What is NFC?
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a wireless technology that enables seamless communication between devices in close proximity, typically within a few centimeters. This technology allows for the exchange of data, including files, contactless payments, and information sharing, simply by bringing NFC-enabled devices close together.
NFC operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where two devices equipped with NFC chips can establish communication when placed near each other. This technology is widely used in various applications, including mobile payments, access control, transportation, and more.
One of the key features of NFC is its ability to facilitate quick and convenient transactions. For instance, with NFC-enabled smartphones, users can make contactless payments at retail stores, restaurants, and other establishments equipped with NFC terminals. This eliminates the need for physical credit cards or cash, offering a more efficient and secure payment method.
Moreover, NFC technology is also utilized for sharing information between devices. For example, users can easily share photos, videos, contact details, and other data by simply tapping their NFC-enabled devices together. This seamless data transfer capability simplifies the process of exchanging information, making it particularly useful in social and professional settings.
In addition to data sharing and contactless payments, NFC plays a crucial role in enabling location-based services. By leveraging NFC technology, devices can interact with NFC tags or stickers embedded in physical locations, triggering specific actions or providing relevant information to users. This capability has significant implications for enhancing user experiences in various contexts, such as retail, tourism, and event management.
Overall, NFC technology offers a versatile and convenient means of communication and interaction between devices. Its applications extend across diverse industries, contributing to the advancement of contactless transactions, seamless data sharing, and location-based services. As NFC continues to evolve, its potential for simplifying everyday tasks and enhancing user experiences remains a driving force in the realm of wireless connectivity.
NFC on iPhone 13
The iPhone 13 series introduces advanced NFC capabilities, leveraging this technology to offer users a seamless and intuitive experience. Equipped with a built-in NFC chip, the iPhone 13 enables a wide range of functionalities that harness the potential of NFC for various applications.
With the NFC feature on the iPhone 13, users can effortlessly engage in contactless transactions using Apple Pay. By simply holding their iPhone 13 near an NFC-enabled payment terminal, users can complete secure and convenient transactions without the need for physical credit or debit cards. This streamlined payment process not only enhances convenience but also prioritizes security, as sensitive payment information is securely stored within the device's NFC chip.
Moreover, the NFC functionality on the iPhone 13 extends beyond payment transactions. This technology enables seamless connectivity with other NFC-enabled devices, allowing for quick and efficient data sharing. Whether it's exchanging contact information, sharing photos, or transferring files, the iPhone 13's NFC capabilities facilitate effortless communication between compatible devices, enhancing user convenience and productivity.
In addition to peer-to-peer communication, the iPhone 13 leverages NFC for location-based services. By interacting with NFC tags or stickers placed in physical locations, users can access relevant information, trigger specific actions, or initiate personalized experiences. This opens up opportunities for innovative applications in retail, tourism, and event management, where users can seamlessly engage with their surroundings through their iPhone 13, enhancing their overall experience.
Furthermore, the iPhone 13's NFC technology supports the integration of smart home devices and accessories. With NFC-compatible smart home products, users can easily pair and control their devices using their iPhone 13, simplifying the management of connected home environments. This seamless integration enhances user convenience and promotes the adoption of smart home technologies, contributing to a more connected and efficient lifestyle.
Overall, the NFC capabilities of the iPhone 13 empower users with a versatile and intuitive platform for contactless transactions, seamless data sharing, location-based interactions, and smart home integration. By harnessing the potential of NFC technology, the iPhone 13 delivers a comprehensive and user-centric experience, aligning with Apple's commitment to innovation and user convenience.
How to Use NFC for Location Services
Utilizing NFC for location services on the iPhone 13 involves a seamless and intuitive process that enhances user interactions with physical environments. By leveraging the NFC capabilities of the device, users can engage with NFC tags or stickers placed in specific locations, triggering customized actions or accessing relevant information. Here's a detailed overview of how to effectively use NFC for location services on the iPhone 13:
-
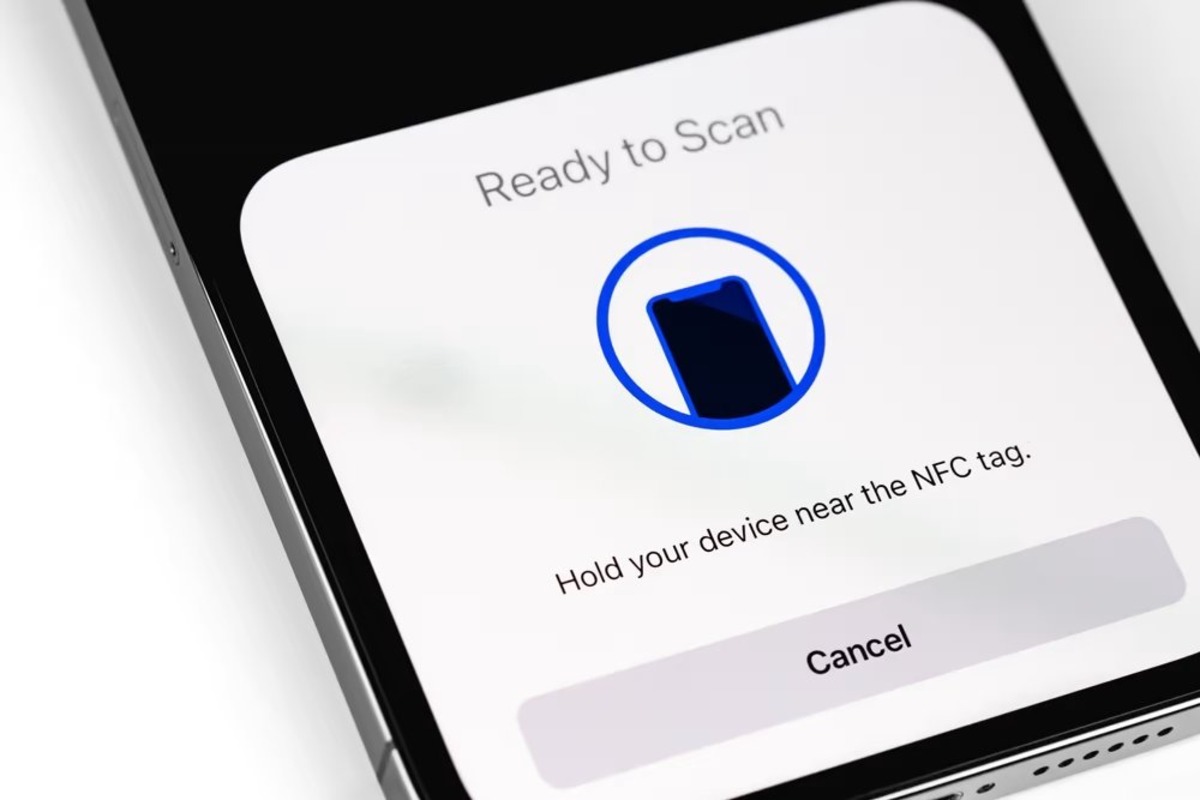
Enabling NFC: To begin using NFC for location services, ensure that NFC is enabled on your iPhone 13. This can be done by accessing the device's settings and enabling the NFC feature. Once activated, the iPhone 13 is ready to interact with NFC tags and stickers in the surrounding environment.
-
Approaching NFC Tags: When in proximity to an NFC tag or sticker, simply bring the iPhone 13 close to the tag to initiate communication. The NFC chip within the device will detect the presence of the tag, enabling seamless interaction without the need for physical contact.
-
Triggering Actions: NFC tags embedded in physical locations can be programmed to trigger specific actions when accessed by an NFC-enabled device. For instance, in a retail setting, an NFC tag placed near a product display can provide users with detailed product information, promotional offers, or the option to make a purchase directly from their iPhone 13.
-
Accessing Information: NFC tags can also be utilized to provide users with relevant information based on their location. For example, in a museum or historical site, NFC tags placed near exhibits can offer detailed descriptions, audio guides, or interactive content, enriching the visitor experience and providing valuable context about the surroundings.
-
Personalized Experiences: With the iPhone 13's NFC capabilities, location-based interactions can be personalized to cater to individual preferences. By tapping their device on an NFC tag, users can access customized content, exclusive offers, or tailored experiences that enhance their engagement with the environment.
-
Integration with Apps: The iPhone 13's NFC functionality seamlessly integrates with compatible apps, allowing for a diverse range of location-based services. Whether it's accessing event information, redeeming rewards, or unlocking exclusive content, the device's NFC technology enhances the overall user experience in various contexts.
By following these steps, users can effectively harness the NFC capabilities of the iPhone 13 for location services, unlocking a myriad of possibilities for seamless interactions with physical environments and personalized experiences tailored to their preferences and interests.
NFC Location Use Cases
NFC technology, when integrated with location-based services, opens up a diverse array of compelling use cases that enhance user experiences across various domains. The iPhone 13's NFC capabilities, combined with its advanced features, enable seamless interactions with NFC tags or stickers placed in physical locations, giving rise to innovative and practical applications. Here are several noteworthy NFC location use cases that demonstrate the versatility and potential of this technology:
-
Retail Enhancements: In retail environments, NFC tags strategically placed near products or promotional displays can provide customers with instant access to detailed product information, pricing, and customer reviews. Additionally, NFC-enabled iPhone 13 devices can facilitate contactless transactions, allowing customers to make purchases directly from their devices by tapping on NFC tags associated with specific products.
-
Tourism and Cultural Sites: NFC tags deployed at tourist attractions, museums, and historical sites can enrich visitors' experiences by offering interactive audio guides, detailed historical information, and multimedia content. Users can simply tap their iPhone 13 on the NFC tags to access relevant and engaging content, enhancing their understanding and appreciation of the cultural and historical significance of the location.
-
Event Management: NFC technology integrated with event management can streamline attendee interactions and enhance event experiences. For instance, at conferences or trade shows, attendees can use their iPhone 13 to tap on NFC tags to access event schedules, speaker details, and exclusive content. Furthermore, NFC-enabled badges or wristbands can simplify check-in processes and enable seamless networking opportunities.
-
Smart Transportation: NFC tags placed at transportation hubs, such as bus stops or train stations, can provide commuters with real-time schedules, service updates, and route information. By tapping their iPhone 13 on the NFC tags, users can conveniently access transportation-related details, facilitating smoother and more informed travel experiences.
-
Interactive Marketing: NFC technology integrated into marketing collateral, such as posters, brochures, or product packaging, can engage consumers in interactive marketing experiences. By tapping their iPhone 13 on NFC-enabled marketing materials, users can access exclusive content, promotional offers, or participate in interactive campaigns, fostering deeper engagement and brand interaction.
-
Healthcare and Wellness: NFC tags incorporated into healthcare facilities or wellness centers can offer patients and visitors access to relevant health information, appointment scheduling, and facility navigation assistance. Patients with NFC-enabled devices, including the iPhone 13, can seamlessly interact with NFC tags to streamline their healthcare experiences and access personalized wellness resources.
These use cases exemplify the diverse applications of NFC technology for location-based services, showcasing its potential to enhance user interactions, streamline processes, and deliver personalized experiences. By leveraging the NFC capabilities of the iPhone 13, these use cases underscore the device's role in facilitating seamless and intuitive interactions with physical environments, ultimately enriching user experiences across various domains.
NFC Location Privacy and Security
Ensuring robust privacy and security measures within NFC-based location services is paramount to safeguarding user data and maintaining trust in the technology. The integration of NFC technology with location-based services on the iPhone 13 necessitates a comprehensive approach to address privacy concerns and mitigate potential security risks.
Privacy Considerations
When utilizing NFC for location-based interactions, preserving user privacy is of utmost importance. The iPhone 13's NFC capabilities must adhere to stringent privacy standards to protect sensitive user information. Privacy considerations include:
-
Data Minimization: NFC interactions should prioritize minimal data exchange, ensuring that only essential information is transmitted during location-based interactions. This approach mitigates the risk of unnecessary data exposure.
-
User Consent: Implementing clear and transparent consent mechanisms is crucial. Users should have full control over their participation in NFC-enabled location services, with the ability to grant or revoke consent for data sharing and interaction.
-
Anonymization: Where applicable, NFC-based location services should prioritize anonymization of user data to prevent the direct association of personal information with location-based interactions, thereby safeguarding user identities.
Security Measures
Robust security measures are essential to protect NFC-enabled location services from potential vulnerabilities and unauthorized access. The iPhone 13's NFC technology must incorporate advanced security protocols to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of user interactions. Security measures include:
-
Encryption: Implementing strong encryption protocols for NFC data transmission is critical to prevent unauthorized interception and ensure the confidentiality of user interactions with NFC tags and stickers.
-
Authentication: Utilizing secure authentication mechanisms within NFC-based location services enhances the trustworthiness of interactions. Authentication protocols validate the legitimacy of NFC tags and stickers, mitigating the risk of fraudulent or malicious activities.
-
Secure Element Integration: Leveraging the secure element within the iPhone 13's NFC chip enhances security by isolating sensitive data and cryptographic operations, safeguarding critical information from unauthorized access.
-
Tamper Resistance: NFC tags and stickers deployed in physical locations should incorporate tamper-resistant features to prevent unauthorized modifications or cloning, thereby maintaining the integrity of location-based interactions.
By prioritizing privacy considerations and implementing robust security measures, the integration of NFC technology with location-based services on the iPhone 13 can foster a trusted and secure environment for user interactions. Upholding stringent privacy standards and advanced security protocols is essential to instill confidence in NFC-enabled location services, ensuring that user data remains protected and interactions remain secure.