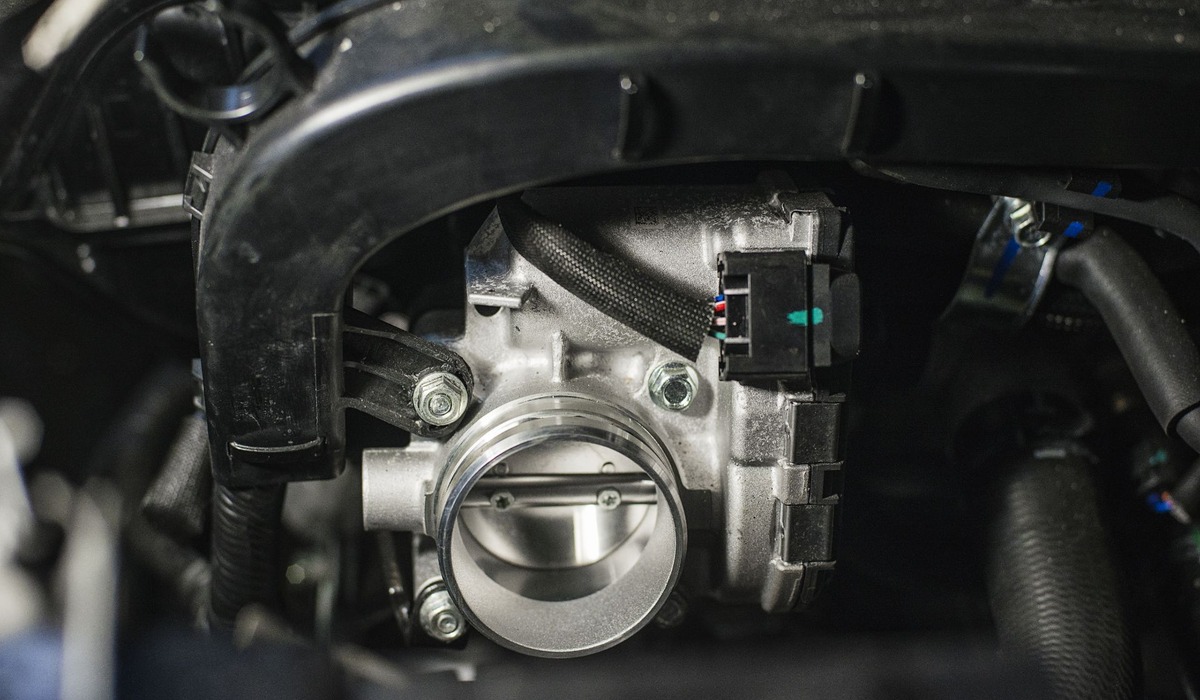
What is Electronic Throttle Control?
Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) is a modern technology used in vehicles to regulate the throttle opening, which controls the amount of air that enters the engine. Instead of the traditional mechanical throttle linkage, ETC uses electronic sensors and actuators to communicate the driver’s throttle input to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU then adjusts the throttle opening accordingly to maintain optimal engine performance.
The ETC system consists of several components, including the electronic throttle body, throttle position sensor, accelerator pedal position sensor, and the ECU. Together, these components ensure smooth vehicle acceleration, enhanced fuel efficiency, and precise throttle control.
The electronic throttle body is a key component of the ETC system. It contains an electric motor that controls the throttle plate’s position based on the driver’s input. This allows for quicker response times and more accurate control of the engine’s airflow. The throttle position sensor measures the throttle plate’s angle and sends this information to the ECU, which then adjusts other engine parameters such as fuel injection and ignition timing.
By eliminating the mechanical linkages, ETC provides several advantages. It allows for the integration of advanced safety features such as traction control and stability control. ETC also enables the implementation of features like adaptive cruise control and throttle-by-wire systems, which can enhance the driving experience and improve overall vehicle performance.
Overall, Electronic Throttle Control is a sophisticated system that has replaced conventional throttle controls in modern vehicles. It offers greater control, improved fuel efficiency, and enables the integration of advanced safety and performance features. Understanding the components and functioning of the ETC system is essential for diagnosing and fixing any issues that may arise with throttle control.
Signs of a Faulty Electronic Throttle Control
Being aware of the signs that indicate a faulty Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system can help you identify and address potential issues before they worsen. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
1. Erratic Acceleration: If you experience sudden surges or delays in acceleration, it could be a sign of a malfunctioning ETC system. The throttle may not respond consistently to your input, leading to unpredictable acceleration patterns.
2. Engine Misfires: A faulty ETC system can cause the engine to misfire, resulting in rough idling or a noticeable decrease in power. This can be attributed to incorrect fuel-air mixture ratios caused by improper throttle control.
3. Unresponsive Throttle: An ETC system issue may cause the throttle to become unresponsive or fail to open fully, even when you press the accelerator pedal. This can lead to a significant reduction in engine power and may compromise your ability to control the vehicle.
4. Warning Lights: If the Check Engine Light or the Electronic Throttle Control warning light illuminates on your vehicle’s dashboard, it is a clear indication of a problem with the ETC system. Do not ignore these warning lights and seek diagnosis and repairs immediately.
5. Poor Fuel Efficiency: A malfunctioning ETC system can disrupt the engine’s fuel injection and air intake, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. If you notice a sudden drop in gas mileage without any other apparent causes, it is worth inspecting the ETC system.
It is important to note that these signs can also overlap with symptoms of other potential issues, so a proper diagnosis is crucial. If you experience any of these signs or suspect ETC system problems, it is advisable to consult a professional mechanic or technician who can perform a thorough inspection and accurately diagnose the issue.
Diagnosing the Problem
When encountering issues with the Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system, it’s important to diagnose the problem accurately before attempting any repairs or replacements. Here are some steps you can take to diagnose ETC problems:
1. Scan for Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any error codes stored in the engine control unit (ECU). These codes provide valuable information about the specific nature of the ETC system malfunction and can guide you towards the appropriate diagnostics.
2. Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Thoroughly examine the wiring harness and connectors associated with the ETC system. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections that could interfere with the proper functioning of the system. Repair or replace any defective components as necessary.
3. Check Throttle Body Operations: Inspect the throttle body for any physical obstructions or carbon buildup that may hinder its movement. Ensure that the throttle plate opens and closes freely without any sticking or binding. Clean the throttle body if necessary to remove any accumulated debris.
4. Test Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the TPS while manually opening and closing the throttle. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly. Replace the TPS if it is out of range.
5. Update Software or Replace Control Module: In some cases, a software update from the vehicle manufacturer may resolve ETC system issues. Check for any available updates and follow the manufacturer’s instructions to perform the update. If the problem persists, a faulty control module may need to be replaced.
It’s important to note that diagnosing ETC system problems can be complex, and in some cases, it may require specialized tools and expertise. If you’re unsure or unable to diagnose the problem yourself, it is recommended to consult a professional technician who specializes in ETC systems. They have the knowledge and equipment to perform advanced diagnostics and troubleshoot more intricate issues effectively.
Check the Throttle Body
The throttle body is a vital component of the Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system and plays a crucial role in regulating the airflow into the engine. If you suspect a problem with the ETC system, it’s essential to check the throttle body for any issues. Here are some steps to help you with the inspection:
1. Locate the Throttle Body: The throttle body is typically located between the air intake duct and the intake manifold. It is connected to the accelerator pedal via a cable or electronically controlled by a motor.
2. Inspect for Physical Obstructions: Carefully examine the throttle body for any physical obstructions that may obstruct the movement of the throttle plate. Debris, such as dirt or carbon deposits, can accumulate over time and hinder its proper operation. Clean out any visible obstructions using a soft brush or a clean cloth.
3. Check for Sticking or Binding: Manually open and close the throttle plate with your hand while observing its movement. It should move smoothly without any sticking or binding. If you notice any resistance or abnormal movement, this could indicate a problem with the throttle body and may require further attention.
4. Inspect the Throttle Plate: Examine the throttle plate for signs of wear or damage. It should be clean and free from any cracks or warping. If you notice any signs of deterioration, it may be necessary to replace the throttle body to ensure proper functionality.
5. Check the Throttle Body Motor: If your vehicle has an electronically controlled throttle body, ensure that the motor is operating correctly. Test the motor’s response by turning the ignition on and off while listening for the sound of the motor. If the motor fails to move or makes unusual noises, it may be defective and require replacement.
Remember, if you’re uncomfortable or unsure about inspecting the throttle body yourself, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a qualified technician. They have the necessary tools and expertise to perform a thorough inspection and make any required repairs or replacements to ensure the proper functioning of the throttle body and the overall ETC system.
Inspect the Wiring and Connectors
When dealing with Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system issues, it’s important to examine the wiring harness and connectors associated with the system. Electrical problems can cause malfunctioning or erratic throttle control. Here are the steps to inspect the wiring and connectors:
1. Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the wiring harness and connectors for any visible signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cuts, or corrosion. Pay special attention to areas where the wiring passes through tight spaces or areas exposed to heat or moisture. Repair or replace any damaged wiring as necessary.
2. Check for Loose Connections: Ensure that all connectors related to the ETC system are securely connected. Loose or poorly connected connectors can disrupt the electrical signal and affect throttle control. Gently tug on each connector to check for any signs of looseness. If a connection feels loose, secure it properly.
3. Inspect for Corrosion: Corrosion on connectors can interrupt the electrical flow and lead to unreliable throttle control. Look for greenish or whitish residue on the connectors and use a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner to remove any corrosion. Apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
4. Check Ground Connections: The ETC system relies on proper grounding to function correctly. Inspect the ground connections associated with the system and ensure that they are clean, tight, and free from corrosion. Clean any dirty connections and secure them properly to ensure a solid ground connection.
5. Verify Power Supply: Check the power supply to the ETC system, including fuses and relays. Use a multimeter to test the voltage at various points along the wiring harness to ensure a consistent and reliable power supply. If you find any voltage abnormalities, investigate and address the issue accordingly.
By thoroughly inspecting the wiring and connectors, you can detect issues that may be causing problems with the ETC system. However, if you are not confident in your ability to perform these inspections, it’s advisable to seek assistance from a qualified technician. They have the expertise and specialized equipment to diagnose and repair any electrical issues affecting the ETC system effectively.
Clean the Throttle Body
Over time, the throttle body of the Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system can accumulate carbon deposits and other debris. These deposits can hinder proper airflow and throttle plate movement, leading to performance issues. Cleaning the throttle body can help restore optimal functionality. Here’s how to clean the throttle body:
1. Gather the necessary tools: You will need a can of throttle body cleaner, a clean cloth or brush, and possibly a small screwdriver (if needed to remove the throttle body for thorough cleaning).
2. Locate the throttle body: The throttle body is typically located between the air intake duct and the intake manifold. It may be secured with bolts or clamps. Refer to the vehicle’s manual for specific instructions on locating and accessing the throttle body.
3. Disconnect the air intake duct: Depending on the design of the throttle body, you may need to disconnect the air intake duct that connects to it. Use a screwdriver or pliers to loosen and remove any clamps securing the duct.
4. Spray throttle body cleaner: With the throttle body exposed, use the throttle body cleaner to spray it thoroughly. Be sure to direct the cleaner towards the throttle plate, ensuring that it reaches all areas where carbon deposits may be present. Follow the instructions on the cleaner can for the recommended spray pattern and dosage.
5. Scrub away deposits: Use a clean cloth or brush to gently scrub away any carbon buildup on the throttle body. Pay close attention to the edges and the area around the throttle plate. Be cautious not to scratch or damage any components.
6. Wipe clean: Use a clean cloth to wipe away any remaining cleaner and debris from the throttle body. Ensure that the throttle plate can move freely and there is no residue left behind.
7. Reassemble the components: Reattach the air intake duct and secure any clamps or bolts as necessary. Ensure that all connections are tight and properly secured.
Cleaning the throttle body can help restore proper airflow and throttle plate movement, resulting in improved engine performance and responsiveness. It is recommended to perform this maintenance task periodically, as carbon buildup can occur over time. However, if you are unfamiliar or uncomfortable with performing this procedure, it is best to consult a professional mechanic for assistance.
Resetting the Electronic Throttle Control
If you’ve encountered issues with the Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system, one troubleshooting step you can take is to reset the system. Resetting the ETC can help recalibrate the throttle position and clear any inconsistencies or faults in the system. Here’s how to reset the Electronic Throttle Control:
1. Turn off the ignition: Ensure that the vehicle’s ignition is turned off before proceeding with the reset process. This will prevent any accidental starting of the engine during the procedure.
2. Disconnect the battery: Locate the vehicle’s battery and disconnect the negative (-) terminal using a wrench or a socket. Wait for approximately 10-15 minutes to allow any residual electrical charge to dissipate.
3. Reconnect the battery: Reconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery and tighten it securely. Make sure there is a solid connection.
4. Turn on the ignition: Turn on the vehicle’s ignition without starting the engine. Allow the system to power up completely. Be patient as this may take a few moments.
5. Step on the accelerator pedal: Press the accelerator pedal to the floor and hold it in that position for approximately 30 seconds. This will help reset the throttle position sensor and allow the system to recalibrate.
6. Release the accelerator pedal: After holding the accelerator pedal for 30 seconds, release it. The throttle control system will now configure and calibrate itself to the new position of the throttle plate.
7. Start the engine: Start the engine as you normally would and allow it to idle for a few minutes. This will enable the ETC system to relearn the idle and throttle control parameters based on the new calibration.
Resetting the Electronic Throttle Control can help resolve certain issues related to throttle responsiveness, idle control, or error codes. However, it’s important to note that not all ETC problems can be resolved by a simple reset. If the issues persist or if you’re uncertain about performing the reset procedure, it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or technician who can diagnose and address any underlying problems with the ETC system.
Replace the Throttle Position Sensor
If you’ve diagnosed a faulty Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) as the cause of Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system issues, replacing the sensor may be necessary. The TPS is responsible for measuring the position of the throttle plate and sending this information to the engine control unit (ECU). Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you replace the TPS:
1. Locate the TPS: The TPS is typically located on the side of the throttle body, directly attached to the throttle shaft. Refer to your vehicle’s manual or consult a repair guide to precisely locate the TPS in your specific vehicle.
2. Disconnect the electrical connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector that connects the TPS to the wiring harness. Depending on the design of the connector, you may need to use a small screwdriver or pry tool to release any locking mechanisms before disconnecting it.
3. Remove the TPS: The TPS is usually secured to the throttle body with a few bolts or screws. Use the appropriate tools (such as a wrench or a screwdriver) to carefully loosen and remove these fasteners. Take note of their locations, as you will need to reattach them when installing the new TPS.
4. Install the new TPS: Take the new TPS and align it with the bolt holes on the throttle body. Carefully insert the bolts or screws and tighten them by hand until snug. Be cautious not to overtighten, as this can damage the TPS or throttle body.
5. Reconnect the electrical connector: Make sure the electrical connector is clean and in good condition. Align the connector with the TPS and securely reconnect it. You may need to apply slight pressure or use locking mechanisms (if present) to ensure a proper connection.
6. Test the new TPS: Start the engine and verify that the new TPS is functioning correctly. Check for any error codes related to the TPS and monitor the throttle response. Ensure that the throttle plate opens and closes smoothly without any hitches or delays.
Replacing the Throttle Position Sensor can significantly improve the performance and responsiveness of the Electronic Throttle Control system. However, if you’re unsure about the replacement process or if you’re experiencing persistent issues, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician. They have the necessary expertise to properly diagnose and replace the TPS, ensuring that the ETC system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Update Software or Replace Control Module
If you’ve exhausted other troubleshooting steps and still encounter issues with the Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system, updating the software or replacing the control module may be necessary. Here are the considerations for each option:
1. Update Software: Manufacturers occasionally release updates or patches for their vehicle’s software. These updates can address ETC system-related issues and improve overall performance. To update the software, you will need to visit a dealership or authorized service center, as they have the necessary tools and access to the latest software updates. They will connect your vehicle to a diagnostic tool to deliver the software update.
2. Replace Control Module: In some cases, a malfunctioning control module may be the root cause of persistent ETC system problems. The control module is responsible for interpreting the throttle input and controlling the throttle plate’s movement. If other troubleshooting steps have failed to resolve the issue, replacing the control module may be necessary. It’s crucial to consult a professional mechanic or technician for this task, as it requires programming and configuring the new module to match your vehicle’s specifications.
When deciding between updating the software or replacing the control module, it’s best to seek advice from a qualified technician. They can diagnose the exact cause of the ETC system problems through thorough testing and analysis. They may also utilize diagnostic tools to retrieve error codes and determine if a software update or control module replacement is warranted.
It’s important to note that updating the software and replacing the control module may require specialized knowledge and tools. Attempting these tasks without proper expertise can lead to further complications or damage to the vehicle. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to rely on professional assistance to ensure a successful update or replacement.
In some cases, the technician may recommend performing a software update first before considering control module replacement. This is because software updates can often resolve common ETC system issues, saving you the cost of replacing the control module. However, the final decision and course of action depend on the technician’s assessment of the specific situation.
By updating the software or replacing the control module, you can address complex ETC system issues and restore optimal performance to your vehicle. Always rely on professional advice and expertise to ensure the most appropriate solution for your specific circumstances.
Seek Professional Help
When it comes to addressing Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) system issues, seeking professional help is often the best course of action. Certified mechanics or technicians have the expertise, experience, and specialized tools to diagnose and resolve complex ETC problems effectively. Here’s why seeking professional help is important:
1. Accurate Diagnosis: Professional technicians have in-depth knowledge of ETC systems and can accurately diagnose the root cause of the issue. They utilize specialized diagnostic tools and techniques to identify specific faults and errors in the system, saving you time and money on unnecessary guesswork or trial and error.
2. Proper Equipment: Professional repair facilities are equipped with the necessary tools and equipment required to work on ETC systems. They have access to diagnostic scanners, software updates, and specialized tools to perform precise repairs and replacements. This ensures that the work is done correctly and that the ETC system functions smoothly afterward.
3. Manufacturer Expertise: Authorized service centers have direct communication with vehicle manufacturers and access to technical support and resources. They stay updated on the latest ETC system technologies, software updates, and diagnostic procedures recommended by the manufacturer. Their expertise ensures that repairs and replacements are carried out according to manufacturer standards.
4. Warranty Considerations: If your vehicle is under warranty, seeking professional help is particularly crucial. Attempting DIY repairs or going to unauthorized repair shops may void your warranty. Authorized service centers ensure that repairs and replacements are conducted within warranty guidelines, protecting your investment in the vehicle.
5. Complex Repairs: Some ETC issues, such as control module replacements or software updates, require specialized knowledge and technical know-how. Professional technicians have the training and experience to perform these complex repairs and ensure that the ETC system functions optimally.
It’s important to communicate your specific concerns and observations with the professional technician. Share any error codes, abnormal symptoms, or recent changes in the vehicle’s behavior. This will assist them in performing a more accurate diagnosis and resolving the ETC issue effectively.
When it comes to the Electronic Throttle Control system, entrusting the repair and maintenance to professionals is the wisest choice. They have the skills, resources, and up-to-date knowledge to properly address the complexities of the system, ensuring that your vehicle operates safely and reliably.