What is CATV?
CATV, also known as Cable Television, is a system that delivers television programming through a network of cables. It stands for “Community Antenna Television” and has been a dominant force in the broadcasting industry since its inception.
Unlike traditional broadcast television, which relies on radio waves to transmit signals, CATV uses coaxial or fiber-optic cables to deliver a wide range of programming options to subscribers. This technology allows for a more reliable and consistent signal, resulting in higher-quality audio and video.
CATV networks are typically operated by cable television companies that provide a variety of channels and services to customers. These networks enable viewers to access an extensive selection of television channels, including local, national, and international broadcasts.
One of the key advantages of CATV is its ability to offer a larger number of channels compared to traditional broadcast television. This allows viewers to have a greater variety of options, including specialized channels that cater to specific interests such as sports, movies, news, and more.
In addition to television programming, CATV networks can also provide other services such as internet access, telephone services, and video on demand. This makes it a versatile and convenient option for subscribers, as they can access multiple services from a single provider.
CATV networks have revolutionized the way people consume television content. With the advent of digital technology and high-definition broadcasting, viewers can now enjoy crystal-clear images and immersive sound quality, enhancing their overall viewing experience.
Another significant advantage of CATV is its accessibility. Unlike satellite television, which requires a clear line of sight to the satellite dish, CATV signals can be transmitted through cables buried underground or attached to utility poles, making it available to a larger population.
Despite the rise of streaming platforms and internet-based services, CATV remains a popular choice for many households around the world. Its reliability, extensive channel lineup, and bundled services continue to attract subscribers who value a seamless entertainment experience.
The History of Cable Television
The roots of cable television can be traced back to the 1940s, when communities in remote areas faced challenges receiving over-the-air broadcast signals. In response to this need, innovative entrepreneurs developed the concept of Community Antenna Television (CATV) systems to deliver television programming through a wired network.
The first known commercial cable television system was established in 1948 in Pennsylvania, USA. The system used a community antenna to capture television signals and distribute them to households through coaxial cables. This breakthrough allowed viewers in areas with poor broadcast reception to enjoy clearer and more reliable television signals.
During the 1950s and 1960s, the cable television industry experienced significant growth. Cable television companies began expanding their network infrastructure, bringing television programming to more communities across the United States.
One of the key milestones in the history of cable television was the launch of HBO (Home Box Office) in 1972. HBO was the first cable network to offer exclusive premium content to subscribers. This marked the start of cable television’s evolution into a provider of specialized programming beyond what was available on broadcast channels.
In the 1980s, the industry faced challenges from satellite television providers, who were able to offer a vast array of channels with their direct-to-home satellite systems. To compete with satellite, cable television companies invested in technological advancements, such as the introduction of fiber-optic cables for improved signal quality and transmission capacity.
The 1990s witnessed a significant transformation in the cable television landscape with the emergence of digital cable. This revolutionary technology allowed for the compression and transmission of digital signals, providing subscribers with clearer picture and sound quality, as well as interactive features and on-screen program guides.
With the dawn of the new millennium, cable television expanded beyond traditional television programming. Internet services were introduced, offering broadband connectivity to households through cable networks. This innovation paved the way for bundled packages that combined television, internet, and telephone services, creating more convenience for subscribers.
Today, cable television continues to evolve with the rise of streaming services and on-demand content. Cable companies have adapted by offering their own streaming platforms and integrating popular streaming services into their cable packages, providing viewers with even more flexibility and choices.
From its humble beginnings as a solution to overcome geographic limitations, cable television has transformed into a versatile and indispensable medium for entertainment, information, and communication.
How CATV Works
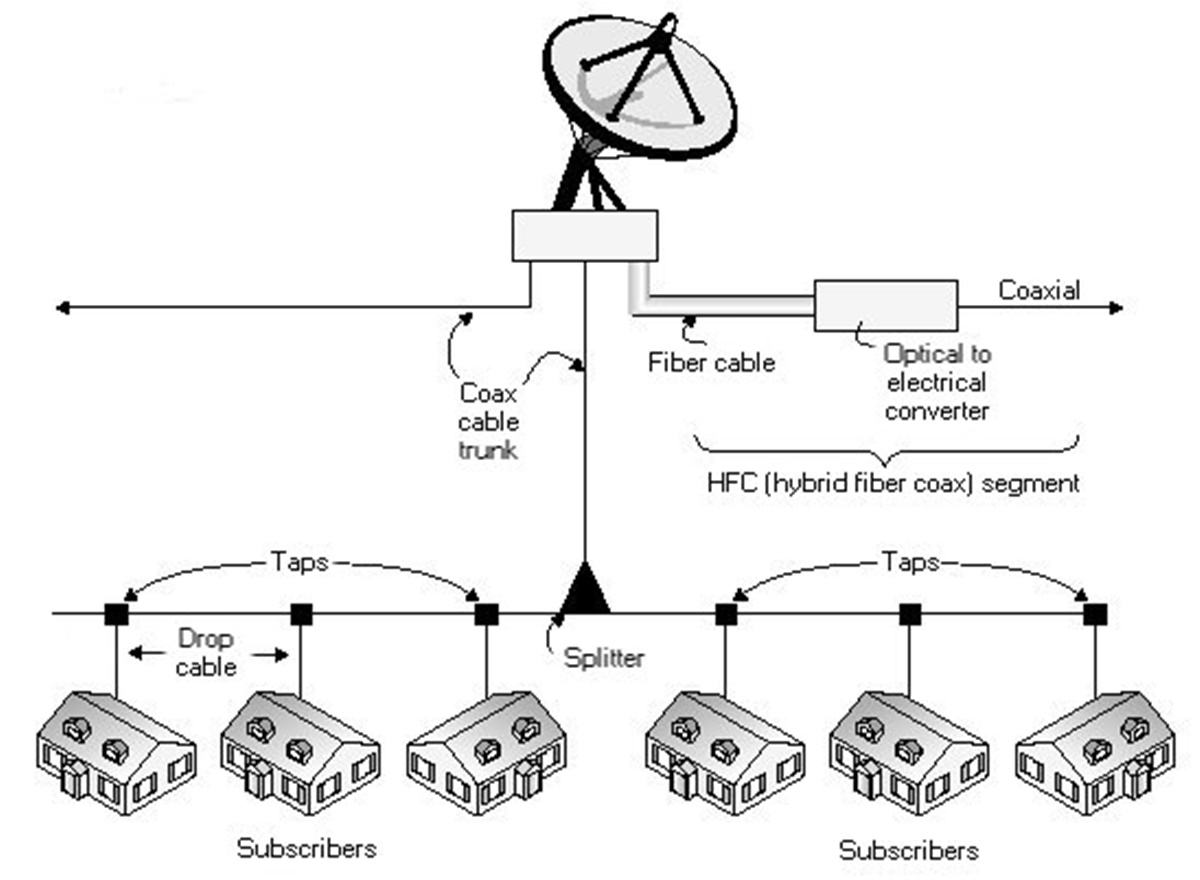
Understanding how CATV works requires a grasp of the technology and infrastructure that underpins the system. At its core, CATV relies on a network of coaxial or fiber-optic cables that transmit television signals from the source to the viewer’s home.
The process begins at the headend, which is the central location where the cable television company receives television signals from various sources. These sources can include local broadcast stations, satellite feeds, and cable networks. The signals are then processed and converted into a format suitable for distribution over the cable network.
Once the signals are prepared, they are sent through a series of amplifiers, known as nodes, that boost the signal strength to overcome any loss as it travels through the cables. These nodes are strategically placed along the network to ensure consistent signal quality throughout the coverage area.
The signals then travel through the distribution fibers or coaxial cables, depending on the type of infrastructure used. Fiber-optic cables offer higher transmission speeds and can carry more information, making them ideal for delivering high-definition and digital signals. Coaxial cables, on the other hand, are often used for transmitting analog signals.
As the signals reach the neighborhood, they are split into individual lines that lead to each subscriber’s home. This branching point is called a tap, and it allows for multiple households to receive independent signals without interfering with each other.
Inside the subscriber’s home, a cable box or set-top box is usually required to decrypt and decode the television signals. These devices often include additional features such as on-screen menus, program guides, and digital video recording capabilities.
With the advent of digital cable, the signals are typically modulated into a digital format and compressed for efficient transmission. Digital compression allows for more channels to be carried on the same bandwidth, increasing the range of programming options available to subscribers.
It is important to note that CATV networks are typically “one-way” systems, meaning that the signals are sent from the headend to the subscribers. However, advancements in technology have enabled two-way communication, allowing subscribers to interact with the cable company for services such as video on demand, pay-per-view, and internet access.
Overall, the intricate infrastructure of CATV networks enables the efficient distribution of television signals to a large number of subscribers. By leveraging the power of cables and advanced signal processing technologies, CATV delivers a wide range of programming options and ensures a reliable and consistent viewing experience for subscribers.
Advantages of CATV Networks
CATV networks offer numerous advantages that have contributed to their widespread adoption and continued popularity among television viewers. These advantages range from the diverse programming options available to subscribers to the reliability and convenience of the system.
One of the key advantages of CATV networks is the extensive range of television channels they provide. Unlike traditional broadcast television, which offers a limited number of channels, CATV networks offer a vast selection of local, national, and international channels. This allows viewers to access a diverse range of content, including news, sports, movies, documentaries, and specialized programming.
In addition to a wide array of channels, CATV networks often offer premium content and packages. Subscribers can choose from various tiers of service that cater to their specific interests and preferences. This flexibility allows individuals to customize their viewing experience and access channels that align with their favorite genres or programs.
CATV networks also deliver consistent and reliable signal quality. Unlike over-the-air broadcasts that can be impacted by weather conditions or geographical limitations, CATV signals are transmitted through cables, providing a more stable and dependable viewing experience. This is particularly beneficial for viewers in rural or remote areas where traditional broadcast signals may be weak or unavailable.
Another advantage of CATV networks is the additional services they provide. Many cable television companies bundle services such as internet access, telephone services, and video on demand with their television packages. This convenient bundling allows subscribers to access multiple services from a single provider, simplifying their home entertainment and communication needs.
Furthermore, CATV networks often offer advanced features and technologies that enhance the user experience. Many cable boxes or set-top boxes provide interactive features, such as on-screen program guides and parental controls, allowing viewers to navigate and customize their viewing preferences easily. Some cable companies also offer digital video recording (DVR) services, enabling subscribers to record and watch their favorite shows at their convenience.
Additionally, CATV networks play a significant role in promoting local content and community engagement. They often include local channels that showcase regional news, events, and cultural programming. This fosters a sense of community and provides a platform for local businesses, organizations, and talent to reach a broader audience.
Finally, CATV networks have a wide coverage area, making television services accessible to a larger population. Unlike satellite television, which requires a clear line of sight to a satellite dish, CATV signals can be transmitted through cables buried underground or attached to utility poles. This accessibility ensures that more households can enjoy television programming and services, regardless of their location.
Overall, the advantages of CATV networks, such as diverse programming options, reliable signal quality, bundled services, advanced features, and wide accessibility, have solidified their position as a preferred choice for television viewers seeking a comprehensive and immersive entertainment experience.
Limitations of CATV Networks
While CATV networks have numerous advantages, they also have certain limitations that are important to consider. Understanding these limitations can help viewers make informed decisions when choosing their television and entertainment options.
One limitation of CATV networks is the potential for signal interference and degradation. The quality of the television signal can be affected by various factors, such as distance from the source, signal attenuation due to long cable runs, and electrical interference from nearby equipment or appliances. This can result in decreased picture quality, audio distortion, or even channel outages.
Another limitation is the potential for service disruptions during severe weather conditions. While CATV networks are generally more reliable than over-the-air broadcasts, they can still be susceptible to interruptions during storms, heavy rain, or other extreme weather events. This can cause temporary loss of service until the issues are resolved.
In some cases, CATV networks may have limited coverage in certain geographical areas. While efforts have been made to expand the reach of cable television, there are still remote or rural locations where the infrastructure is not available or economically feasible. As a result, some households may not have access to CATV services and rely solely on alternative forms of television broadcasting.
Another consideration is the potential for channel blackouts or disputes between cable companies and content providers. Sometimes, negotiations between cable networks and television channels can break down, resulting in the temporary removal of certain channels from the CATV lineup. This can be frustrating for subscribers who may lose access to their favorite shows or sports events during these disputes.
Additionally, CATV networks often require equipment, such as cable boxes or set-top boxes, to access the full range of services and features. While these devices offer added functionality, they can be an additional cost for subscribers. Furthermore, the complexity of the equipment and interfaces may present challenges for some users, especially those who are less technologically inclined.
An ongoing concern related to CATV networks is the issue of data privacy and security. With the convergence of television, internet, and other services, cable television companies collect and store customer data, including viewing habits and personal information. This raises questions about how this data is used, protected, and shared, and the potential for it to be accessed or misused by unauthorized parties.
Lastly, the increasing popularity of streaming services and online content consumption has impacted the relevance of traditional CATV networks. Many viewers are opting for internet-based streaming platforms that offer a wider range of content and on-demand access. This shift in consumer behavior is prompting CATV networks to adapt and offer their own streaming services to remain competitive.
Despite these limitations, CATV networks continue to be a widely popular choice for television viewers, thanks to their diverse programming options, reliability, and bundled service offerings. However, it is important for viewers to evaluate their specific needs and preferences in order to determine if CATV is the right fit for them.
The Expansion of CATV Networks
The expansion of CATV networks has been a remarkable journey, as cable television has evolved and grown to become a staple in millions of households around the world. The advancements in technology, infrastructure, and content offerings have contributed to the widespread availability and popularity of CATV networks.
In the early days of CATV, cable television was primarily focused on providing enhanced television reception to rural and remote areas. However, as the technology improved, cable companies began expanding their networks into urban and suburban areas, offering television services to a larger population.
During the 1980s and 1990s, CATV networks experienced a period of rapid expansion. The demand for cable television services increased as viewers sought greater channel variety and access to premium content. Cable companies invested in infrastructure upgrades, including the laying of more coaxial and fiber-optic cables to extend their reach and improve signal quality.
The expansion of CATV networks was also driven by the introduction of new services and features. As technology advanced, cable companies started offering internet access over their networks, capitalizing on the increasing demand for broadband connectivity. This expansion into internet services allowed cable operators to provide bundled packages, combining television, internet, and telephone services into a single subscription.
In recent years, CATV networks have faced new challenges and opportunities with the rise of streaming services and the shift towards digital content consumption. Recognizing the changing landscape, cable television companies have expanded their offerings to include their own streaming platforms and on-demand content. This adaptation has allowed them to cater to the preferences of viewers who are increasingly consuming content through online platforms.
The expansion of CATV networks is not limited to geographical coverage and service offerings. Cable companies have also embraced technological advancements to enhance the viewing experience. High-definition (HD) and Ultra HD (4K) programming have become more prevalent, offering stunning visuals and immersive audio. Cable companies have also introduced advanced features such as video on demand (VOD), digital video recording (DVR), and interactive programming guides, further enhancing the overall television experience for subscribers.
Additionally, the expansion of CATV networks has also facilitated the dissemination of localized content and community engagement. Cable companies often include local channels that showcase regional news, events, and cultural programming, contributing to an increased sense of community connection and participation.
The expansion of CATV networks continues to push boundaries, with ongoing investment in infrastructure and technological advancements. The deployment of fiber-optic cable networks, for example, promises even faster and more reliable connections for subscribers.
As CATV networks expand, they are also exploring new horizons, such as exploring Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) applications, as well as partnerships with emerging technologies, like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT). These innovations have the potential to reshape the future of cable television and further enhance the entertainment experience for viewers.
The Role of CATV in Modern Society
CATV, or Cable Television, plays a significant role in modern society, shaping the way we consume media, stay informed, and connect with the world. As a versatile and comprehensive entertainment medium, CATV serves as a vital source of information, entertainment, and community engagement.
One of the key roles of CATV is providing access to a wide range of television programming. With its diverse channel lineup, CATV allows viewers to stay updated on local, national, and international news, providing a platform for informed decision-making and fostering a sense of global awareness.
CATV also serves as an indispensable source of entertainment, offering a plethora of channels and genres to suit different interests and preferences. Whether it’s sports, movies, documentaries, or educational content, CATV networks provide viewers with an extensive array of options, allowing individuals to relax, unwind, and explore new worlds from the comfort of their homes.
Furthermore, CATV networks bring communities together by showcasing local events, cultural programming, and regional news. By highlighting local talent and providing a platform for community engagement, CATV acts as a catalyst for fostering a sense of connection, pride, and unity within neighborhoods and regions.
The role of CATV expands beyond traditional television programming. By offering bundled packages that include internet, telephone services, and on-demand content, cable television companies contribute to the connectivity and convenience of modern society. Subscribers can access a range of services from a single provider, simplifying their communication needs and enhancing their overall digital experience.
CATV plays a crucial role in bridging the digital divide, ensuring that even remote or rural areas have access to the same quality of television programming as urban areas. By leveraging the infrastructure and reach of cable networks, CATV brings television services to households that would otherwise have limited access to entertainment and information.
In addition, CATV networks often provide emergency alert systems, broadcasting vital information during natural disasters, public safety emergencies, or other urgent situations. This role in disseminating critical information helps to keep communities informed and safe, demonstrating the societal importance of cable television networks.
Furthermore, CATV networks support the local economy by providing advertising opportunities for local businesses. By reaching a wide audience through television commercials, local businesses can promote their products and services, stimulating economic growth and supporting local employment.
Overall, CATV plays a multifaceted role in modern society, serving as a source of information, entertainment, community engagement, connectivity, and economic support. Through its extensive programming options, local content, and technological advancements, CATV continues to play an integral part in shaping our daily lives and contributing to the well-being of individuals and communities.
The Future of CATV Technology
The future of CATV technology holds exciting possibilities as the industry continues to innovate and adapt to the evolving needs and preferences of viewers. Advancements in technology, infrastructure, and content delivery are set to shape the future of cable television, enhancing the user experience and expanding the capabilities of CATV networks.
One area of future development is the continued expansion of high-definition (HD) and Ultra HD (4K) programming. As consumer demand for higher resolution content grows, cable companies are likely to offer even more channels and shows in stunning visual quality. This will provide viewers with a more immersive and engaging television experience.
Another key area of focus is the integration of online streaming and on-demand content into CATV networks. Cable companies are recognizing the shifting viewing habits of consumers, who now expect access to their favorite shows and movies anytime, anywhere. By integrating streaming services and offering seamless access to on-demand content, CATV networks can provide a comprehensive and unified entertainment experience for subscribers.
The future of CATV technology also holds promise in terms of interactive and personalized programming. Viewers can expect more customizable options, such as personalized recommendations based on individual preferences and viewing history. This level of personalization will enable viewers to discover new content and enjoy tailored recommendations that align with their interests.
Continued advancements in network infrastructure will also shape the future of CATV technology. The deployment of fiber-optic cables will enhance transmission speeds and capacity, supporting the delivery of higher-quality content and more interactive features. Faster internet speeds and improved network reliability will enrich the overall viewing experience and enable seamless access to online services.
As technology progresses, CATV networks may also embrace emerging technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR). These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way viewers interact with television content, offering immersive and interactive experiences that blur the line between the virtual and physical world.
Additionally, the future of CATV technology may see the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance content recommendations and deliver more personalized experiences. AI-powered algorithms can analyze viewing patterns, preferences, and social media data to offer a curated selection of content, improving viewer satisfaction and engagement.
Furthermore, the expansion of smart home technology and Internet of Things (IoT) devices presents opportunities for CATV networks to integrate with other connected devices. Cable companies can leverage these technologies to offer seamless integration and control of various home entertainment and automation systems, providing a centralized hub for smart home management powered by CATV networks.
The future of CATV technology is undoubtedly an exciting one, as cable television companies continue to innovate and adapt to the changing landscape of the media industry. With advancements in resolution, interactive features, personalization, network infrastructure, and integration with emerging technologies, CATV networks will continue to be a leading source of entertainment and information for viewers around the world.