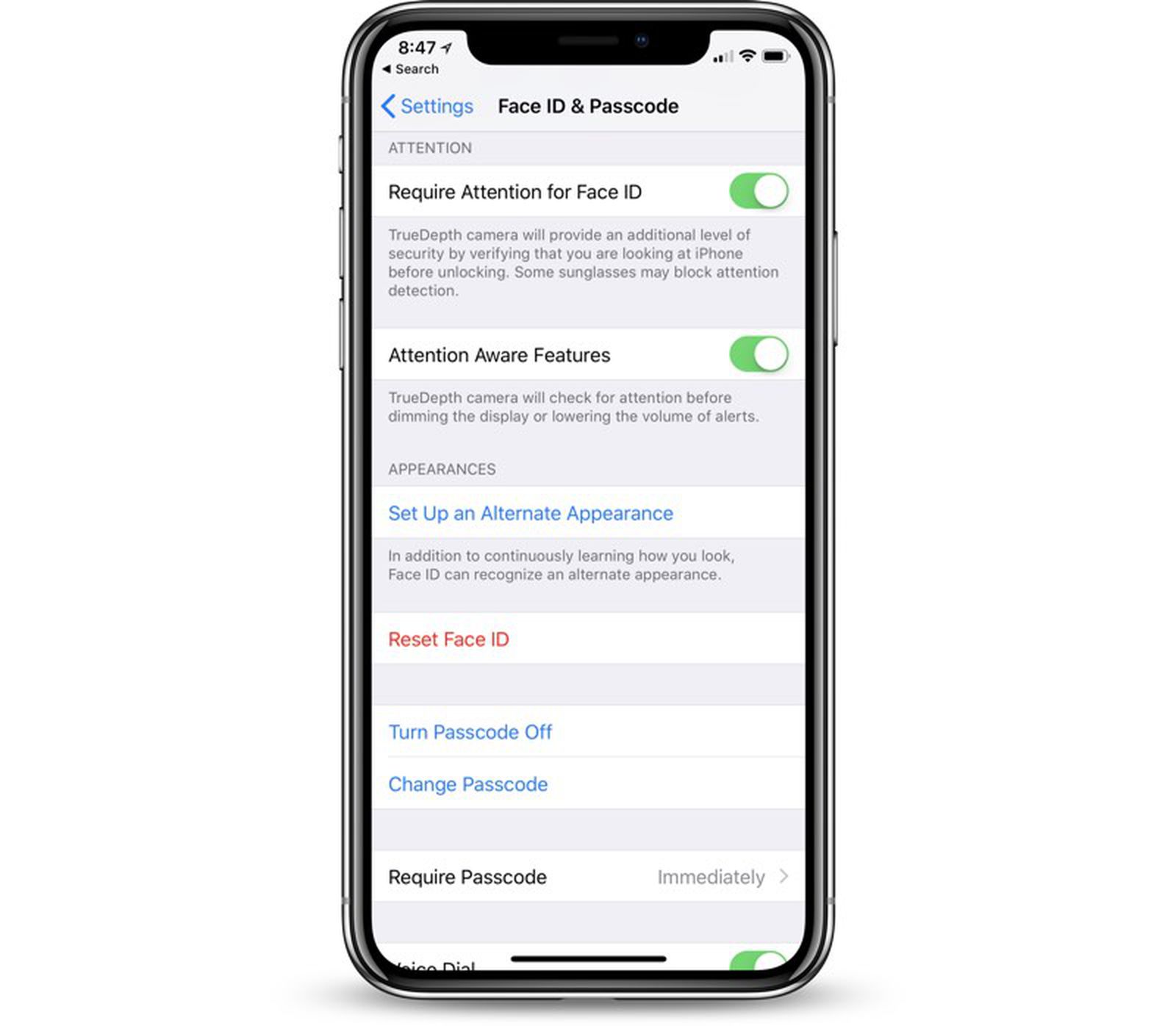
The Importance of Passcode Security
In today's digital age, where our smartphones contain a treasure trove of personal and sensitive information, the importance of passcode security cannot be overstated. The passcode serves as the first line of defense, safeguarding our data from unauthorized access and potential security breaches. Whether it's personal photos, confidential emails, or sensitive financial information, the passcode acts as a crucial barrier, preventing unauthorized individuals from gaining access to our private data.
With the advent of biometric authentication such as Face ID and Touch ID, the significance of passcode security might seem diminished. However, it's essential to recognize that the passcode remains a fundamental layer of protection, especially in scenarios where biometric authentication may not be feasible or reliable. Moreover, in the event of unforeseen circumstances such as a damaged or non-responsive biometric sensor, the passcode serves as a reliable fallback, ensuring continued access to the device.
Furthermore, the passcode plays a pivotal role in securing our devices in the event of loss or theft. By setting a strong passcode, users can mitigate the risk of unauthorized individuals gaining access to their personal information, thereby safeguarding their privacy and preventing potential identity theft or financial fraud.
In the context of enterprise mobility, where employees use their iPhones to access corporate resources and sensitive data, passcode security becomes even more critical. A robust passcode policy enforced by organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized data breaches and ensure compliance with industry regulations and data protection standards.
In essence, the importance of passcode security extends beyond mere device protection; it encompasses the safeguarding of personal privacy, sensitive data, and corporate assets. By recognizing the pivotal role of passcodes in maintaining the security and integrity of our digital lives, users can adopt proactive measures to create and maintain strong, unique passcodes, thereby fortifying the defense mechanisms of their iPhones and upholding the confidentiality of their information.
Common Methods for Breaking into iPhone Passcode
When it comes to breaking into an iPhone passcode, several methods have been employed, each with varying degrees of complexity and success. It's important to note that attempting to bypass the passcode of an iPhone without proper authorization may violate privacy laws and ethical standards. However, understanding these methods can shed light on the vulnerabilities that exist within passcode security systems and prompt users to adopt stronger security measures.
-
Brute Force Attack: This method involves systematically trying every possible combination of digits until the correct passcode is discovered. While this approach can theoretically unlock an iPhone, the sheer number of potential combinations (up to 10,000 for a 4-digit passcode) makes it a time-consuming and impractical method, especially with the built-in security measures that delay and restrict repeated passcode attempts.
-
Shoulder Surfing: In scenarios where an individual observes someone entering their passcode, either directly or via surveillance cameras, the passcode can be obtained through unauthorized means. This method relies on exploiting human error rather than technical vulnerabilities.
-
Social Engineering: By manipulating individuals into revealing their passcodes through deception or psychological manipulation, attackers can gain unauthorized access to iPhones. This method often involves exploiting trust, authority, or urgency to coerce individuals into divulging their passcodes.
-
Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities: Sophisticated attackers may attempt to exploit software vulnerabilities in the iPhone's operating system to bypass the passcode. This can involve leveraging zero-day exploits or security flaws to gain unauthorized access to the device.
-
Use of Forensic Tools: Law enforcement agencies and forensic experts may utilize specialized tools and techniques to extract data from iPhones, including bypassing the passcode. These tools often exploit vulnerabilities in older iOS versions or rely on physical access to the device.
It's important to emphasize that the majority of these methods require a certain level of technical expertise, and some may even necessitate physical access to the device. Additionally, many of these methods may infringe upon legal and ethical boundaries, underscoring the importance of respecting privacy and adhering to applicable laws and regulations.
By understanding the common methods employed to break into iPhone passcodes, users can gain insight into the potential vulnerabilities of their devices and take proactive measures to enhance their passcode security. This awareness can empower individuals to adopt strong, unique passcodes, stay vigilant against social engineering tactics, and remain informed about the latest security updates and best practices to safeguard their iPhones from unauthorized access.
The Risks of Attempting to Break into an iPhone Passcode
Attempting to break into an iPhone passcode carries inherent risks that extend beyond the potential legal and ethical implications. These risks encompass technical, security, and privacy concerns that can have far-reaching consequences for both individuals and organizations.
One of the primary risks associated with attempting to bypass an iPhone passcode is the potential for irreversible damage to the device's security mechanisms. Many of the methods used to circumvent passcode protection involve exploiting vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the device's operating system or security protocols. In doing so, attackers may inadvertently compromise the integrity of the iPhone's software, leaving it susceptible to further exploitation and unauthorized access. This can result in the exposure of sensitive data, unauthorized remote control of the device, or the installation of malicious software, posing significant security threats to the user's personal and professional information.
Moreover, attempting to break into an iPhone passcode can lead to the loss of data and functionality. In the process of employing various bypass methods, there is a risk of triggering security features designed to protect the device from unauthorized access. For instance, repeated failed passcode attempts can trigger the iPhone's self-defense mechanisms, such as data erasure or temporary lockouts, leading to potential data loss and disruption of device functionality. Additionally, certain bypass techniques may inadvertently corrupt the device's data or render it inoperable, resulting in the loss of valuable information and the need for extensive technical intervention to restore the device to a functional state.
Beyond technical risks, individuals attempting to bypass iPhone passcodes may inadvertently expose themselves to legal and regulatory repercussions. Unauthorized access to a device, regardless of the intent, can violate privacy laws, intellectual property rights, and data protection regulations. This can lead to legal action, financial penalties, and reputational damage for the individuals involved. Furthermore, organizations or individuals found to be engaging in unauthorized access to iPhones may face civil litigation, criminal charges, or regulatory sanctions, underscoring the severe legal implications of attempting to break into an iPhone passcode.
In summary, the risks associated with attempting to bypass an iPhone passcode are multifaceted, encompassing technical, security, privacy, and legal considerations. By understanding these risks, individuals can appreciate the gravity of unauthorized access attempts and recognize the importance of upholding the integrity of passcode security. It is imperative for users to prioritize the adoption of strong, unique passcodes and adhere to legal and ethical standards to safeguard their iPhones and protect the privacy and security of their data.
Legal and Ethical Considerations for Accessing an iPhone Passcode
The pursuit of accessing an iPhone passcode raises profound legal and ethical considerations that demand careful contemplation. From the standpoint of legality, it is crucial to recognize that attempting to access an iPhone passcode without proper authorization may contravene privacy laws, data protection regulations, and intellectual property rights. The unauthorized circumvention of passcode security constitutes a violation of the user's privacy and the sanctity of their personal data. Moreover, it infringes upon the legal framework that safeguards individuals' rights to digital privacy and data security.
Ethically, the act of accessing an iPhone passcode without explicit consent raises fundamental questions about integrity, trust, and respect for individual autonomy. It challenges the ethical principles that underpin the relationship between technology users and their right to privacy. By breaching the passcode security, individuals intrude upon the digital boundaries of others, undermining the fundamental trust that underlies personal and professional interactions. This erosion of trust can have far-reaching implications, impacting relationships, reputations, and the broader societal fabric.
Furthermore, from a professional and organizational perspective, the ethical considerations of accessing an iPhone passcode extend to the realm of corporate governance, data protection, and compliance. Organizations and employees are bound by ethical obligations to uphold the confidentiality and security of sensitive corporate data. Unauthorized access to an employee's iPhone passcode not only violates their individual privacy but also compromises the integrity of corporate information, potentially leading to legal liabilities, reputational damage, and regulatory non-compliance.
In navigating the complex landscape of legal and ethical considerations surrounding iPhone passcode access, individuals and organizations must prioritize the adherence to established laws, regulations, and ethical standards. This entails respecting the privacy rights of individuals, obtaining explicit consent for access when warranted, and upholding the principles of data protection and digital ethics. By embracing a conscientious approach to passcode security, users can foster a culture of trust, integrity, and respect for privacy, thereby contributing to a more ethical and legally compliant digital ecosystem.
In essence, the legal and ethical considerations for accessing an iPhone passcode underscore the imperative of upholding privacy rights, data protection principles, and ethical standards in the realm of digital security. By embracing a principled approach to passcode access, individuals and organizations can cultivate a culture of ethical responsibility, trust, and respect for privacy in the digital domain.
Tips for Creating a Strong Passcode for iPhone 10
Creating a robust passcode is paramount in fortifying the security of your iPhone 10 and safeguarding your personal data from unauthorized access. By adhering to best practices for passcode creation, you can significantly enhance the resilience of your device's security measures. Here are essential tips for crafting a strong passcode:
-
Length and Complexity: Opt for a passcode that is at least six digits long. Consider using a longer alphanumeric passcode, comprising a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters, to bolster its complexity and resilience against brute force attacks.
-
Avoid Common Patterns: Refrain from using easily guessable patterns such as repetitive or sequential numbers (e.g., 123456) or keyboard patterns (e.g., 2580). Instead, opt for a non-sequential, non-repetitive arrangement of characters to enhance the unpredictability of your passcode.
-
Unique and Personalized: Create a passcode that is unique to you and not easily associated with publicly available personal information. Avoid using easily guessable information such as birthdates, anniversaries, or phone numbers, as these can be exploited through social engineering or targeted guessing.
-
Biometric Fallback: While biometric authentication methods such as Face ID and Touch ID offer convenience, it is crucial to have a strong passcode as a fallback option. In situations where biometric authentication may not be feasible or reliable, a robust passcode serves as a dependable alternative for accessing your device.
-
Regular Updates: Periodically update your passcode to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access. Changing your passcode at regular intervals can thwart potential unauthorized attempts to gain access to your device, thereby enhancing its overall security posture.
-
Memorization and Safekeeping: Commit your passcode to memory and refrain from recording it in easily accessible locations such as notes, messages, or unsecured digital platforms. If necessary, consider utilizing secure password management tools to store and manage your passcode securely.
By implementing these tips, you can bolster the security of your iPhone 10 and fortify its defenses against unauthorized access attempts. A strong passcode serves as a fundamental pillar of your device's security, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of your personal data in an increasingly interconnected digital landscape.