Advantages of Rooting an Android Phone
Rooting an Android phone gives users access to a whole new level of control and customization options. While rooting may not be for everyone, it offers several advantages for those who want to take their Android experience to the next level.
One of the main benefits of rooting is the ability to remove pre-installed apps, also known as bloatware. These apps often take up valuable storage space and can’t be uninstalled without rooting. With root access, users can take complete control of their device and free up storage by removing unnecessary apps, thereby improving performance.
Another advantage of rooting is the ability to overclock or underclock the device’s CPU. Overclocking allows users to increase the processor speed, resulting in faster performance. Conversely, underclocking can conserve battery life by reducing the processor’s speed when high performance is not required.
Rooting also provides users with increased backup options. While most Android phones offer basic backup features, rooted devices can utilize advanced backup apps that allow for complete system backups, including all data, apps, and settings. This can be particularly useful when switching to a new device or recovering from a software issue.
Access to advanced apps and features is another advantage of rooting. Certain apps require root access to unlock their full potential. These apps can perform tasks such as better ad-blocking, advanced file management, customizing system fonts, and even enabling features from the latest Android versions on older devices.
However, it is important to note that rooting an Android phone also comes with some drawbacks. It can potentially brick your device, rendering it unusable. Additionally, rooting voids the warranty provided by the manufacturer, which means that any future repairs or replacements may incur additional costs.
Another concern with rooting is security risks and vulnerabilities. By gaining root access, the device becomes more susceptible to malware and other security threats. Users must exercise caution when installing apps from unknown sources and regularly update their device’s security software.
Compatibility issues may also arise with certain apps that rely on a non-rooted environment. While most apps work fine on rooted devices, some may not function properly or refuse to run altogether. This can limit the usability of certain apps, particularly those that rely on strict security measures.
Rooting an Android phone requires a certain level of technical knowledge and expertise. The process can be complicated, and mistakes can lead to data loss or even permanent damage to the device. It is crucial to follow reliable guides and understand the risks involved before attempting to root a phone.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that rooting may lead to a potential loss of data. As the rooting process modifies the system files, there is a chance that data can be erased accidentally. It is essential to back up all important data before proceeding with rooting.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that rooting an Android phone may breach the terms and conditions set by the device manufacturer or carrier. This can result in legal issues and may void any warranty or support services offered by the company. Users should carefully consider the implications and consequences before deciding to root their Android phone.
Disadvantages of Rooting an Android Phone
While rooting an Android phone offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider the potential drawbacks before taking the plunge. Here are some of the disadvantages associated with rooting:
1. Voiding Warranty: Rooting your Android phone typically voids the manufacturer’s warranty. If your device encounters any hardware or software issues, the manufacturer may refuse to provide support or charge additional fees for repairs.
2. Security Risks: Rooting exposes your device to increased security risks. By gaining root access, malicious apps or malware may have greater control over sensitive information, potentially compromising your personal data and privacy.
3. Compatibility Issues: Rooting can lead to compatibility issues with certain apps that rely on a non-rooted environment. Some apps may not function correctly or refuse to run altogether on rooted devices, limiting their usefulness.
4. Complexity and Technical Knowledge: Rooting an Android phone can be a complex process that requires technical knowledge and expertise. Mistakes during the rooting process can result in data loss or even permanent damage to your device.
5. Potential Loss of Data: As rooting involves modifying system files, there is a risk of accidental data loss. It is crucial to back up all important data before attempting to root your device.
6. Brace for Bricking: Rooting your phone incorrectly or using incompatible firmware may result in “bricking” your device, rendering it inoperable and difficult to recover.
7. Legal Issues: Rooting an Android phone may breach the terms and conditions set by the device manufacturer or carrier. This could lead to legal issues and potential violations of software licensing agreements.
8. No Over-the-Air Updates: Rooting typically disables over-the-air (OTA) updates provided by the manufacturer. To update your device’s software, you will need to manually install custom ROMs or firmware updates, which can be more time-consuming.
9. Compromised System Stability: With root access, there is a greater risk of modifying critical system files, which may destabilize the operating system. This could lead to software glitches, crashes, or inconsistent performance.
10. Difficulty in Unrooting: Unrooting an Android phone can be challenging and may not always be reversible. It may require technical knowledge and expertise, and there is a risk of losing data during the unrooting process.
It is important to carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of rooting before deciding whether it is the right choice for you. Consider your technical abilities, willingness to take risks, and the impact it may have on the functionality and security of your Android phone.
Increased Control and Customization Options
Rooting an Android phone provides users with an unparalleled level of control and customization options, offering a personalized experience that goes beyond the default settings. Here are some of the ways rooting enhances control and customization:
1. Custom ROMs: By rooting your Android phone, you gain access to custom ROMs (Read-Only Memory) which are modified versions of the Android operating system. These ROMs allow for a range of customization options, including unique themes, fonts, icons, and even different UI layouts. Custom ROMs can significantly alter the look and feel of your device, offering a fresh and personalized interface.
2. Deep System Modifications: Root access allows users to make deep system modifications, such as tweaking the CPU clock speed, adjusting the voltage, and modifying system-level settings that are typically inaccessible on non-rooted devices. These modifications can greatly enhance performance, battery life, and overall user experience.
3. Ad-Blocking: Rooting enables the use of ad-blocking apps that can effectively eliminate intrusive advertisements from various apps and websites. This not only enhances the user experience by removing distractions but can also improve device performance and reduce data usage.
4. Custom Kernel: By replacing the device’s stock kernel, which controls the interactions between the hardware and software, users can optimize their Android phone’s performance and battery efficiency according to their preferences. Custom kernels offer a wide range of options, including CPU and GPU overclocking, undervolting, and fine-tuning power management features.
5. Advanced Backup and Restore: Rooting enables users to perform full device backups, including all installed apps, settings, and data. These comprehensive backups can be easily restored in case of a device malfunction or when switching to a new phone. With root access, you can use powerful backup apps that offer more refined control over what gets backed up and restored.
6. System-Level App Management: Rooting allows users to uninstall or freeze pre-installed apps, also known as bloatware. These apps often consume valuable storage space and system resources. By removing or disabling them, users can free up storage, improve device performance, and have more control over what apps are installed on their Android phone.
7. Customization Through Xposed Framework: Rooting enables compatibility with the Xposed Framework, a powerful tool that allows users to make extensive modifications to the Android system without flashing custom ROMs. Xposed modules offer a vast array of customization options, ranging from UI tweaks to adding new features, giving users the ability to tailor their Android experience to their liking.
It is important to note that while increased control and customization options are a significant advantage of rooting, users should exercise caution and ensure they understand the potential risks involved. Modifying critical system files without proper knowledge or care can lead to instability or even brick the device. Always follow reliable guides and consult experienced users for advice when performing system modifications.
Ability to Remove Pre-installed Apps
One of the advantages of rooting an Android phone is the ability to remove pre-installed apps, also known as bloatware. Bloatware refers to the apps that come pre-loaded on your device by the manufacturer or carrier. While some of these apps can be useful, many are unnecessary and take up valuable storage space. Rooting offers users the freedom to take full control of their device and remove these unwanted apps. Here are the benefits of being able to remove pre-installed apps through rooting:
1. Free Up Storage Space: Pre-installed apps can consume a significant amount of space on your Android phone’s internal storage, restricting the available capacity for your own apps, files, and media. By removing bloatware, you can free up valuable storage space, allowing for better device performance and more room for your own content.
2. Improve Performance: Bloatware often runs in the background, consuming system resources and RAM. This can lead to slower device performance and decreased responsiveness. By removing pre-installed apps, you can reduce the burden on your device’s system, resulting in improved overall performance and smoother multitasking.
3. Increase Battery Life: Some pre-installed apps run processes and notifications in the background, even if you rarely use them. These background activities can have a negative impact on your battery life, causing unnecessary drain. By uninstalling or disabling these apps, you can extend your device’s battery life and enjoy longer usage times between charges.
4. Reduce Clutter: Bloatware can clutter your app drawer, making it difficult to find and access the apps you actually use. Removing pre-installed apps declutters your app drawer, making it easier to navigate and find the apps you need without having to sift through unnecessary ones.
5. Personalize Your Device: Removing bloatware allows you to personalize your device by only keeping the apps that are relevant and useful to you. This customization can help streamline your Android experience and create a device that is tailored to your preferences and needs.
6. Minimize Software Updates: Some pre-installed apps receive occasional updates that are bundled with the system updates provided by the manufacturer. By removing unnecessary apps, you can reduce the number of software updates your device needs, saving data and time spent on updating these apps that you don’t use.
7. Enhanced Security: Pre-installed apps may have vulnerabilities that can be exploited by hackers or malicious actors. By removing these apps, you can reduce the potential attack surface of your device and mitigate risks associated with vulnerable apps.
It is important to note that while removing pre-installed apps through rooting offers benefits, it can also have potential drawbacks. Care should be taken to ensure that the right apps are being removed, as removing critical system apps can lead to instability or limited functionality. Additionally, removing certain pre-installed apps may affect the functionality of other apps or features that rely on them. It is recommended to research and exercise caution when removing apps and create a backup before making any changes to the system.
Overclocking and Underclocking
Rooting an Android phone offers the ability to overclock or underclock the device’s CPU (Central Processing Unit). Overclocking means increasing the clock speed of the CPU to make it run at a faster rate, while underclocking refers to reducing the clock speed to make the CPU run at a slower rate. Both of these processes can have advantages and disadvantages for users, giving them more control over their device’s performance. Here are the benefits and considerations of overclocking and underclocking:
1. Overclocking: By overclocking the CPU, users can achieve faster processing speeds, resulting in snappier app launches, smoother multitasking, and quicker overall device performance. This can be particularly useful for running computationally intensive tasks, such as gaming or multimedia editing, which require additional processing power. Overclocking can provide a noticeable performance boost, especially on older or lower-end devices.
Advantages of Overclocking:
- Faster Performance: Overclocking the CPU can result in improved device performance, allowing apps to run more smoothly and reducing lag.
- Enhanced Gaming Experience: Overclocking can provide a performance boost for gaming, enabling higher frame rates and smoother gameplay.
- Reduced Loading Times: Faster CPU processing speeds can decrease app loading times and improve overall responsiveness.
However, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks of overclocking:
- Increased Power Consumption: Overclocking the CPU usually requires more power, which can lead to increased battery drain, shorter battery life, and potentially higher device temperatures.
- Reduced Stability: Overclocking can make the device less stable, potentially resulting in crashes, app freezes, or system reboots. This is especially true if the device is pushed beyond its capabilities.
- Voided Warranty: Overclocking your device typically voids the manufacturer’s warranty, meaning any hardware or software issues that may arise won’t be covered by them.
2. Underclocking: On the other hand, underclocking the CPU involves reducing its clock speed, which can have its own set of benefits. By underclocking, users can conserve battery life, reduce heat generation, and potentially increase the overall lifespan of the device. Underclocking is particularly useful for users who prioritize battery longevity and device temperature management over high-performance computing tasks.
Advantages of Underclocking:
- Battery Conservation: Underclocking reduces CPU power consumption, resulting in extended battery life, especially during light usage or standby periods.
- Cooler Device: By reducing the clock speed, underclocking can help reduce the generation of heat, leading to a cooler device, improved thermal management, and potentially longer-lasting hardware components.
- Improved Stability: Underclocking can enhance device stability by reducing the chances of overheating and preventing thermal throttling, which can cause performance degradation or forced system shutdowns.
Nevertheless, underclocking also has its own considerations:
- Reduced Performance: Underclocking the CPU can result in slower device performance, leading to potential lags or delays, especially when running resource-intensive apps or tasks.
- Incompatible Apps: Some apps or games may have minimum requirements regarding CPU clock speed or performance levels. Underclocking may render these apps incompatible or cause them to malfunction.
It is important to note that overclocking and underclocking should be done with caution and within the limits set by your device’s hardware. Extreme overclocking or underclocking can lead to device instability, reduced lifespan, or even permanent damage. It is recommended to thoroughly research the capabilities and risks associated with overclocking or underclocking your specific device model and use reliable tools or apps designed for these purposes.
Increased Backup Options
Rooting an Android phone unlocks a range of advanced backup options that go beyond the standard backup features provided by the default Android operating system. These enhanced backup capabilities provide users with more comprehensive and customizable backup solutions. Here are the advantages of increased backup options after rooting:
1. Complete System Backups: Rooting enables users to perform full system backups that include not only personal data and apps but also system files, settings, and configurations. This comprehensive backup ensures that you can restore your device to its exact state, including all personalized settings and preferences.
2. App Data Backup: With root access, users can backup and restore individual app data. This includes saved game progress, login credentials, preferences, and other app-specific information. Having the ability to back up and restore app data allows for a seamless transition between devices or when resetting your device to a factory state.
3. Titanium Backup: Titanium Backup is a popular third-party app that requires root access and offers extensive backup functionality. It allows users to back up individual apps, app data, system settings, and even the entire system. Titanium Backup also offers features like scheduled backups, batch restores, and the ability to freeze apps to prevent them from running or being updated.
4. Nandroid Backups: Nandroid backups are complete image backups of your device’s entire system partition. These backups capture the operating system, apps, data, and even the kernel. Nandroid backups are widely recognized as one of the most comprehensive backup options available to rooted Android users, providing a complete snapshot of the device’s state.
5. Custom Recovery: Rooting allows users to install a custom recovery, such as ClockworkMod Recovery or TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project). These custom recoveries provide advanced backup and restore options, including the ability to create full system backups, restore individual partitions, and even clone devices. Custom recoveries offer more flexibility and control over the backup process compared to the stock Android recovery.
6. Easy Device Migration: Rooting and using advanced backup options can make device migration seamless. Whether moving to a new device or restoring your current device after a factory reset, the ability to perform a complete system restore ensures that all apps, settings, and personal data are transferred effortlessly.
While increased backup options after rooting provide several advantages, it is essential to consider potential limitations and factors to ensure successful backups:
- Storage Requirements: Full system backups or extensive app data backups can occupy a significant amount of storage space. Ensure that you have sufficient storage capacity on your device or an external storage device to store the backup files.
- Backup Frequency: Regularly backing up your device is crucial to avoid losing important data. Set up automated backups or establish a backup routine based on your usage patterns and the frequency of data changes.
- Compatibility: Certain apps or data may not be compatible with different device models or Android versions. Verify app compatibility after restoring backups to ensure proper functionality.
- Security Considerations: Backing up personal data, especially sensitive information, requires proper security measures. Ensure that backup files are stored securely and protected against unauthorized access.
With increased backup options available after rooting, users can have greater peace of mind knowing that their valuable data and settings can be easily protected, restored, and migrated to new devices. It is important to research and understand the specifications and requirements of the backup solutions available, along with any potential risks associated with the rooting process.
Access to Advanced Apps and Features
Rooting an Android phone opens up a whole new world of advanced apps and features that are otherwise inaccessible on non-rooted devices. These apps and features offer enhanced customization, improved performance, and expanded functionality. Here are the benefits of accessing advanced apps and features after rooting:
1. Ad-Blocking: Rooting allows users to install powerful ad-blocking apps that can effectively eliminate intrusive and annoying advertisements from various apps and websites. By blocking ads, users can enjoy a cleaner and more streamlined browsing experience, save data usage, and reduce distractions.
2. Custom ROMs: Rooting unlocks the ability to install custom ROMs, which are modified versions of the Android operating system. Custom ROMs provide features and optimizations not found in the stock software provided by the manufacturer. These ROMs offer a range of customization options, allowing users to personalize their device’s appearance, add new features, and improve performance and battery life.
3. System-level File Management: With root access, users can access and modify system files and directories that are otherwise restricted. Advanced file managers with root access allow for advanced file operations, such as moving or deleting system files, managing app data, and tweaking system configurations. This level of file management can offer more control over the device’s operating system and optimize its performance.
4. CPU Control: Rooting enables users to have direct control over the CPU (Central Processing Unit). Advanced CPU control apps allow for underclocking and overclocking the CPU, adjusting voltage settings, and tweaking the CPU’s performance parameters. This level of fine-tuning allows users to optimize their device’s performance, power consumption, and heat generation according to their specific needs.
5. Backup and Restore Apps without Data: Rooting provides the ability to backup and restore apps without their associated data. While non-rooted devices usually require a full app and data backup, root access allows for more flexibility by selectively preserving only the app itself. This can save time and storage space when reinstalling apps or performing system updates.
6. Advanced Battery Management: Rooting allows users to access advanced battery management apps that offer granular control over power-saving features and battery usage. These apps provide detailed insights into battery consumption, allow users to customize power-saving profiles, and enable aggressive battery-saving measures that are not available on non-rooted devices.
7. Emulation and Virtualization: Rooted devices can take advantage of apps that enable the emulation of other devices or operating systems. With root access, users can run virtual machines, enable game console emulators, or even emulate other Android versions, expanding the device’s capabilities and compatibility with legacy or foreign apps.
8. Hacking and Tweaking: While not for everyone, rooting opens the door to advanced hacking and tweaking apps that offer extensive system customization. These apps enable users to modify system settings, experiment with experimental features, and fine-tune various aspects of the Android operating system to their liking.
It is important to remember that while accessing advanced apps and features after rooting offers numerous benefits, it also comes with certain risks and considerations. The installation and use of advanced apps require caution, as they have the potential to modify critical system files or expose the device to security vulnerabilities. Users should exercise discretion and research apps and features before installing them on their rooted device.
Risk of Bricking Your Phone
When it comes to rooting an Android phone, one of the significant risks involved is the possibility of “bricking” your device. Bricking refers to rendering your phone completely unusable, essentially turning it into a lifeless brick. While the risk of bricking can be intimidating, understanding the causes and taking precautions can help minimize this risk. Here’s an overview of the risk of bricking your phone when rooting:
1. Wrong Procedure or Software: The most common cause of bricking a phone is using the wrong rooting procedure or incompatible software. Each device model and Android version may require different rooting methods, so using incorrect tools or following unreliable guides can result in critical errors that lead to a bricked phone. It is essential to thoroughly research and follow trusted and verified instructions specific to your device.
2. Flashing Custom ROMs: Installing custom ROMs, while providing numerous benefits, can also increase the risk of bricking your phone if not done correctly. Flashing an incompatible or poorly developed custom ROM may disrupt critical system functions, leading to a bricked device. It’s crucial to ensure the custom ROM is specifically designed for your device model and follow the installation instructions carefully.
3. Unlocking the Bootloader: Rooting often involves unlocking the bootloader, a process that permits the installation of custom firmware. Mishandling the bootloader unlocking process can have severe consequences, potentially resulting in a bricked phone. It is important to understand the bootloader unlocking method for your specific device and carefully follow the provided instructions.
4. Interrupting the Rooting Process: Interrupting the rooting process, such as disconnecting the device or powering it off, can pose a risk of bricking. Rooting procedures modify critical system files, and interrupting the process midway can leave the device in an unstable state, preventing it from booting up properly. It is crucial to ensure a stable power supply and follow the rooting process without interruption.
5. Modifying System Files: Rooting grants users access to system files, allowing them to modify various aspects of the device’s software. However, modifying critical system files without proper knowledge or care can lead to errors that result in a bricked phone. It is crucial to be cautious when making any modifications and understand the potential consequences before proceeding.
6. Unknown Third-Party Apps: Installing unknown or dubious third-party apps after rooting can introduce malware or malicious code to your device, potentially causing system instability or bricking. It is recommended to only install apps from trusted sources and conduct thorough research before downloading and installing any apps on your rooted device.
While the risk of bricking exists, taking the following precautions can help minimize the chances:
- Do Thorough Research: Before rooting your device, extensively research the process, proper rooting procedure, and compatible tools applicable to your specific device model and Android version.
- Backup Critical Data: Back up all important data and create a complete system backup using appropriate tools or custom recoveries. This will allow you to restore your device in case of any issues.
- Follow Verified Sources: Only use reputable and trustworthy sources or developers for rooting instructions, tools, custom ROMs, and other necessary files.
- Be Patient and Cautious: Follow the rooting process step-by-step, ensuring each action completes successfully before proceeding to the next. Avoid rushing or taking shortcuts that may compromise the stability of the process.
- Consult Experienced Users: Seek advice from experienced Android users or communities who have successfully rooted the same device model or have relevant expertise.
Understanding the risks involved in rooting and taking necessary precautions can help minimize the possibility of bricking your phone. It is essential to proceed with caution, ensuring that you have a solid understanding of the rooting process and the specific requirements for your device. Rooting can offer many benefits, but it is crucial to weigh those benefits against the risks and make an informed decision before proceeding.
Voiding Warranty
One of the significant considerations when rooting an Android phone is that the process usually voids the manufacturer’s warranty. Warranty coverage protects your device from defects in materials and workmanship, providing you with free repairs or replacements within a specified period. Rooting a phone involves modifying the operating system or unlocking system restrictions, which is typically against the terms and conditions set by manufacturers. Here are the key things to know about voiding the warranty when rooting:
1. Warranty Policy: Each manufacturer has its own warranty policy, which explicitly mentions that any modifications to the device’s software or hardware, including rooting, will void the warranty. It is important to read and understand the warranty terms and conditions before deciding to root your Android phone.
2. Software Modifications: Rooting involves making changes to the software on your device, potentially altering critical system files. Manufacturers consider this as a violation of their warranty policy, as they cannot guarantee the device’s stability, security, or proper functioning after rooting.
3. Hardware Modifications: Rooting often requires unlocking the bootloader, which can be considered a hardware modification. Altering the device’s hardware in any way or tampering with the internal components also voids the warranty, as it can impact the device’s performance or cause physical damage.
4. Third-Party Repairs: Once your device is rooted, manufacturers generally do not provide warranty coverage for repairs or replacements, even for issues unrelated to the root process. Authorized service centers may refuse to service a rooted device or charge additional fees for repairs, parts, or labor.
5. Limited Manufacturer Support: After rooting, official technical support from the manufacturer or carrier may no longer be available for your device. They might not assist with software-related issues or provide software updates, as rooting invalidates their responsibility to ensure the device’s proper functioning.
6. Unrooting and Warranty Restoration: In some cases, unrooting your device may bring back the warranty coverage. However, unrooting can be challenging, and there is no guarantee that manufacturers will reinstate the warranty, as they may still detect signs of previous rooting attempts.
Before deciding to root your device, consider the following:
- Weighing the Benefits: Assess the advantages of rooting against the potential loss of warranty coverage. Determine if the benefits obtained from rooting outweigh the potential costs associated with repairs or replacements.
- Non-Root Alternatives: Explore alternative methods or apps that can achieve your desired customization or functionality without the need for root access. Many features and customization options can be achieved through non-root means.
- Third-Party Repair Services: If you encounter issues with your rooted device, consider seeking repairs from third-party repair services. However, be aware that these repairs may come at additional costs and may not provide the same level of warranty coverage as official manufacturer repairs.
Always remember that rooting your Android phone is a personal decision that comes with trade-offs. While rooting can unlock various benefits and customization options, it is crucial to consider the implications of voiding the warranty. Carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages before proceeding with rooting your Android phone.
Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
Rooting an Android phone carries inherent security risks and vulnerabilities that users need to be aware of. When you root your device, you gain elevated privileges and access to the system, but at the same time, you expose your device to potential security threats. Here are some of the key security risks and vulnerabilities associated with rooting:
1. Malware and Security Exploits: Rooting bypasses the built-in security features and restrictions put in place by the Android operating system. This can make your device more susceptible to malware attacks and security exploits, as unauthorized apps or other malicious software may gain root access without your knowledge or consent.
2. Removal of System-level Protections: Rooting involves modifying system files and removing certain system-level protections, such as the Verify Apps feature. Verify Apps scans and verifies the integrity of the apps installed on your device, protecting against potentially harmful apps. Disabling or removing this feature can leave your device vulnerable to the installation of malicious or compromised apps.
3. Access to Sensitive Data: With root access, apps and processes on your device can potentially access sensitive user data that would otherwise be protected. This includes personal information, passwords, banking credentials, and other sensitive data stored on your device, increasing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
4. Insecure Apps and Sources: Rooted devices may have access to apps and app stores outside of the official Google Play Store, opening the door to potentially insecure or malicious apps. These third-party sources may not have the same level of scrutiny or security measures in place compared to official app stores, increasing the risk of unwittingly installing harmful apps.
5. Loss of Security Updates: Rooted devices often miss out on security updates provided by the device manufacturer or carrier. These updates include critical patches and fixes that address newly discovered vulnerabilities, leaving your device exposed to known security risks.
6. Bricking Recovery Tools: Downloading and using unreliable or malicious recovery tools to root your device can result in damage or “bricking” your device. These tools may contain malware or can be modified to include malicious code, compromising your device’s security.
7. Root Access Abuse: If your device becomes rooted and falls into the wrong hands, an unauthorized user with root access can perform malicious activities, such as stealing personal data, installing spyware, or even taking control of your device remotely.
To minimize the security risks associated with rooting:
- Research Before Rooting: Thoroughly research the potential security risks involved in rooting, understand the process, and familiarize yourself with the security implications specific to your device model and Android version.
- Use Trusted Sources: Only download and install apps from reputable sources and stick to official app stores like Google Play Store, which implement stringent security measures and regularly scan apps for potential threats.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your device’s operating system and security patches provided by the manufacturer. These updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities, protecting your device against potential exploits.
- Install Security Software: Use a reputable mobile security app that provides real-time protection against malware and monitors app behavior for suspicious activities. This can help mitigate the risks associated with rooting and add an extra layer of security to your device.
Ultimately, rooting your device requires a careful balance between the benefits of customization and the associated security risks. By remaining vigilant, using trusted sources, and keeping your device and apps up to date, you can minimize the chances of encountering security issues while enjoying the advantages of rooting.
Compatibility Issues with Certain AppsRooting an Android phone can introduce compatibility issues with certain apps that rely on a non-rooted environment. Although most apps function properly on rooted devices, there may be cases where certain apps encounter problems or refuse to run altogether. These compatibility issues arise due to the modifications made to the system during the rooting process. Here are some of the key considerations regarding compatibility issues with certain apps when rooting:
1. Compatibility Dependencies: Some apps have specific dependencies related to the device’s software or hardware configuration, such as a specific Android version, system libraries, or hardware features. Rooting can modify aspects of the device’s software and potentially interfere with these dependencies, leading to compatibility issues.
2. Security Measures: Certain apps, especially those related to banking, payment gateways, or high-security applications, employ strict security measures to protect user data. These apps may have built-in checks to detect if a device is rooted, and if so, they may block access for security reasons.
3. Safetynet API and DRM: Many apps, particularly those related to online streaming, digital rights management (DRM), or financial services, use Google’s Safetynet API to perform safety checks on the device. If Safetynet detects that the device is rooted, these apps may refuse to function or restrict certain features to maintain security and prevent unauthorized access.
4. App Certification: Some apps on the Google Play Store are certified by Google, ensuring compatibility and adherence to specific security standards. Rooted devices are often considered uncertified as they do not meet the requirements imposed by Google, limiting access to certified apps or causing compatibility issues.
5. Incompatible Root Management: Certain root management tools or modifications that are incompatible with specific apps might trigger compatibility issues. This can include system-level modifications, custom frameworks, or other root-related modifications that interfere with the app’s normal functioning.
6. Safety Measures and Access Restrictions: Apps that deal with sensitive, secure, or potentially dangerous functionalities, such as antivirus apps, firewalls, or device management apps, may restrict access on rooted devices to prevent misuse or unauthorized modifications.
To address compatibility issues with certain apps:
- Use Root Management Apps: Utilize root management apps, such as Magisk, to hide root access from certain apps. These apps can help bypass compatibility checks and ensure that specific apps function correctly on rooted devices.
- Unroot Temporary: Temporarily unroot your device when you need to use specific apps that are incompatible with rooted devices. Many rooting methods allow for temporary unrooting, which can be easily reversed when needed.
- Search for Alternatives: Find alternative apps that provide similar functionalities but do not impose compatibility restrictions on rooted devices. These apps may offer comparable features and ensure seamless compatibility with your rooted device.
- Custom ROMs: Consider installing custom ROMs that are known to have better compatibility with apps. Some custom ROMs are specifically designed to address compatibility issues and ensure a smooth experience for rooted devices.
Keep in mind that while many compatibility issues can be resolved, there may be cases where certain apps are inherently incompatible with rooted devices due to their security or certification requirements. Evaluate your app usage priorities and compatibility needs before proceeding with rooting to ensure a seamless experience with your preferred apps.
Complexity and Technical Knowledge Required
Rooting an Android phone is a technical process that requires a certain level of complexity and technical knowledge. While rooting can offer numerous benefits, it’s important to understand the complexity involved and the skills required before attempting the process. Here are some key considerations regarding the complexity and technical knowledge required for rooting:
1. Understanding of Device and Android System: Rooting involves modifying the operating system of your device. It requires a solid understanding of how the Android system works, including its file structure, system components, and software architecture. Without a basic understanding of these elements, it can be challenging to navigate the rooting process successfully.
2. Familiarity with Device Model and Android Version: Each device model and Android version may have its own specific rooting methods and compatibility requirements. It is essential to research and understand the specific rooting instructions and tools applicable to your device model and its corresponding Android version.
3. Technical Terminology and Concepts: The rooting process involves technical terminology and concepts that may be unfamiliar to beginners. It is essential to familiarize yourself with terms such as bootloader, custom recovery, flash, ROMs, and rooting utilities to understand and follow the instructions accurately.
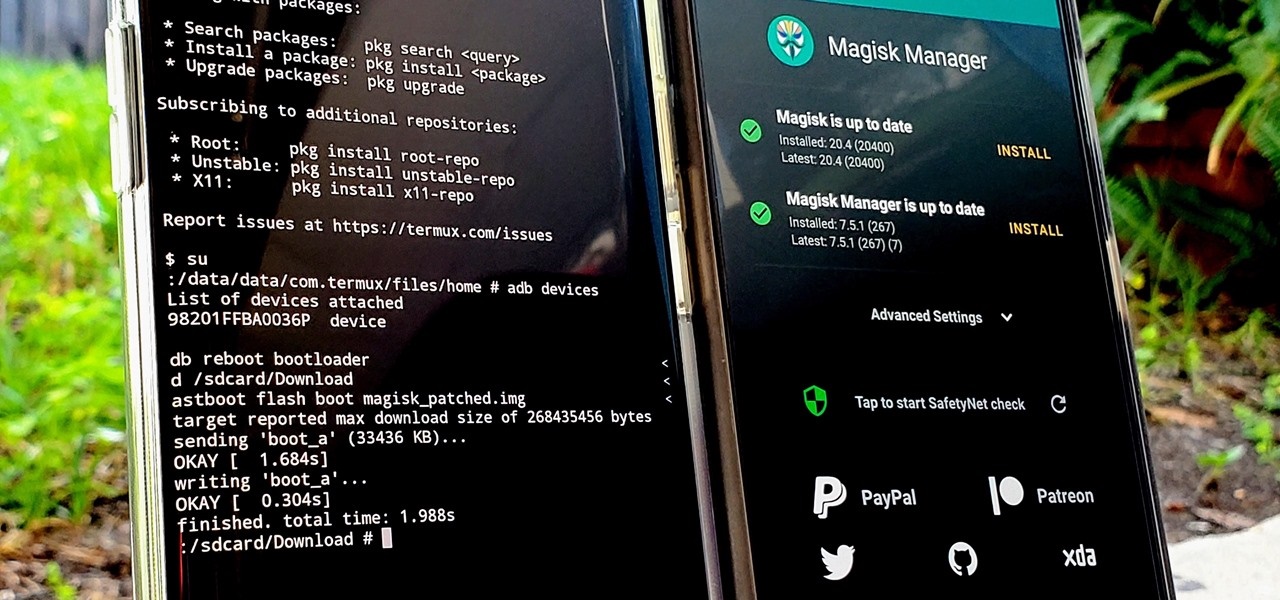
4. Command Line Interface (CLI) Knowledge: Some rooting methods require the use of the command line interface (CLI). Knowledge of basic CLI operations, such as executing commands, navigating directories, and transferring files, is beneficial in successfully completing the rooting process.
5. Awareness of Risks and Consequences: Technical knowledge also includes understanding the risks and consequences associated with rooting. This includes potential data loss, bricking the device, voiding the manufacturer’s warranty, and exposing the device to security vulnerabilities. Being aware of these risks allows individuals to make informed decisions and exercise caution during the rooting process.
6. Troubleshooting Skills: Rooting is not always a straightforward process, and complications can arise. Having troubleshooting skills, such as researching and diagnosing problems, following guides, and applying solutions, can help overcome issues that may occur during the rooting process.
To navigate the complexity and technical knowledge required for rooting:
- Thoroughly Research: Invest time in researching and understanding the rooting process, including the specific requirements and risks associated with your device model and Android version.
- Follow Trusted Sources: Rely on reputable sources, forums, and community discussions to acquire accurate and reliable instructions. Ensure the information is up-to-date and relevant to your specific device model and Android version.
- Consult Knowledgeable Individuals: Seek guidance from experienced root users or online communities who can provide insights, advice, and troubleshooting tips during the rooting process.
- Start with Beginner-Friendly Methods: If you are new to rooting, begin with beginner-friendly methods or tools that offer automated processes and simplified instructions. This can help build your confidence and understanding before attempting more advanced rooting techniques.
- Back Up Data: Prioritize data backup before starting the rooting process. This ensures that you have a copy of your important files and can restore your device to a previous state if necessary.
While rooting an Android phone may seem intimidating, approaching the process with technical knowledge, patience, and a cautious mindset can help navigate the complexity successfully. It’s crucial to continuously educate yourself, stay updated with the latest rooting techniques, and never hesitate to seek assistance when needed.
Potential Loss of Data
When rooting an Android phone, there is a potential risk of data loss during the process. Rooting involves making modifications to the operating system, which can result in the deletion or corruption of important data stored on the device. Understanding the potential loss of data is crucial before proceeding with rooting. Here are some key considerations regarding the potential loss of data:
1. System File Modifications: Rooting requires modifying system files, which can inadvertently lead to the loss of critical system data if not done correctly. Mishandling these modifications can result in system instability, leading to data corruption or even rendering the device inoperable.
2. Unlocking Bootloader or Installing Custom Recovery: Some rooting methods involve unlocking the bootloader or installing custom recovery on the device. These procedures often require performing a “wipe” or factory reset, which erases all data on the device’s internal storage. It is essential to back up your data before attempting these processes, as they will result in a complete loss of data stored on the device.
3. User Error: Rooting requires following specific instructions and commands accurately. Human error, such as selecting the wrong option or executing unintended commands, can result in unintentional data loss. It is crucial to carefully read and understand the instructions and double-check your actions to minimize the risk of data loss.
4. Incompatible Modifications or Apps: Rooted devices allow for installing custom ROMs, apps, or modifications that may not be fully compatible with the device’s hardware or software. These incompatible modifications can lead to data corruption or instability, resulting in potential data loss.
5. Lack of Data Backup: Neglecting to back up your data before rooting increases the risk of permanent data loss. If any unexpected issues arise during the rooting process, or if you encounter compatibility problems with certain apps or modifications, you may need to perform a factory reset to restore the device’s functionality, leading to the loss of all data stored on the device.
6. External Storage Considerations: While most rooting methods primarily affect the device’s internal storage, it is essential to note that external storage, such as microSD cards, may also be impacted. It is advisable to safely remove and back up any data stored on external storage devices before proceeding with rooting.
To mitigate the potential loss of data:
- Back Up Your Data: Before rooting, perform a complete data backup of your device using reliable backup methods, such as cloud storage or transferring data to a computer. This ensures that your important files, photos, contacts, and app data are safely stored elsewhere in case of data loss.
- Make Multiple Backups: It is recommended to create multiple backups of your data on separate storage devices or platforms to provide additional redundancy and safeguard against any potential backup failures.
- Research Reliable Rooting Methods: Thoroughly research trusted rooting methods specific to your device model and Android version. Choose methods that have a proven track record of success and minimal risk of data loss.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Read and understand the rooting instructions and guides thoroughly before initiating the process. Pay close attention to each step and proceed cautiously to minimize the risk of errors that could lead to data loss.
- Consider Professional Assistance: If you are unsure or feel uncomfortable performing the rooting process yourself, consider seeking assistance from professionals who have experience in rooting devices to minimize the risk of data loss.
While potential data loss is a concern when rooting an Android phone, taking appropriate precautions and performing data backups can significantly reduce the risk. By being informed and prepared, you can ensure the safety of your data and minimize the impact of any unforeseen issues that may arise during the rooting process.
Legal Issues and Breach of Terms and Conditions
Rooting an Android phone often involves modifications to the device’s software, potentially leading to legal issues and a breach of the terms and conditions set by the device manufacturer or carrier. It is crucial to understand the legal implications before deciding to root your device. Here are some key considerations regarding legal issues and breaches of terms and conditions:
1. Voiding Manufacturer’s Warranty: Rooting your device typically results in the voiding of the manufacturer’s warranty. The warranty agreement explicitly states that any modifications to the software or hardware, including rooting, will nullify the warranty coverage. This means that the manufacturer will no longer be responsible for providing repairs, replacements, or support for your device.
2. Violation of Carrier Agreements: Carriers often include clauses in their service agreements or terms of use that prohibit customers from modifying their devices in ways that breach the terms and conditions. Rooting your device may violate these provisions, potentially leading to service termination, additional charges, or other penalties imposed by the carrier.
3. Legal Implications: Depending on local laws and regulations, rooting your Android phone may be illegal or in violation of digital rights management (DRM) laws, copyright laws, or software license agreements. Engaging in activities that bypass security measures or tamper with software integrity can lead to legal consequences and possible legal action.
4. App Restrictions and Incompatibility: Some apps and services, particularly those related to financial transactions, online streaming, or high-security functions, may impose restrictions on rooted devices. These restrictions serve to protect the app’s integrity, user privacy, and prevent unauthorized modifications. Rooted devices may encounter limitations, including restricted access to certain apps or features.
5. Unauthorized System Modifications: Rooting can involve modifying the system files and software of your device, which may be viewed as unauthorized access and tampering by software and device manufacturers. This can potentially infringe upon intellectual property rights and breach terms of use agreements.
To mitigate legal issues and breaches of terms and conditions:
- Read and Understand Terms and Conditions: Thoroughly review the terms and conditions provided by the device manufacturer and carrier. Understand the clauses related to software modifications, warranty coverage, and device usage restrictions.
- Evaluate Risks and Legal Consequences: Assess the legal implications of rooting based on your location, local laws, and the specific agreements you have with the manufacturer and carrier. Consult legal professionals when necessary to ensure compliance.
- Consider Alternative Methods: Explore non-root alternatives, such as third-party apps or launcher apps that provide customization options without the need for root access. These alternatives may allow you to achieve similar functionalities while staying within the boundaries of the manufacturer’s warranty and legal agreements.
- Unroot as Necessary: If legal or compliance concerns arise, unroot your device to revert it to its original, unmodified state. Unrooting can help reinstate warranty coverage and comply with terms and conditions.
Understanding the legal implications and the potential breach of terms and conditions is crucial when considering the decision to root your Android phone. It is important to weigh the benefits of rooting against the potential legal risks and repercussions to make an informed decision that aligns with local laws and regulatory requirements.