Common PC Hotspot Connection Issues
When attempting to connect to a PC hotspot, users may encounter various issues that can disrupt their connectivity. Understanding these common problems is essential for effective troubleshooting and resolution.
Unstable Connection
An unstable connection is a prevalent issue when using a PC hotspot. This can manifest as frequent disconnections or slow, inconsistent speeds. Users may experience difficulties in maintaining a steady connection, hindering their ability to perform tasks seamlessly.
Limited Range
Another common issue involves the limited range of the PC hotspot. Users may find that the signal strength diminishes significantly beyond a certain distance from the hotspot. This limitation can restrict mobility and hinder the convenience of using the hotspot in various locations.
Authentication Errors
Authentication errors often arise when attempting to connect to a PC hotspot. Users may encounter difficulties in entering the correct credentials or may receive error messages indicating authentication failures. This can prevent successful connection to the hotspot and impede the user's ability to access the internet.
Device Compatibility
Compatibility issues between the PC hotspot and the user's device can lead to connection problems. Certain devices may struggle to establish a stable connection with the hotspot, resulting in intermittent or no connectivity at all. Understanding and addressing compatibility issues is crucial for seamless hotspot usage.
Overheating
Overheating of the PC or the hotspot device can also contribute to connectivity issues. Prolonged usage or inadequate ventilation can lead to overheating, causing the hotspot to malfunction or disconnect intermittently. Resolving overheating issues is essential for maintaining a stable connection.
Bandwidth Limitations
Bandwidth limitations can impact the performance of a PC hotspot. Users may experience slow internet speeds or difficulty accessing certain online content due to restricted bandwidth. Understanding and managing bandwidth limitations is essential for optimizing hotspot performance.
Network Congestion
Network congestion can affect the performance of a PC hotspot, particularly in crowded or densely populated areas. Users may encounter slow speeds and connectivity issues during peak usage times, making it challenging to maintain a reliable connection.
Interference
Interference from other electronic devices or physical obstructions can disrupt the signal of a PC hotspot. Users may experience connectivity issues when signal interference hinders the effective transmission of data between the hotspot and their devices.
Understanding these common PC hotspot connection issues is the first step toward effective troubleshooting and resolution. By identifying the specific problem affecting the connection, users can implement targeted solutions to restore seamless connectivity and enhance their overall hotspot experience.
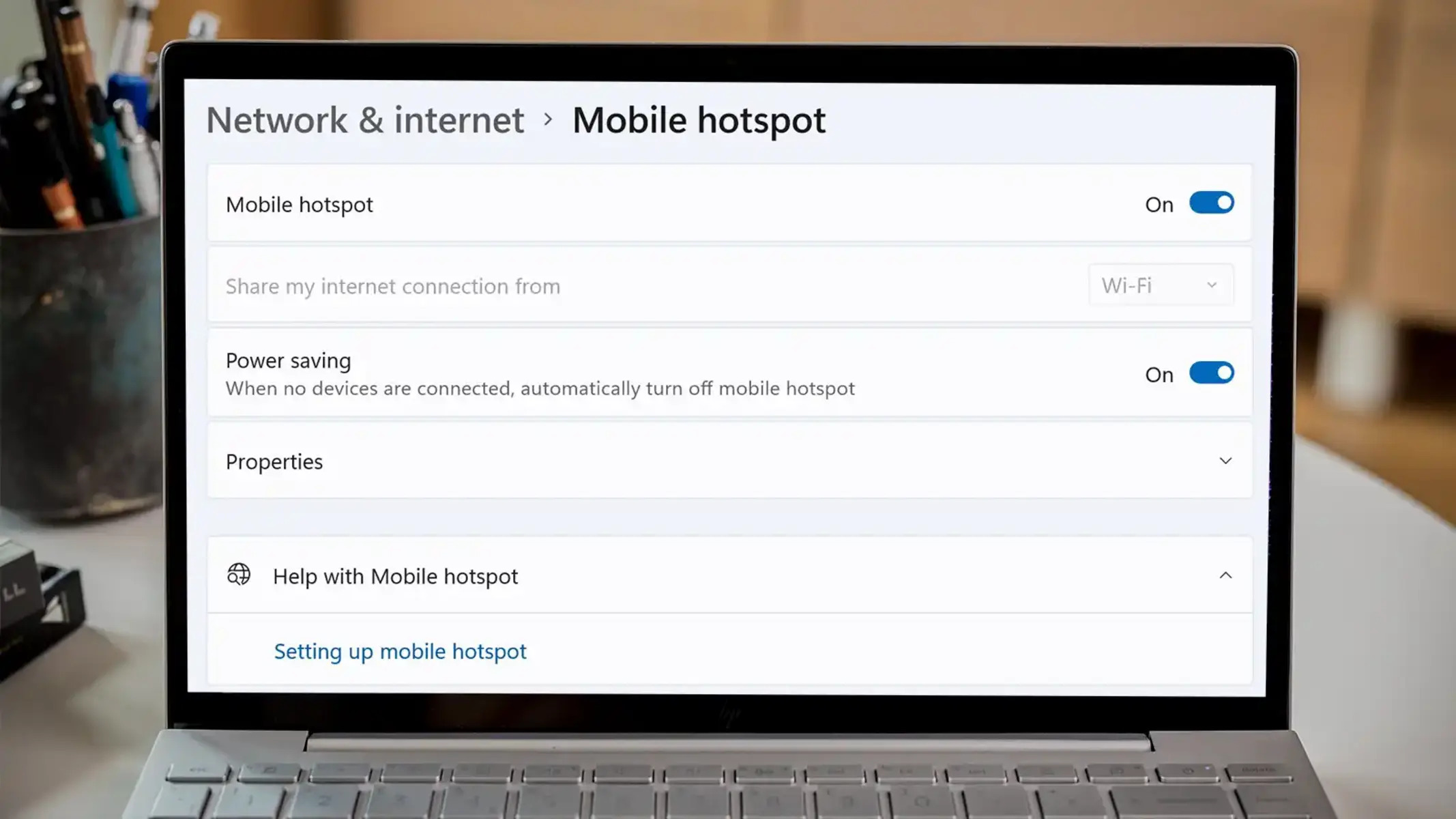
Checking Network Settings
When encountering PC hotspot connection issues, it is crucial to start the troubleshooting process by examining the network settings. By carefully reviewing and adjusting these settings, users can address potential configuration issues that may be impeding their ability to connect to the hotspot.
Verify Hotspot Configuration
Begin by confirming the configuration of the PC hotspot. Ensure that the hotspot is enabled and broadcasting a signal. Users should also check the network name (SSID) and password to ensure that they are correctly entered on the device attempting to connect. Verifying these details can eliminate potential configuration errors that may be causing connectivity issues.
Check Network Mode
Review the network mode settings on the PC hotspot. Depending on the device and network capabilities, users may need to select the appropriate network mode, such as 2.4GHz or 5GHz. Ensuring that the network mode aligns with the device’s compatibility can optimize the connection and minimize potential interference.
Inspect IP Configuration
Examine the IP configuration settings to ensure that the device attempting to connect to the hotspot is assigned a valid IP address. Users can check for IP conflicts or incorrect settings that may hinder successful connectivity. Adjusting the IP configuration as needed can resolve potential conflicts and facilitate a stable connection.
Review Firewall and Security Settings
Inspect the firewall and security settings on both the hotspot device and the connecting device. Firewalls or security protocols may inadvertently block or restrict hotspot connections, leading to connectivity issues. Users should review and adjust these settings to permit the necessary network access without compromising security.
Update Network Drivers
Ensure that the network drivers on the connecting device are up to date. Outdated or incompatible network drivers can impede the device’s ability to establish a connection with the PC hotspot. Updating the network drivers to the latest versions can resolve compatibility issues and enhance connectivity.
Perform Network Diagnostics
Utilize built-in network diagnostic tools to identify and address potential network configuration issues. Running network diagnostics can pinpoint specific problems affecting the connection and provide actionable recommendations for resolving them. This proactive approach can streamline the troubleshooting process and expedite the resolution of network configuration issues.
By meticulously reviewing and adjusting network settings, users can effectively troubleshoot and resolve PC hotspot connection issues. This methodical approach empowers users to identify and address potential configuration errors, ultimately restoring seamless connectivity and optimizing their hotspot experience.
Restarting the Hotspot
When grappling with PC hotspot connection issues, restarting the hotspot device can serve as a simple yet effective troubleshooting step. This process can help address underlying technical glitches or temporary network disruptions that may be impeding the hotspot’s functionality and connectivity.
Power Cycle the Hotspot
Initiate the troubleshooting process by power cycling the hotspot device. This involves turning off the device, unplugging it from the power source, and waiting for a brief period before plugging it back in and powering it on. Power cycling can clear temporary system errors and refresh the device’s network functionality, potentially resolving connectivity issues.
Allow for Cool Down
If the hotspot device has been in use for an extended period, overheating may contribute to connectivity issues. Allowing the device to cool down before restarting it can mitigate potential overheating-related problems. This simple step can help restore the device to optimal operating conditions and improve its overall performance.
Check Signal Strength
Prior to restarting the hotspot, assess the signal strength and quality. Users should position the hotspot in an optimal location to ensure maximum signal coverage. Checking the signal strength can help identify potential signal-related issues that may be affecting connectivity. Adjusting the hotspot’s placement can enhance signal reception and improve connection stability.
Perform a Soft Reset
If the hotspot device allows for a soft reset, users can initiate this process to refresh the device’s network functionality. A soft reset typically involves accessing the device’s settings or control panel to initiate a network reset without disrupting the device’s overall operation. This can effectively address minor network disruptions and restore connectivity.
Update Firmware
Ensure that the hotspot device’s firmware is up to date. Outdated firmware can contribute to connectivity issues and hinder the device’s performance. Updating the firmware to the latest version can introduce bug fixes and optimizations that address underlying connectivity problems.
Monitor Device Status
After restarting the hotspot, monitor the device’s status to ensure that it successfully re-establishes network connectivity. Users should observe for any error messages, indicator lights, or on-screen prompts that may indicate ongoing issues. This proactive monitoring can help identify persistent problems that may require further troubleshooting steps.
Restarting the hotspot serves as a fundamental troubleshooting measure to address PC hotspot connection issues. By power cycling the device, allowing for cool down, and performing necessary resets, users can effectively resolve network disruptions and optimize the functionality of their hotspot, ultimately restoring seamless connectivity.
Updating Network Drivers
Ensuring that network drivers are up to date is crucial for addressing PC hotspot connection issues. Outdated or incompatible network drivers can impede the device’s ability to establish a stable connection with the hotspot. By updating the network drivers, users can resolve compatibility issues and optimize network functionality, ultimately enhancing their hotspot experience.
Identify Network Adapter
Begin by identifying the network adapter installed on the device. Users can access the Device Manager or network settings to locate the network adapter and verify its make and model. This information is essential for identifying the correct drivers for the network adapter.
Download Latest Drivers
Visit the manufacturer’s official website or the device’s support page to download the latest network drivers. Users should ensure that they download the drivers compatible with their specific network adapter and operating system. It is advisable to obtain the drivers directly from the manufacturer to guarantee authenticity and compatibility.
Uninstall Outdated Drivers
Prior to installing the new drivers, it is recommended to uninstall the outdated or incompatible network drivers from the device. Users can access the Device Manager to locate the network adapter, right-click on it, and select the option to uninstall the drivers. This process ensures a clean installation of the updated drivers without potential conflicts.
Install Updated Drivers
Once the outdated drivers are uninstalled, proceed to install the updated network drivers that were previously downloaded. Users can follow the installation prompts and guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure a seamless driver update process. After installation, it is advisable to restart the device to apply the changes effectively.
Verify Driver Functionality
After updating the network drivers, users should verify the functionality of the network adapter. This involves checking for any error messages, ensuring that the adapter is recognized by the device, and testing its connectivity to the PC hotspot. Users can also assess the overall network performance to confirm that the updated drivers have optimized the connection.
Automate Driver Updates
To streamline the process of keeping network drivers up to date, users can consider utilizing driver update software or enabling automatic driver updates through the device’s settings. Automating driver updates can ensure that the network drivers remain current, thereby minimizing the risk of connectivity issues related to outdated drivers.
Updating network drivers is a proactive measure to address PC hotspot connection issues. By obtaining and installing the latest drivers, users can resolve compatibility issues, optimize network functionality, and establish a stable connection with the hotspot, ultimately enhancing their overall connectivity experience.
Checking for Interference
Interference from external sources can significantly impact the performance of a PC hotspot, leading to connectivity issues and signal disruptions. By identifying and addressing potential sources of interference, users can optimize their hotspot’s signal strength and stability, ultimately enhancing their overall connectivity experience.
Assess Nearby Devices
Begin by assessing the presence of nearby electronic devices that could potentially interfere with the PC hotspot’s signal. Common culprits include wireless routers, cordless phones, microwave ovens, and Bluetooth devices. Users should identify the proximity of these devices to the hotspot and consider relocating them to minimize interference.
Observe Physical Obstructions
Physical obstructions such as walls, furniture, and large appliances can impede the transmission of the hotspot’s signal. Users should evaluate the positioning of the hotspot and the presence of any physical barriers that may obstruct signal propagation. Adjusting the location of the hotspot can mitigate the impact of physical obstructions on connectivity.
Utilize Signal Analyzing Tools
Utilize signal analyzing tools or mobile apps that can detect and visualize wireless signals in the vicinity. These tools can provide insights into signal strength, channel congestion, and potential sources of interference. Users can leverage this information to make informed decisions about optimizing the hotspot’s signal and minimizing interference.
Optimize Channel Selection
If the PC hotspot allows for channel selection, users can optimize the wireless channel to mitigate interference from neighboring networks. By selecting a less congested channel, users can minimize the impact of overlapping signals and enhance the hotspot’s signal quality and reliability. This can be particularly beneficial in densely populated areas with numerous wireless networks.
Upgrade to 5GHz Band
If the hotspot and connected devices support 5GHz connectivity, consider utilizing this band to minimize interference from devices operating on the 2.4GHz band. The 5GHz band offers a wider range of non-overlapping channels, reducing the likelihood of interference and enhancing the overall signal quality and stability.
Implement Signal Boosting Solutions
Consider implementing signal boosting solutions such as Wi-Fi repeaters, range extenders, or mesh network systems to enhance the hotspot’s signal coverage and minimize the impact of interference. These solutions can effectively amplify the signal strength and extend the coverage area, mitigating the effects of interference and improving connectivity.
By proactively checking for interference and implementing targeted solutions, users can optimize the performance of their PC hotspot and mitigate the impact of external factors on connectivity. Addressing potential sources of interference can significantly enhance the hotspot’s signal strength, stability, and overall reliability, ultimately improving the user’s connectivity experience.
Resetting Network Settings
When confronted with persistent PC hotspot connection issues, resetting the network settings can serve as an effective troubleshooting step to address underlying configuration errors and restore connectivity. By resetting network settings, users can eliminate potential inconsistencies and restore the network to a stable state, ultimately optimizing their hotspot experience.
Perform a Network Reset
Initiate the troubleshooting process by performing a network reset on the device experiencing connectivity issues. This process typically involves accessing the network settings or control panel to initiate a full network reset. Users should be aware that this action will reset all network configurations, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Ethernet settings.
Clear Network Cache
Clearing the network cache can help eliminate temporary data and configurations that may be contributing to connectivity issues. Users can access the device’s network settings to locate the option for clearing the network cache. This action can effectively remove outdated or corrupted network data, potentially resolving connectivity problems.
Reset Wi-Fi Profiles
If the hotspot connection issues persist, consider resetting the Wi-Fi profiles on the connecting device. This involves deleting existing Wi-Fi profiles and reconnecting to the hotspot as a new network. Users should ensure that the correct network credentials are entered during the reconnection process to establish a fresh network profile.
Reconfigure Network Settings
After performing a network reset, users should reconfigure the network settings to align with the requirements of the PC hotspot. This includes entering the correct network name (SSID), password, and any additional network-specific configurations. Reconfiguring the network settings ensures that the device is properly set up to connect to the hotspot.
Restart the Device
Following the network reset and reconfiguration, it is advisable to restart the device to apply the changes effectively. Restarting the device can help finalize the network settings and ensure that the device establishes a fresh connection to the PC hotspot. This step can facilitate a seamless transition to the updated network configurations.
Perform Network Diagnostics
After resetting the network settings, users can perform network diagnostics to assess the impact of the reset on connectivity. Network diagnostic tools can identify any remaining issues and provide insights into the network’s performance and stability. This step can help verify the effectiveness of the network reset in resolving connectivity problems.
Resetting network settings is a valuable troubleshooting method for addressing PC hotspot connection issues. By eliminating configuration inconsistencies and refreshing network data, users can restore stable connectivity and optimize their overall hotspot experience, ultimately ensuring seamless and reliable network access.
Verifying Hotspot Compatibility
Ensuring compatibility between the PC hotspot and the connecting devices is essential for establishing a stable and reliable connection. Incompatibility issues can lead to connectivity problems and hinder the seamless operation of the hotspot. By verifying compatibility and addressing any discrepancies, users can optimize their hotspot experience and mitigate potential connection issues.
Check Device Specifications
Begin by reviewing the specifications of the devices attempting to connect to the PC hotspot. This includes assessing the supported wireless standards, such as 802.11n, 802.11ac, or 802.11ax, as well as the compatibility with specific frequency bands, such as 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Understanding the device specifications is crucial for identifying potential compatibility issues.
Evaluate Hotspot Capabilities
Assess the capabilities and specifications of the PC hotspot, including its supported wireless standards, frequency bands, and network modes. Users should verify that the hotspot aligns with the connectivity requirements of the devices seeking to connect. This evaluation can reveal any disparities that may impact compatibility.
Verify Security Protocols
Ensure that the security protocols and encryption methods employed by the PC hotspot are compatible with the connecting devices. Mismatched security protocols can impede the establishment of a secure connection and lead to authentication errors or connectivity issues. Aligning the security settings can enhance compatibility and facilitate seamless connectivity.
Confirm Wireless Standards
Verify that the wireless standards supported by the PC hotspot are compatible with the connecting devices. Incompatibility in wireless standards can result in limited connectivity or suboptimal performance. Users should ensure that the hotspot and devices support mutually compatible wireless standards to facilitate a stable connection.
Assess Signal Strength and Range
Evaluate the signal strength and range of the PC hotspot to ensure that it meets the connectivity needs of the devices. Inadequate signal strength or limited coverage can impede the connection and result in intermittent connectivity. Optimizing the hotspot’s signal strength and range can enhance compatibility and improve the overall connectivity experience.
Update Hotspot Firmware
If the PC hotspot allows for firmware updates, ensure that the firmware is up to date. Updated firmware can introduce improvements in compatibility, performance, and feature support. Keeping the hotspot’s firmware current can address compatibility issues and optimize its functionality for seamless connectivity.
By meticulously verifying the compatibility between the PC hotspot and the connecting devices, users can proactively address potential compatibility issues and optimize the connectivity experience. Aligning device specifications, evaluating hotspot capabilities, and ensuring compatibility with security protocols and wireless standards are essential steps in mitigating connectivity problems and enhancing the overall performance of the hotspot.
Contacting ISP or Hotspot Provider
When all other troubleshooting methods have been exhausted and PC hotspot connection issues persist, reaching out to the Internet Service Provider (ISP) or the hotspot provider can provide valuable support and assistance. By engaging with the provider, users can access expert guidance, address underlying network issues, and explore potential solutions to restore seamless connectivity.
Verify Service Status
Prior to contacting the ISP or hotspot provider, users should verify the service status to ensure that there are no widespread outages or service disruptions affecting connectivity. Checking the provider’s official website or contacting their customer support can provide insights into any known service issues that may be impacting the hotspot’s performance.
Report Connectivity Issues
Communicate the specific connectivity issues experienced with the PC hotspot to the ISP or hotspot provider’s customer support team. Providing detailed information about the nature of the problems, including error messages, connection failures, and the duration of the issues, can assist the provider in diagnosing and addressing the root cause of the connectivity problems.
Seek Technical Assistance
Request technical assistance from the ISP or hotspot provider to troubleshoot the connectivity issues. The provider’s support team can guide users through additional troubleshooting steps, remotely diagnose network configurations, and perform tests to identify and resolve any underlying network issues contributing to the connectivity problems.
Discuss Equipment Compatibility
Engage in a discussion with the ISP or hotspot provider regarding the compatibility of the connected devices with the provided hotspot equipment. The provider can offer insights into potential compatibility issues, recommend suitable configurations, or provide alternative hotspot equipment that better aligns with the connectivity needs of the devices.
Explore Network Optimization
Request guidance on optimizing the network settings and configurations to enhance the performance of the PC hotspot. The ISP or hotspot provider can offer recommendations for adjusting network parameters, optimizing signal strength, and minimizing interference to improve the overall connectivity experience.
Request On-Site Support
If the connectivity issues persist despite troubleshooting efforts, users can request on-site support from the ISP or hotspot provider. On-site technicians can assess the network environment, inspect the hotspot equipment, and perform diagnostic tests to identify and address any physical or technical factors contributing to the connectivity problems.
By contacting the ISP or hotspot provider, users can leverage expert support and resources to address persistent PC hotspot connection issues. Engaging with the provider’s support team, seeking technical assistance, and exploring network optimization options can lead to the effective resolution of connectivity problems, ultimately restoring seamless and reliable network access.