Reasons to Roll Back a Driver in Windows
Updating drivers is an essential task for any Windows user, as it ensures that the hardware devices on your system work smoothly and efficiently. However, there may come a time when you need to roll back a driver to a previous version. Here are a few reasons why you might consider rolling back a driver in Windows:
- Compatibility issues: Sometimes, after updating a driver, you may experience compatibility issues with your software, causing crashes, errors, or malfunctions. Rolling back the driver to a previous version can help resolve these compatibility issues.
- Performance problems: Occasionally, a driver update can have unintended negative effects on the performance of your devices. If you notice a sudden decrease in performance or stability after updating a driver, rolling back to a previous version might help restore optimal performance.
- Driver conflicts: In certain situations, different drivers may conflict with one another, leading to erratic behavior or system crashes. Rolling back a driver can help resolve conflicts between different driver versions and restore system stability.
- Malfunctioning hardware: There may be instances where a newly updated driver causes hardware devices to malfunction, such as a printer not recognizing ink cartridges or a graphics card displaying distorted images. Rolling back the driver to a previous version can often resolve these hardware-related issues.
- Regression in functionality: Sometimes, an updated driver may introduce changes or remove features that were present in the previous version. If you rely on a specific feature or functionality that is no longer available after an update, rolling back to the previous driver version can restore that functionality.
Rolling back a driver is a straightforward process that involves uninstalling the current driver and installing an older version. The method to roll back a driver may vary depending on the Windows version and the driver update tool you are using. In the following sections, we will explore different methods you can use to roll back a driver in Windows, including using Device Manager, Windows Update, Driver Booster, and System Restore.
Checking the Driver Version
Before you proceed with rolling back a driver in Windows, it is important to check the current driver version to ensure that you are rolling back to the correct version. Here is how you can check the driver version:
- Open Device Manager by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting “Device Manager” from the menu.
- Navigate to the device category for which you want to check the driver version. For example, if you want to check the display driver version, expand the “Display adapters” category.
- Right-click on the device and select “Properties” from the context menu.
- In the Properties window, go to the “Driver” tab.
- Look for the “Driver version” or “Driver date” information, which will display the current version installed on your system.
Make a note of the driver version, as you will need this information when rolling back the driver to the previous version.
It is worth mentioning that manually checking the driver version in Device Manager can be a time-consuming process, especially if you have multiple devices with different drivers. Alternatively, you can use driver update tools like Driver Booster, which can automatically scan your system and provide you with a detailed report of all the drivers along with their versions.
Once you have verified the current driver version, you can proceed with rolling back the driver using the appropriate method. In the next sections, we will discuss various methods to roll back a driver in Windows, including using Device Manager, Windows Update, Driver Booster, and System Restore.
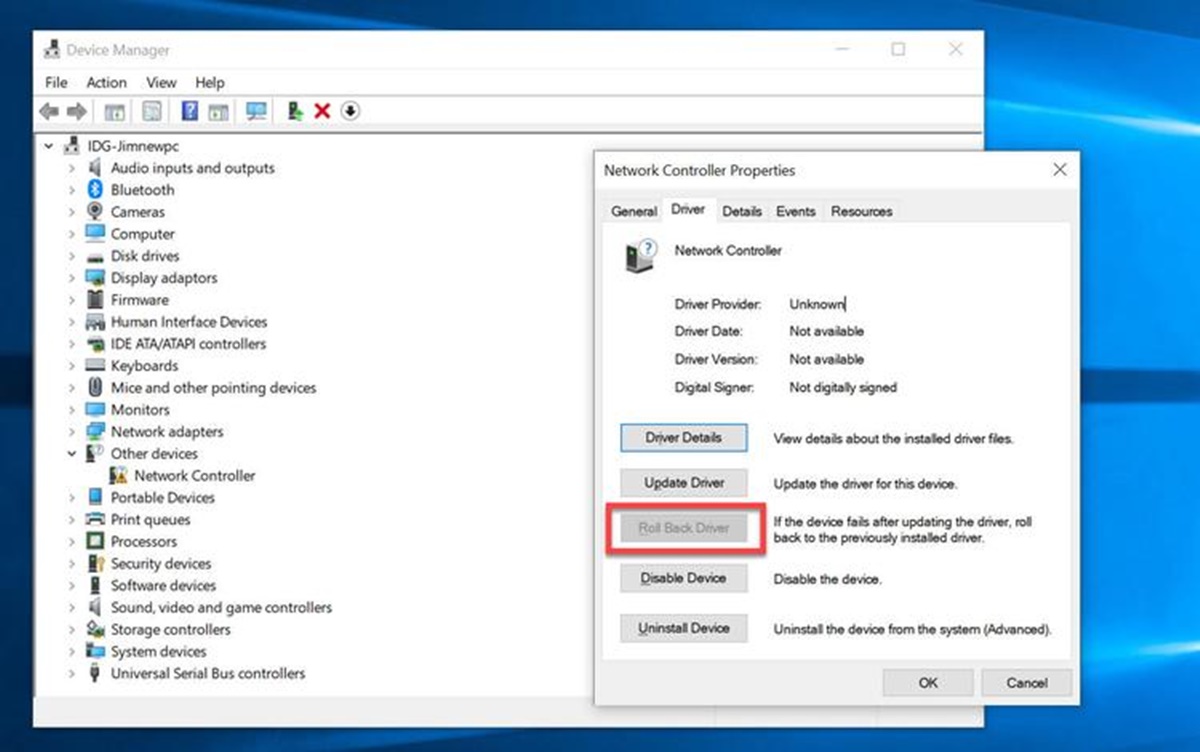
Roll Back a Driver Using Device Manager
Device Manager is a built-in Windows tool that allows you to manage and control hardware devices on your system. It also provides the option to roll back a driver to a previous version. Here is how you can roll back a driver using Device Manager:
- Open Device Manager by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting “Device Manager” from the menu.
- Navigate to the device category for which you want to roll back the driver. For example, if you want to roll back the display driver, expand the “Display adapters” category.
- Right-click on the device and select “Properties” from the context menu.
- In the Properties window, go to the “Driver” tab.
- Click on the “Roll Back Driver” button.
- Windows will ask you to confirm the action. You can select a reason for rolling back the driver, or you can leave it blank.
- Click on “Yes” to proceed with the rollback process.
- Wait for Windows to uninstall the current driver and install the previously installed driver.
- Once the rollback process is complete, you may be prompted to restart your computer. If so, click on “Restart Now” to restart your system.
It is important to note that the availability of the “Roll Back Driver” button in Device Manager depends on whether there is a previously installed driver on your system. If there is no previous driver available, the button will be grayed out and unavailable.
Rolling back a driver using Device Manager can be a simple way to revert to a previous driver version if you are experiencing compatibility issues or performance problems. However, it is not always guaranteed to solve the problem. If rolling back the driver does not resolve the issue, you may want to explore other methods, such as using Windows Update or third-party driver update tools.
Roll Back a Driver Using Windows Update
Windows Update is a service provided by Microsoft that allows users to download and install the latest updates for their operating system and device drivers. Windows Update also keeps a record of previously installed drivers, making it possible to roll back to a previous version if needed. Here is how you can roll back a driver using Windows Update:
- Open the Start menu and go to “Settings.”
- Click on “Update & Security.”
- In the left sidebar, select “Windows Update.”
- Click on “View update history.”
- In the update history window, click on “Uninstall updates.”
- A list of installed updates will appear. Look for the driver update that you want to roll back and select it.
- Click on the “Uninstall” button at the top of the list.
- Windows will ask you to confirm the action. Click on “Yes” to proceed with the uninstallation.
- Once the driver update is uninstalled, your system should automatically revert to the previously installed driver version.
- Restart your computer if prompted to complete the rollback process.
Rolling back a driver using Windows Update can be a convenient option if you have recently installed a driver update through this service. However, keep in mind that Windows Update may not always have the previous version of the driver available for rollback. In such cases, you may need to use alternative methods, such as using Device Manager or third-party driver update tools.
It is also worth noting that rolling back a driver using Windows Update only applies to updates that have been installed through this service. If you have installed drivers manually or through other sources, those drivers may not appear in the list of installed updates in Windows Update. In such cases, you will need to use alternative methods to roll back the driver.
Roll Back a Driver Using Driver Booster
Driver Booster is a popular third-party driver update tool that can automatically scan, download, and install the latest drivers for your system. It also offers the option to roll back a driver to a previous version if needed. Here is how you can roll back a driver using Driver Booster:
- Launch Driver Booster on your computer.
- Click on the “Scan” button to initiate a scan for outdated drivers.
- After the scan is complete, Driver Booster will display a list of drivers that have updates available.
- Locate the driver that you want to roll back in the list and click on the “Rollback” button next to it.
- Driver Booster will ask you to confirm the rollback action. Click on “Yes” to proceed.
- Wait for Driver Booster to uninstall the current driver and install the previous version.
- Once the rollback process is complete, you may need to restart your computer to apply the changes.
Driver Booster is a convenient option for rolling back drivers because it keeps track of previously installed driver versions and allows you to easily revert to a previous version with just a few clicks. However, it is important to note that the availability of rollback options may depend on the specific driver update and its compatibility with Driver Booster.
Additionally, while Driver Booster can be a reliable tool for updating and rolling back drivers, it is always recommended to create a system restore point before making any driver changes. This allows you to revert your system back to its previous state in case any issues arise during the rollback process.
If you find that rolling back a driver using Device Manager or Windows Update is not possible or does not resolve the issue, trying a third-party driver update tool like Driver Booster can be a viable alternative to consider.
Roll Back a Driver Using System Restore
System Restore is a built-in Windows feature that allows you to restore your computer to a previous state, including previous driver versions. By using System Restore, you can roll back a driver to a previous version and potentially resolve any issues that occurred after a driver update. Here is how you can roll back a driver using System Restore:
- Open the Start menu and search for “System Restore.”
- Select “Create a restore point.”
- In the System Protection tab, click on the “System Restore” button.
- Click on “Next” to proceed.
- You will be presented with a list of available restore points. Select a restore point that was created before the driver update.
- Click on “Next” and then “Finish” to start the restoration process.
- Confirm your decision to proceed with the system restore.
- Your computer will restart and initiate the system restore process.
- Once the restoration is complete, your system should now be running with the previous driver version.
System Restore is a powerful tool that can not only rollback driver updates but also undo any system changes that may have caused issues. However, it is important to note that rolling back a driver using System Restore will affect any other system changes made between the restore point and the current state of your system.
It’s worth mentioning that System Restore relies on the presence of restore points created on your system. Therefore, it is recommended to regularly create restore points or enable automatic restore point creation in order to have the option to roll back a driver or undo system changes when needed.
If you have exhausted other options or encountered persistent driver issues, using System Restore to revert your system to a previous state can be an effective solution.
Common Issues When Rolling Back a Driver
While rolling back a driver can often help resolve compatibility or performance issues, it is important to be aware of potential problems that may arise during the rollback process. Here are some common issues that you may encounter when rolling back a driver:
- Lack of previous driver version: In some cases, there may not be a previous driver version available for rollback. This can happen if the previous driver was not automatically backed up or if you do not have a restore point that includes the previous driver version.
- Unstable system: Rolling back a driver can sometimes lead to an unstable system, causing crashes or errors. This can occur if the driver rollback is not fully compatible with your hardware or software configuration.
- Incompatibility with other drivers: Rolling back a driver may introduce compatibility issues with other drivers on your system. This can result in conflicts or system instability that may require further troubleshooting or driver updates.
- Functionality limitations: It is possible that rolling back to a previous driver version may remove certain features or functionality that were present in the updated driver. This can impact the performance or capabilities of your hardware devices.
- Reinstallation requirements: In some cases, rolling back a driver may require you to reinstall certain software or reconfigure your system settings. This additional effort may be necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the rolled-back driver.
If you experience any of these issues when rolling back a driver, it is recommended to perform additional troubleshooting steps. Some options you can consider include updating other drivers, performing a clean installation of the driver, or seeking assistance from the hardware manufacturer’s support team.
It is important to note that rolling back a driver should be approached with caution and used as a troubleshooting step when necessary. If you are not experiencing any issues with a driver update, it is generally advisable to keep your drivers up to date to ensure optimal performance and security.