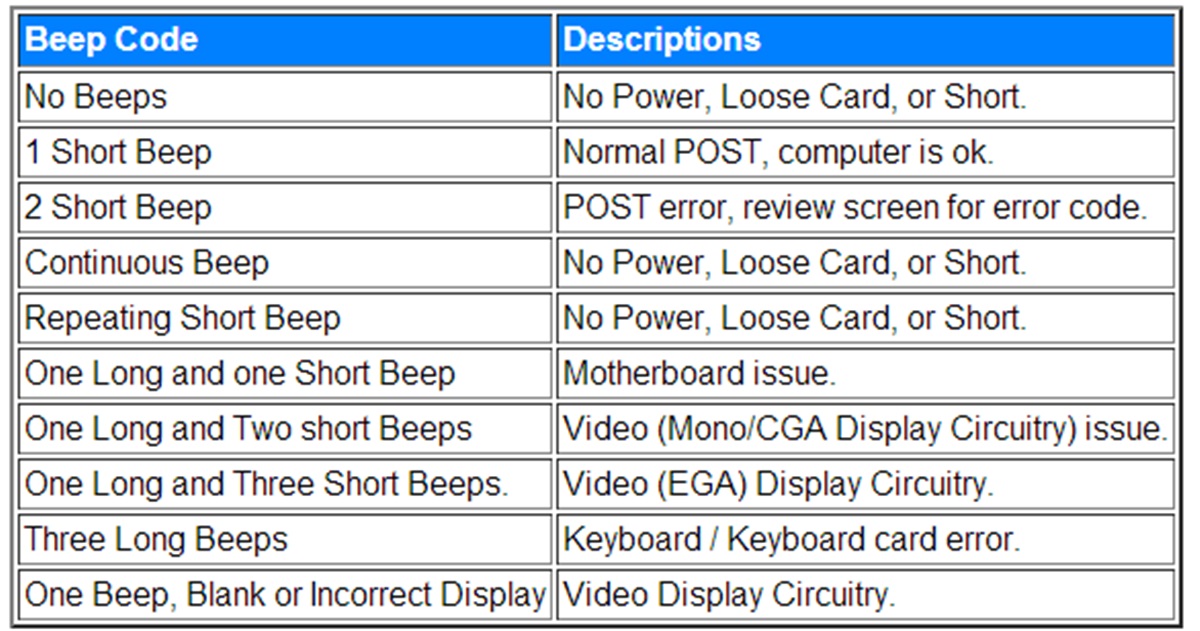
What is a Beep Code?
A beep code is a series of audible signals that a computer system emits during the boot process. It is a diagnostic tool used by the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) to indicate any hardware issues or errors that may be occurring. These beeping sounds serve as a way for the computer to communicate with the user and provide information about the nature of the problem.
Beep codes have been around for decades and are an integral part of the startup process for many computers. They help technicians and users identify potential hardware failures early on, allowing for timely troubleshooting and necessary repairs.
Each type of beep code has a different meaning and corresponds to a specific hardware issue. The length, frequency, and pattern of the beeps can vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the computer system.
Beep codes play a vital role in diagnosing hardware problems, especially when a computer fails to boot or displays error messages. By decoding these beeping sounds, users and technicians can identify the specific component or subsystem that is causing the issue.
Beep codes are commonly used in desktop computers, servers, and laptops. They provide a quick and efficient way to pinpoint hardware failures, even before the operating system has loaded.
Understanding beep codes is crucial for anyone involved in computer troubleshooting, maintenance, or repair. It is an essential skill for technicians and enthusiasts looking to diagnose and fix hardware-related issues.
Purpose of Beep Codes
The primary purpose of beep codes is to communicate hardware errors or issues to the user or technician during the boot process. These audible signals serve as a diagnostic tool that can help identify and troubleshoot problems with the computer’s hardware components.
Beep codes are programmed into the computer’s BIOS and are triggered when the system encounters a hardware error during the startup sequence. The specific pattern and duration of the beeps can provide valuable information about the nature of the problem.
One of the main advantages of beep codes is their ability to notify users about hardware issues even before the operating system has loaded. This early warning system allows for quick identification of potential failures and prompt action to resolve them.
Beep codes can indicate various hardware problems, including issues with the CPU, memory, graphics card, hard drive, or other peripheral devices. By interpreting the beeping sounds, technicians can narrow down the specific component that may be causing the problem, saving time and effort in the troubleshooting process.
Furthermore, beep codes help in distinguishing between different types of errors. They can indicate critical errors that prevent the system from booting, as well as non-critical errors that may still allow the system to start up but with limited functionality.
Another purpose of beep codes is to assist in diagnosing hardware failures during the POST (Power-On Self-Test) process. This self-testing mechanism checks the functionality of various hardware components, and any issues detected are indicated through the use of these audio signals.
Overall, the purpose of beep codes is to provide a simple and efficient way of alerting users and technicians to potential hardware problems. They serve as an invaluable tool in diagnosing and troubleshooting computer systems, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly for optimal performance and system reliability.
How Beep Codes Work
Beep codes are generated by the computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) during the boot process. The BIOS is responsible for initializing the hardware components and preparing the system for the operating system to take over.
When the computer starts up, the BIOS performs a series of tests and checks on the hardware to ensure everything is functioning properly. These tests are known as the Power-On Self-Test (POST). If the BIOS detects any errors during the POST, it triggers the corresponding beep code to indicate the nature of the problem.
The beep codes are generated by the computer’s speaker or by the audio hardware on the motherboard. They consist of a series of beeping sounds with specific patterns and durations. The number and sequence of beeps vary depending on the type of error and the manufacturer of the computer or motherboard.
Each beep code has its own meaning, which can range from indicating a minor issue to a critical failure. The length of each beep, the pauses between beeps, and the overall pattern of the codes are used to convey specific information about the hardware problem.
For example, a single short beep may indicate a successful POST with no errors, while a continuous beep or a series of long beeps may indicate a critical hardware failure, such as a faulty RAM module or a disconnected graphics card.
Some systems may also use a combination of beeps to indicate different types of errors. For instance, two short beeps followed by one long beep may signal a video card error, while three short beeps followed by four long beeps may indicate a memory error.
To interpret beep codes correctly, users and technicians need to refer to the computer’s or motherboard’s documentation. The documentation usually includes information about the specific beep codes used by that particular system, along with their meanings and possible troubleshooting steps.
Modern systems sometimes offer visual indicators, such as LEDs, in addition to beep codes, making it easier to identify the hardware issue without relying solely on the audio signals.
Understanding how beep codes work allows users and technicians to diagnose hardware problems early on and take the necessary steps to resolve them. It is an essential skill for troubleshooting and maintaining computer systems.
Different Types of Beep Codes
Beep codes can vary in their patterns and durations, depending on the manufacturer and model of the computer or motherboard. Here are some of the different types of beep codes commonly encountered:
- Single Beep: A single beep typically indicates a successful POST with no hardware errors. It is considered a normal indication of a healthy system.
- Continuous Beep: A continuous beep that persists without any breaks could signal a critical hardware failure. This could be due to issues such as a faulty power supply or a disconnected component.
- Repeating Short Beeps: Repeating short beeps often indicate a problem with the power supply or other power-related issues. It could suggest a faulty power connection or a malfunctioning power supply unit.
- Repeating Long Beeps: Repeating long beeps are typically associated with memory-related failures. They might indicate a problem with the RAM modules, such as a loose connection or faulty RAM sticks.
- Multiple Short Beeps: Multiple short beeps are commonly associated with graphics card or display-related issues. It could indicate problems like a loose video card or incompatible display settings.
- High-Pitched Beeps: High-pitched beeps may suggest overheating issues. It could be a sign of a faulty cooling system or insufficient airflow inside the computer case.
- Low-Pitched Beeps: Low-pitched beeps are usually associated with CPU-related problems. It could indicate issues like a malfunctioning processor or problems with the motherboard’s CPU socket.
It is important to note that the exact meaning of these beep codes may vary between different computer manufacturers and models. Therefore, it is crucial to consult the motherboard’s or computer’s documentation to accurately interpret the beep codes specific to the system in question.
Being familiar with the various types of beep codes can help users and technicians identify and troubleshoot hardware issues effectively. By understanding the meaning behind the beeping patterns, they can narrow down the potential problem areas and take appropriate action to resolve the issue.
Common Beep Codes and their Meanings
While beep codes can vary depending on the computer or motherboard manufacturer, there are some common beep codes and their general meanings that can help in diagnosing hardware issues. Here are a few examples:
- 1 Beep: This beep is often an indication of a successful POST. It typically means that the system has passed the initial hardware tests and is ready to boot.
- Continuous Long Beeps: Continuous long beeps usually indicate a RAM (Random Access Memory) error. This can be caused by faulty RAM modules or a problem with the memory slots. Troubleshooting steps may involve reseating or replacing the memory modules.
- Continuous Short Beeps: Continuous short beeps are often associated with power-related issues. This may point to problems such as a faulty power supply or a loose power connector. Verifying the power connections and checking the power supply unit can help resolve the issue.
- 3 Long Beeps: Three long beeps typically indicate a problem with the graphics card. This could mean a loose connection, an incompatible card, or a malfunctioning GPU (Graphics Processing Unit). Verifying the connection and compatibility of the graphics card may be necessary.
- 1 Long, 2 Short Beeps: This beep pattern often points to a video card issue. It could be due to problems like a faulty card or incompatible video settings. Verifying the video card connection, checking for compatibility, or updating the driver might be required.
It is important to note that these interpretations are general guidelines and may not apply to all systems. Consulting the motherboard or computer documentation is crucial for accurate beep code interpretation specific to the system in question. Additionally, beep codes can sometimes vary even within the same manufacturer’s product line.
By understanding common beep codes and their meanings, users and technicians can gain valuable insights into the potential hardware issues their systems may be experiencing. This knowledge can aid in troubleshooting and resolving problems efficiently.
Troubleshooting Beep Codes
When encountering beep codes during the boot process, it is essential to troubleshoot and identify the underlying hardware issue. Here are some steps to help troubleshoot beep codes:
- Refer to the Documentation: Consult the motherboard’s or computer’s documentation to understand the specific beep codes used by your system. The documentation will provide information about the meanings and troubleshooting steps associated with each beep code.
- Check Hardware Connections: Ensure that all hardware components, including RAM modules, graphics card, and power connectors, are properly seated and connected. Loose connections can cause beep code errors.
- Reseat or Replace RAM: If the beep codes indicate a RAM error, try reseating the memory modules by removing them and reinstalling them firmly. If the problem persists, try testing with a different set of RAM modules or individual modules to isolate the faulty component.
- Verify Graphics Card: If the beep codes suggest a graphics card issue, double-check the card’s connection to ensure it is securely inserted into the PCI-E slot. Additionally, ensure compatibility with the motherboard and update drivers if necessary.
- Check Power Supply: Power-related issues can cause beep codes. Verify that the power supply is functioning correctly and all connections, including the main power connector to the motherboard, are secure.
- Temperature and Cooling: Overheating can trigger beep codes. Ensure that the computer’s cooling system is working properly and that the vents and fans are clean and free from dust build-up. Consider monitoring the temperatures using software utilities.
- Consult Manufacturer or Technical Support: If troubleshooting on your own does not resolve the issue, reach out to the manufacturer’s technical support for further assistance. They can provide specific guidance based on your system’s beep codes and help diagnose the problem accurately.
Remember that beep codes can vary, so it is crucial to review the specific beep code information for your system. Following these troubleshooting steps can help identify and resolve hardware-related issues indicated by the beep codes, leading to a successful boot and system functionality.
Interpreting Beep Codes on Different BIOS Manufacturers
Beep codes can vary between different BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) manufacturers. It is crucial to understand the beep code patterns specific to your system’s BIOS to accurately interpret the error messages. Here are some examples of how beep codes can differ based on different BIOS manufacturers:
- AMI (American Megatrends, Inc.): AMI BIOS uses a series of beeps to indicate various hardware errors. For example, a single beep typically indicates a successful POST, while a continuous long beep suggests a RAM failure. AMI beep codes can have slight variations between different motherboard models.
- Phoenix BIOS: Phoenix BIOS uses a combination of beeps and pauses to convey error messages. For instance, two short beeps followed by a long beep may indicate a video card error. The actual meanings may differ depending on the motherboard’s model and revision.
- IBM BIOS: IBM BIOS typically uses beep codes to indicate specific hardware issues. For example, one beep followed by two beeps may indicate a display adapter error. It is essential to refer to the IBM motherboard documentation to accurately interpret the beep codes.
Other BIOS manufacturers, such as Award BIOS, use their own unique beep codes as well. Each manufacturer may have its own specific meanings and patterns associated with the beep codes they utilize.
To accurately interpret beep codes, consult the motherboard or computer documentation. It will provide a comprehensive list of the specific beep codes for your system’s BIOS manufacturer, along with their meanings and possible troubleshooting steps. This ensures you can identify the hardware-related issues correctly and take appropriate action.
In some cases, the motherboard manufacturer may provide BIOS updates that address specific beep code issues. Keeping the motherboard’s BIOS up to date with the latest firmware can also help in resolving certain problems related to beep codes.
Remember that beep codes are a system-specific feature, and their interpretation can vary. Understanding the specific beep code information for your BIOS manufacturer will enable you to effectively troubleshoot and resolve hardware-related issues indicated by the beep codes on your system.
Importance of Beep Codes in Diagnosing Hardware Issues
Beep codes play a crucial role in diagnosing hardware issues in computer systems. They serve as an invaluable tool for technicians and users in identifying and troubleshooting hardware failures. Here are some reasons highlighting the importance of beep codes:
- Early Error Detection: Beep codes provide early detection of hardware errors. By sounding the alarm during the boot process, they alert users and technicians to potential issues even before the operating system loads. This enables timely intervention and reduces the risk of further damage to the system.
- Quick Troubleshooting: Beep codes provide a quick and efficient way to identify potential hardware failures. By decoding the specific patterns and durations of the beeps, technicians can pinpoint the specific component or subsystem that is causing the issue. This allows for targeted troubleshooting and reduces the time required to identify and resolve the problem.
- Faster Repairs: With the help of beep codes, technicians can quickly diagnose the underlying hardware problem. This helps in determining the necessary repairs or replacements, ensuring that the faulty component is addressed promptly. Minimizing the downtime reduces the impact on productivity and ensures a more efficient repair process.
- Preventive Maintenance: Beep codes also serve as a preventive maintenance tool. Regularly checking the system’s startup beep codes can help identify potential hardware issues before they escalate. This allows for proactive maintenance and replacement of faulty components, reducing the risk of sudden failures and unexpected downtime.
- Cost-Effective Repairs: By accurately identifying the hardware issue through beep codes, technicians can avoid unnecessary repairs or component replacements. This targeted troubleshooting approach saves both time and money by ensuring that only the affected component is addressed, rather than replacing multiple parts or performing extensive diagnostic procedures.
- User-Friendly Troubleshooting: Beep codes provide a user-friendly method of troubleshooting for individuals with little technical expertise. By referring to the system’s documentation or online resources, users can understand the meaning of the beep codes and take initial steps in resolving the hardware issue without extensive technical knowledge.
Overall, beep codes are an essential diagnostic tool for identifying and troubleshooting hardware issues in computer systems. Their importance lies in their ability to provide early error detection, quick troubleshooting, and cost-effective repairs. By understanding and effectively utilizing beep codes, technicians can ensure timely resolution of hardware problems, minimizing downtime and optimizing system performance.
Understanding Beep Codes in Different Computer Systems
Beep codes are not universal and can vary between different computer systems. Understanding and interpreting beep codes correctly is important to diagnose and resolve hardware issues effectively. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to understanding beep codes in different computer systems:
- Manufacturer-Specific Beep Codes: Different computer manufacturers may use their own beep code systems. Each manufacturer often has a specific set of beep codes with different meanings. For example, Dell, HP, and Lenovo may have different beep code patterns for the same hardware failure. It is crucial to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or website for accurate information about the beep codes used in their systems.
- Motherboard-Specific Beep Codes: Beep codes can also vary based on the specific motherboard model and revision. Even within the same computer brand, different motherboard models may have their own beep code systems. The motherboard’s documentation or website is the most reliable source to understand the beep codes specific to that particular model.
- BIOS Manufacturer: The BIOS manufacturer also plays a role in determining the beep code system. Each BIOS manufacturer, such as AMI (American Megatrends, Inc.), Phoenix, or IBM, may have its own set of beep codes. The documentation provided by the BIOS manufacturer specifies the meanings of the beep codes used in their systems.
- Changes Over Time: Beep codes can change over time as computer systems and hardware evolve. As new components and technologies are introduced, the beep code systems may be adjusted or updated. It is essential to ensure that the documentation or resources being referred to are up to date with the latest beep code information for the specific computer system.
- Online Resources: Various online resources are available to help understand and interpret beep codes for different computer systems. Manufacturer websites, dedicated forums, and technical support websites often provide beep code information specific to their systems. These resources can be valuable references when trying to decipher the meaning of beep codes.
Given the variations in beep codes across different computer systems, it is crucial to rely on accurate and up-to-date information. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation, motherboard documentation, or BIOS manufacturer’s documentation is the best approach to ensure correct interpretation of beep codes specific to the computer system in question.
Understanding beep codes in different computer systems allows users and technicians to effectively diagnose and troubleshoot hardware problems, leading to timely and accurate resolutions for optimal system performance.
How to Disable Beep Codes
If you find the beep codes during the computer startup process to be disruptive or unnecessary, you may want to disable them. Here are several methods for disabling beep codes:
- BIOS Settings: The most common way to disable beep codes is through the computer’s BIOS settings. During the boot process, you can access the BIOS by pressing a specific key (such as Del, F2, or F10, depending on your system) as indicated on the screen. Once in the BIOS settings, look for an option related to “Power-On Self-Test (POST)” or “Beep Codes.” Disable this option to silence the beep codes. Note that the exact location and terminology may vary depending on the BIOS version and manufacturer.
- Jumpers or DIP Switches: Some motherboards have physical jumpers or DIP switches that control the behavior of the beep codes. Check the motherboard’s documentation to identify the location and function of any relevant jumpers or DIP switches. By changing the position of these switches, you can disable or modify the beep codes.
- Remove the PC Speaker: The PC speaker is responsible for producing the beep codes. If you are comfortable opening your computer case, you can physically disconnect the PC speaker from the motherboard. This will completely silence the beep codes. Be cautious when working inside your computer and ensure that you have proper knowledge or guidance.
- Software Utilities: Some operating systems or BIOS software utilities provide options to disable or modify beep codes. Check the manufacturer’s website for any available utility programs specifically designed for your system. These utilities may allow you to customize the beep code behavior or silence them altogether.
It’s essential to note that while disabling beep codes can eliminate the audible alerts, it also means that you won’t receive valuable diagnostic information in case of hardware failures during the boot process. If you choose to disable the beep codes, make sure you have other means of monitoring hardware issues, such as visual indicators or diagnostic software.
Remember that the methods to disable beep codes can vary depending on the computer’s hardware, BIOS version, and operating system. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation or website for the most accurate and system-specific instructions on how to disable beep codes.
Disabling beep codes can be helpful for those who find them unnecessary or disruptive, but it’s important to weigh the benefits against the potential loss of diagnostic information in case of hardware failures.