What is Bi-Wiring?
Bi-wiring is a technique used to enhance the performance of stereo speakers by separating the frequencies that are sent to the speaker’s woofer and tweeter drivers. Typically, traditional speaker setups use a single set of cables to connect the amplifier to the speaker’s terminals, with the audio signal being shared across the entire frequency spectrum.
However, with bi-wiring, the speaker is equipped with separate terminals for the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers, allowing for the use of two sets of cables. One set connects the amplifier to the woofer terminals, carrying the lower frequencies, while the second set connects the amplifier to the tweeter terminals, carrying the higher frequencies.
The idea behind bi-wiring is to minimize interference between the different frequencies by providing a cleaner and more direct signal path to each driver. By separating the signal, it is believed that this method can improve sound clarity, reduce distortion, and enhance overall audio performance.
It is important to note that bi-wiring is not the same as bi-amping. Bi-amping involves using multiple amplifiers to separately power the high and low-frequency drivers, while bi-wiring focuses on the separation of the frequencies through the use of different speaker cables.
Bi-wiring is primarily applicable to speakers that have been designed with this feature in mind. These speakers will have two sets of binding posts or connectors, one set for the high-frequency driver and another set for the low-frequency driver. It is essential to check the specifications of your speakers to determine if they support bi-wiring.
Benefits of Bi-Wiring
Bi-wiring offers several potential benefits that can improve the performance of your stereo speakers:
- Improved Clarity: By separating the frequencies and providing dedicated cables for the woofer and tweeter drivers, bi-wiring can help reduce interference and improve the clarity of the audio. This can result in sharper and more defined sound reproduction, allowing you to enjoy your music or movies with greater detail.
- Reduced Distortion: Bi-wiring can minimize the distortion that can occur when the different frequencies interact with each other. By using separate cables, the risk of signal cross-talk and interference is reduced, ensuring that each driver receives a clean and undistorted signal. This can lead to a more accurate and faithful reproduction of the original audio.
- Enhanced Soundstage: The separation of frequencies through bi-wiring can contribute to an improved soundstage. With a wider soundstage, the audio can appear more spacious and three-dimensional, creating a more immersive listening experience. Instruments and vocals can be better positioned within the soundstage, providing a sense of depth and realism.
- Better Control: Bi-wiring allows for greater control over the different drivers within the speaker. As each driver receives its own signal, the amplifier can have better control over the power and dynamics delivered to each driver. This increased control can result in tighter bass response, accurate midrange reproduction, and more detailed highs.
- Customization: Bi-wiring provides an additional level of customization for your audio setup. You can experiment with different cables for the high and low-frequency drivers, allowing you to tailor the sound to your preferences. This flexibility enables you to fine-tune the performance of your speakers to match your specific listening environment and personal taste.
While the benefits of bi-wiring can vary depending on the specific system and speakers used, many audio enthusiasts find that it offers noticeable improvements in sound quality. However, it is important to remember that not all speakers will benefit from bi-wiring, and it may not be necessary or practical for every setup. It is always recommended to consult the user manual or manufacturer’s guidelines for your speakers before attempting to bi-wire them.
Understanding Speaker Cables
When it comes to bi-wiring your stereo speakers, choosing the right speaker cables is crucial. The quality and design of the cables can significantly impact the performance and sound reproduction of your speakers. Here are some key factors to consider when understanding speaker cables:
- Gauge: The gauge of a speaker cable refers to its thickness or diameter. In general, a lower gauge number indicates a thicker cable. Thicker cables tend to have lower resistance and can provide better conductivity, resulting in less signal loss and improved audio quality. For bi-wiring, it is recommended to use cables with a suitable gauge for the power requirements of your speakers.
- Metal Composition: Speaker cables are typically made of copper or a combination of copper and other metals. Copper is an excellent conductor of electric signals and is widely used for its conductivity and affordability. Some high-end cables may use pure copper or higher-grade copper alloys for improved performance. It is important to balance the cost and the desired audio quality when choosing the metal composition of the speaker cables.
- Length: The length of the speaker cables plays a role in maintaining signal integrity. Longer cables can introduce resistance and capacitance, leading to signal degradation. While it is recommended to keep the speaker cables as short as possible, consider the layout of your setup and the distance between your amplifier and speakers to determine the appropriate cable length.
- Termination: Speaker cables have different types of terminations at each end, such as banana plugs, spade connectors, or bare wire ends. The choice of termination depends on the binding posts or connectors on your speakers and amplifier. Ensure that the terminations are securely connected and provide a reliable and solid connection for optimal signal transfer.
- Build Quality: The build quality of the speaker cables can impact their durability and longevity. Look for cables with proper insulation to avoid electrical interference and cable damage. High-quality connectors and well-made cable junctions can also ensure a secure and stable connection, minimizing signal loss and improving overall performance.
Ultimately, the choice of speaker cables depends on your budget, preferences, and the specific requirements of your audio setup. It is recommended to research and read reviews to find cables that are well-regarded for their performance and affordability. Additionally, experimenting with different cables can offer insights into how they affect the sound reproduction of your bi-wired stereo speakers.
Speaker Terminals and Connections
When bi-wiring your stereo speakers, understanding the speaker terminals and making proper connections is essential for optimal performance. Here’s what you need to know:
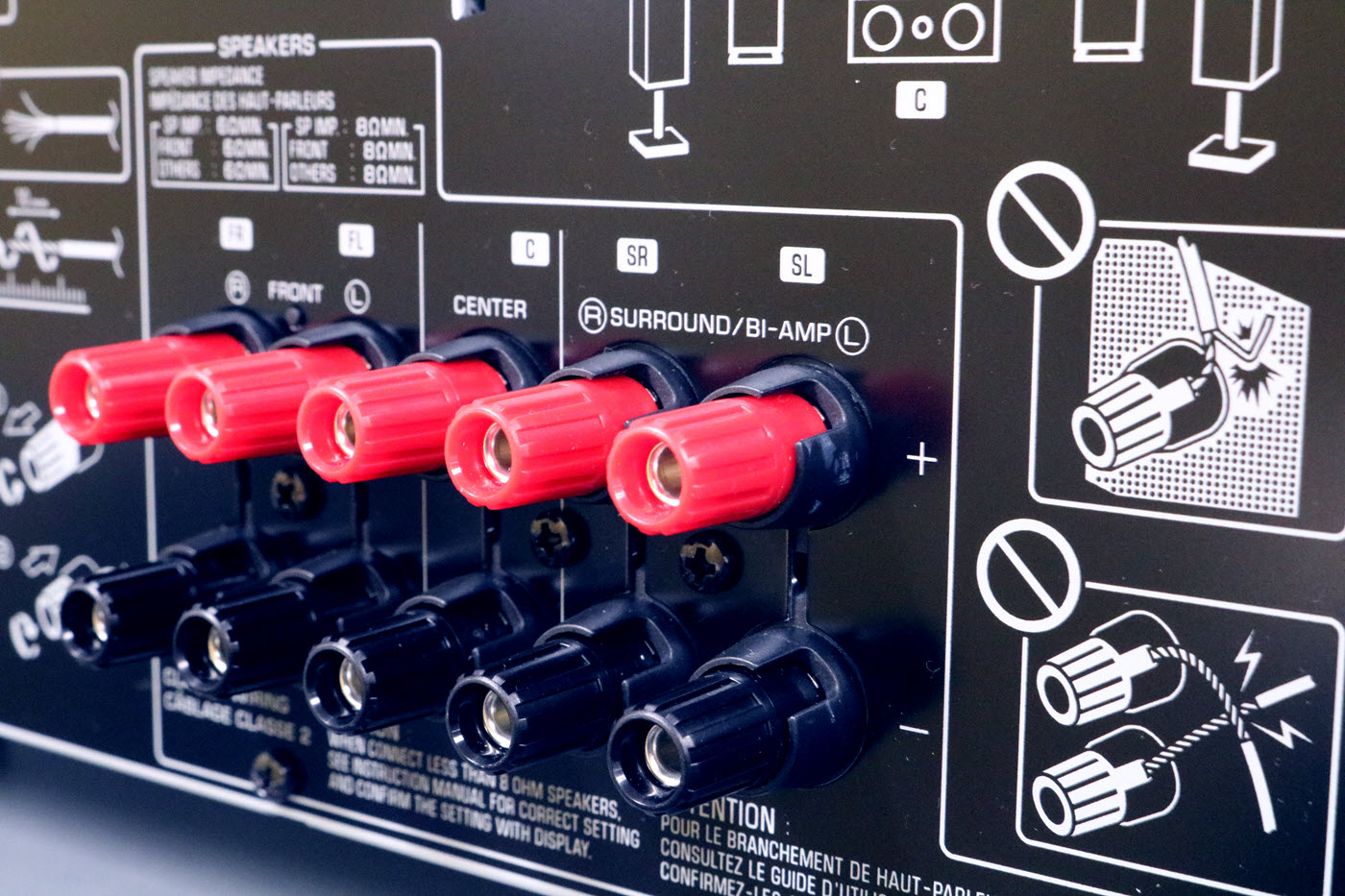
Speaker terminals: Most modern speakers designed for bi-wiring feature two sets of binding posts or connectors. One set is dedicated to the woofer driver, while the other is for the tweeter driver. Each set of terminals has a positive (+) and negative (-) post or connector. It’s crucial to identify and differentiate between these terminals to ensure correct wiring.
Speaker cables: For bi-wiring, you will need two separate sets of speaker cables – one pair for the woofer terminals and another pair for the tweeter terminals. Each cable set should be correctly labeled or color-coded for easy identification. It is crucial to use cables of appropriate gauge and quality to minimize signal loss and ensure the best possible audio performance.
Connecting cables: To connect the speaker cables to the terminals, follow these steps:
- Strip the ends of each cable to expose the bare wire or connectors.
- For each set of speaker terminals, hook the positive (+) wire or connector to the corresponding positive (+) terminal, and the negative (-) wire or connector to the negative (-) terminal.
- Ensure that each connection is secure and tight, providing a reliable electrical contact.
It’s crucial to maintain proper polarity while making the connections. This means that the positive terminal of the amplifier should be connected to the positive terminal of the speaker driver, and the negative terminal to the negative terminal. Connecting the cables with improper polarity can result in phase cancellation and poor sound quality.
Some speakers may come with jumpers or bridges pre-installed between the two sets of terminals. These metal strips or wires connect the woofer and tweeter terminals together, configuring the speaker for standard single-wire connection. When bi-wiring, it’s important to remove these jumpers to separate the frequency paths and allow for independent wiring to the woofer and tweeter drivers.
Always refer to the owner’s manual or consult the manufacturer’s guidelines when making connections and removing jumpers to ensure the correct and safe setup of your bi-wired stereo speakers.
How to Bi-Wire Stereo Speakers
Bi-wiring your stereo speakers involves separating the frequencies and using two sets of speaker cables to connect the amplifier to the bi-wire capable speakers. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to bi-wire your stereo speakers:
- Step 1: Prepare Your Equipment
Gather the necessary equipment, including the bi-wire capable stereo speakers, suitable speaker cables for bi-wiring, and an amplifier or receiver that supports bi-wiring. - Step 2: Connect the Speaker Cables
For each speaker, connect one pair of speaker cables to the amplifier’s positive (+) and negative (-) terminals for the low-frequency or woofer drivers. Connect the second pair of speaker cables to the amplifier’s positive (+) and negative (-) terminals for the high-frequency or tweeter drivers. Ensure each connection is secure and tight. - Step 3: Adjust Settings on Your Receiver or Amplifier
Check the settings on your receiver or amplifier to configure it for bi-wiring. Some amplifiers may have a specific setting or mode for bi-wiring. Make sure you follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult the user manual for appropriate setup guidance. - Step 4: Test the Bi-Wired Setup
Once the speaker cables are connected and the amplifier is set for bi-wiring, play some audio through your stereo system and listen for any improvements in audio quality. Pay attention to the clarity, detail, and overall sound reproduction. If necessary, make any adjustments to the speaker placement or settings on your amplifier to optimize the performance of your bi-wired stereo speakers.
Note that bi-wiring may not necessarily result in noticeable improvements for all speakers or setups. It’s important to consult the user manual or specifications of your speakers to determine if they support bi-wiring, and to experiment and assess the impact on audio quality based on your specific setup and listening preferences.
By properly bi-wiring your stereo speakers and ensuring secure connections, you can potentially enhance the clarity, detail, and overall performance of your audio system, allowing you to enjoy your favorite music, movies, and soundtracks with a heightened audio experience.
Step 1: Prepare Your Equipment
Before bi-wiring your stereo speakers, it is essential to gather the necessary equipment and ensure everything is in order. Here’s what you need to do:
1. Bi-Wire Capable Stereo Speakers: Make sure that your speakers are designed to support bi-wiring. Check the manufacturer’s specifications or consult the user manual to verify if your speakers are bi-wire capable. Bi-wire capable speakers typically have two sets of binding posts or connectors, one for the high-frequency driver (tweeter) and the other for the low-frequency driver (woofer).
2. Speaker Cables for Bi-Wiring: Acquire two sets of suitable speaker cables for bi-wiring. It is recommended to use high-quality cables with ample gauge to ensure optimal audio transmission. The length of the cables should be appropriate for the distance between your amplifier or receiver and the speakers.
3. Amplifier or Receiver: Ensure that your amplifier or receiver supports bi-wiring. Refer to the user manual or check the manufacturer’s specifications to verify if your audio equipment has the necessary bi-wiring capabilities. It is important to use an amplifier with two sets of output terminals or a receiver with separate outputs for the low-frequency and high-frequency drivers.
4. Cable Strippers or Cutters: To prepare the speaker cables for connection, have cable strippers or cutters on hand. These tools will be used to strip the insulation from the ends of the cables, allowing for a clean and secure connection.
5. Labeling or Color Coding: If your speaker cables are not already labeled or color-coded, consider using markers or tape to distinguish between the cables intended for the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers. This will help ensure that you make the correct connections to the appropriate terminals.
6. Safety Measures: It is always important to prioritize safety when working with audio equipment. Before starting the bi-wiring process, ensure that all components are turned off and unplugged. This will protect both you and the equipment from any potential damage or accidents.
By gathering and preparing the necessary equipment, you will set the foundation for successfully bi-wiring your stereo speakers. This initial step ensures that you have the appropriate cables, a compatible amplifier or receiver, and the necessary tools to proceed with the subsequent wiring process.
Step 2: Connect the Speaker Cables
Once you have prepared your equipment for bi-wiring your stereo speakers, it’s time to connect the speaker cables. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to properly make the connections:
- Identify the High-Frequency and Low-Frequency Terminals: Examine your bi-wire capable speakers and identify the terminals dedicated to the high-frequency (tweeter) and low-frequency (woofer) drivers. These terminals are typically labeled or color-coded to indicate their purpose. The high-frequency terminals are often marked as “HF” or “Tweeter,” while the low-frequency terminals may be labeled as “LF” or “Woofer.”
- Prepare the Speaker Cables: Take each pair of speaker cables and use cable strippers or cutters to remove a small portion of the insulation from the ends. This will expose the bare wire or connectors, allowing for a proper connection to the speaker terminals.
- Connect the Low-Frequency Cables: Take one pair of speaker cables and connect the positive (+) end to the positive (+) terminal of the low-frequency driver on the speaker. Connect the negative (-) end to the corresponding negative (-) terminal. Ensure that the connections are secure by tightening any binding posts or connectors.
- Connect the High-Frequency Cables: Take the second pair of speaker cables and connect them to the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the high-frequency driver on the speaker. Similar to the previous step, ensure that the connections are secure and tight.
- Verify Polarity: Polarity is critical when making speaker connections. It ensures that the positive (+) terminal of the amplifier is connected to the positive (+) terminal of the corresponding driver, and the negative (-) terminal is connected to the negative (-) terminal. Double-check that the polarity is consistent for both the high-frequency and low-frequency connections.
- Repeat for the Other Speaker: If you have a pair of speakers, repeat the connection process for the second speaker using the same steps.
Remember to handle the speaker cables and connections with care to avoid any damage or strain on the cables. Make sure the connections are secure, as loose or faulty connections can result in sound distortion or intermittent audio issues.
By properly connecting the speaker cables to the appropriate terminals, you ensure a clean and direct signal path for both the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers. This separation of frequencies is a key aspect of bi-wiring that can potentially enhance the performance and sound quality of your stereo speakers.
Step 3: Adjust Settings on Your Receiver or Amplifier
After connecting the speaker cables to your bi-wire capable stereo speakers, the next step is to adjust the settings on your receiver or amplifier to optimize the bi-wiring setup. Here’s what you need to do:
- Refer to the User Manual: Consult the user manual provided with your receiver or amplifier to understand the specific instructions for configuring it for bi-wiring. Different models may have unique settings or modes specifically designed for bi-wiring setups.
- Power Off Your Receiver or Amplifier: Before making any adjustments, power off your receiver or amplifier and ensure it is completely unplugged from the power source. This prevents any potential electrical mishaps while handling the settings.
- Locate the Bi-Wire Interface: Look for the bi-wire interface or settings on your receiver or amplifier. It may be labeled as “Bi-Wire,” “Speaker Configuration,” or something similar. Refer to the user manual if you’re having difficulty locating the appropriate settings.
- Select Bi-Wiring Mode: Once you’ve found the bi-wire interface, select the appropriate mode for bi-wiring. This mode is specifically designed to allocate separate signals to the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers of your speakers. Follow the instructions provided in the user manual to ensure the correct configuration.
- Adjust Frequency Crossover Settings: Some receivers or amplifiers allow you to adjust the crossover frequency, which determines at which point the signal transitions from the low-frequency driver to the high-frequency driver. This may vary depending on your personal preference and speaker specifications. Experiment with different crossover settings to find the balance that suits your audio preferences.
- Double-Check Connections: While adjusting the settings, ensure that the speaker connections remain secure and properly connected. Loose or incorrect connections can compromise the effectiveness of bi-wiring and result in degraded sound quality.
- Power On and Test: Once you have adjusted the settings, power on your receiver or amplifier. Test the audio by playing various types of music or test tones. Pay attention to the clarity, balance, and overall sound quality. Make further adjustments if needed, based on your listening preferences.
Remember to consult your receiver or amplifier’s user manual as different models may have specific setup instructions for bi-wiring. Adjusting the settings correctly ensures that your system is optimized for bi-wiring, allowing you to take full advantage of the potential audio enhancements this configuration can offer.
Step 4: Test the Bi-Wired Setup
After completing the bi-wiring process and adjusting the settings on your receiver or amplifier, it’s important to test the bi-wired setup to ensure optimal performance and sound quality. Here’s how to proceed:
- Play Different Types of Audio: Choose a variety of audio sources, such as music tracks or movies with different soundscapes, to test the capabilities of your bi-wired stereo speakers. This will allow you to evaluate the range, clarity, and overall reproduction of the audio.
- Listen for Clarity and Detail: Pay close attention to the clarity and detail in the sound. Listen for improved instrument separation, vocal clarity, and overall tonal balance. Bi-wiring can potentially enhance these aspects, resulting in a more immersive and engaging listening experience.
- Assess Soundstage and Imaging: Evaluate the soundstage and imaging of your stereo system. Notice if the audio feels more spacious and three-dimensional. Instruments and vocals should be accurately positioned within the soundstage, giving you a better sense of depth and realism.
- Check for Bass Response: Listen for improved bass response and control. The separation of frequencies in a bi-wired setup can contribute to tighter and more defined bass performance. Pay attention to the impact and articulation of low-frequency sounds, ensuring they are well-balanced with the rest of the audio spectrum.
- Make Adjustments if Necessary: If you notice any areas that could be improved, consider making further adjustments to the speaker placement, room acoustics, or additional settings on your receiver or amplifier. Experiment with different configurations to find the optimal setup that suits your preferences and room environment.
Remember, the effectiveness of bi-wiring can vary depending on factors such as the quality of your equipment, speaker design, and personal listening preferences. While some individuals may notice significant improvements, others may experience more subtle changes. Take the time to evaluate the bi-wired setup and make adjustments as needed to achieve the best possible audio performance.
Enjoy the enhanced sound quality and immerse yourself in the rich and detailed audio experience that bi-wiring can provide.
How to Bi-Amp Stereo Speakers
Bi-amping is a technique used to improve the audio performance of stereo speakers by separately powering the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers using multiple amplifiers. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to bi-amp your stereo speakers:
- Step 1: Determine if Your Speakers and Amplifier Support Bi-Amping
Check the specifications of your speakers and amplifier to ensure they have the necessary capabilities for bi-amping. Your speakers should have separate binding posts or connectors for the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers, and your amplifier should have multiple channels or be bi-amp capable. - Step 2: Prepare Your Equipment
Gather the required equipment, including your stereo speakers, multiple amplifiers (one for each driver), suitable speaker cables, and an active crossover. The active crossover is crucial for dividing the audio signal between the amplifiers and ensuring correct frequency allocation. - Step 3: Connect the Cables
Connect one set of speaker cables from the high-frequency driver terminals on your speakers to the corresponding amplifier’s output channels. Use another set of speaker cables to connect the low-frequency driver terminals to the corresponding amplifier channels. Make sure the connections are secure and tight. - Step 4: Adjust Settings on Your Receiver or Amplifier
Configure your receiver or amplifier for bi-amping. If your amplifier has multiple channels, set each channel to the appropriate frequency range (high or low) for each driver. You may need to consult the amplifier’s user manual for instructions on setting up bi-amping. - Step 5: Test the Bi-Amped Setup
Power on your system and play various audio sources to test the bi-amped setup. Listen for improvements in clarity, detail, and overall sound quality. Pay attention to the separation and balance between the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers, as well as the overall cohesiveness of the audio.
As with bi-wiring, the effectiveness of bi-amping can vary depending on factors such as the specific equipment used and personal preferences. It’s essential to experiment with different settings and configurations to find the optimal setup for your stereo speakers and listening environment.
By successfully bi-amping your stereo speakers, you can potentially achieve improved audio performance with greater control over each frequency range, resulting in enhanced clarity, detail, and overall sound reproduction.
Step 1: Determine if Your Speakers and Amplifier Support Bi-Amping
Before attempting to bi-amp your stereo speakers, it’s crucial to confirm that both your speakers and amplifier have the necessary capabilities to support bi-amping. Here’s how to determine if your equipment is compatible:
1. Check Your Speakers: Examine the specifications or user manual of your speakers to confirm if they have separate binding posts or connectors for the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers. Bi-amp capable speakers will typically have two sets of terminals, allowing you to connect multiple amplifiers to power each driver independently.
2. Verify Amplifier Channels: Check your amplifier’s specifications or user manual to determine if it has multiple channels or is specifically labeled as “bi-amp capable.” Bi-amp capable amplifiers have separate amplification channels that allow you to assign each channel to a specific frequency range. For example, you would assign one channel to the high-frequency driver and another channel to the low-frequency driver.
3. Assess Power Requirements: Take note of the power requirements for both your speakers and amplifier. Make sure that the amplifiers you plan to use can provide sufficient power for each driver. It’s essential to ensure that the amplifiers can handle the impedance and power demands of your speakers to avoid damaging the equipment.
4. Consider an Active Crossover: Bi-amping requires an active crossover to divide the audio signal into separate frequency ranges before being sent to the corresponding amplifier channels. If your amplifier does not have built-in crossover functionality, you will need to acquire an external active crossover to ensure proper frequency allocation.
5. Seek Manufacturer Information: If you’re unsure about the compatibility of your speakers or amplifier for bi-amping, consider reaching out to the manufacturers for clarification. They can provide specific information and guidance based on the model and specifications of your equipment.
It is essential to determine if your speakers and amplifier support bi-amping before proceeding with the setup. Attempting to bi-amp with incompatible equipment may lead to undesired results and potential damage to your equipment.
Once you have confirmed that your speakers and amplifier are compatible, you can proceed to the next steps in the bi-amping process, preparing your equipment and making the appropriate connections to optimize the performance of your stereo speakers.
Step 2: Prepare Your Equipment
In order to successfully bi-amp your stereo speakers, it is important to gather and prepare the necessary equipment. Here’s what you need to do:
1. Bi-Amp Compatible Stereo Speakers: Ensure that your stereo speakers are capable of bi-amping. Check the specifications or consult the user manual to verify if your speakers have separate binding posts or connectors for the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers. Bi-amp compatible speakers usually have two sets of terminals, allowing for independent amplification of each driver.
2. Multiple Amplifiers: Bi-amping requires the use of multiple amplifiers. You will need one amplifier for each driver – one to power the high-frequency driver and another to power the low-frequency driver. Ensure that you have the necessary amplifiers with enough power output to meet the requirements of your speakers.
3. Suitable Speaker Cables: Acquire high-quality speaker cables that are appropriate for the power requirements and impedance of your speakers. Make sure you have enough cable length to reach from each amplifier to the corresponding driver connectors on your speakers. It is recommended to use cables of sufficient gauge to ensure minimal signal loss and optimal performance.
4. Active Crossover: If your amplifier does not have built-in crossover functionality, you will need an external active crossover. An active crossover is essential for dividing the audio signal into separate frequency ranges and directing them to the respective amplifiers. Ensure that the chosen active crossover is compatible with your amplifier and provides the necessary crossover points for your specific speakers.
5. Prepare the Amplifiers: Set up and configure each amplifier for its designated frequency range. Assign one amplifier to power the high-frequency driver and the other amplifier to power the low-frequency driver. Consult the amplifier’s user manual for specific instructions on configuring each channel accordingly.
6. Cable Management: Organize your cables to ensure clean and tidy connections. Avoid routing the cables near sources of interference or electrical noise, as this can impact the audio quality. Proper cable management will help maintain signal integrity and prevent any unintended cable damage.
By properly preparing your equipment, you lay the foundation for a successful bi-amping setup. Double-check the compatibility of your speakers and amplifiers, acquire the necessary cables and active crossover if required, and ensure each component is properly configured and ready for bi-amping.
Step 3: Connect the Cables
Once you have prepared your equipment for bi-amping, the next step is to connect the necessary cables. Properly connecting the cables will ensure a clean and secure signal transmission. Here’s how you can connect the cables for bi-amping:
- High-Frequency Driver Connections: Take one set of speaker cables and connect the positive (+) wire or connector to the positive (+) terminal of the high-frequency driver on your bi-amp compatible speakers. Connect the negative (-) wire or connector to the corresponding negative (-) terminal. Ensure that these connections are secure and tight.
- Low-Frequency Driver Connections: Take the second set of speaker cables and connect the positive (+) wire or connector to the positive (+) terminal of the low-frequency driver on your speakers. Connect the negative (-) wire or connector to the corresponding negative (-) terminal. Again, ensure that these connections are secure and tight.
- Connect the Amplifiers: Connect the other ends of the speaker cables to the appropriate channels on each amplifier. Connect the cables from the high-frequency driver to the corresponding channels on the amplifier designated for the high-frequency range. Likewise, connect the cables from the low-frequency driver to the corresponding channels on the amplifier designated for the low-frequency range. Double-check that each connection is secure.
- Connect the Active Crossover: If you are using an external active crossover, connect the output of the active crossover to the input of each amplifier. Ensure that you adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for proper connection and polarity. This connection is crucial for dividing the audio signal between the amplifiers and directing the correct frequencies to the respective drivers.
- Verify Polarity: It is essential to verify and maintain proper polarity throughout the connections. Ensure that the positive (+) terminal of the amplifier is connected to the corresponding positive (+) terminal on the speaker’s driver, and the negative (-) terminal is connected to the corresponding negative (-) terminal. Incorrect polarity can result in phase cancellation and diminished sound quality.
- Double-Check Connections: Once all the cables are connected, double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and properly connected. Loose or faulty connections can result in degraded sound quality or intermittent audio issues.
By properly connecting the cables for bi-amping, you ensure that each driver is receiving its dedicated power from the respective amplifier. This separation of amplification allows for greater control and optimization of each frequency range, potentially enhancing the overall audio performance of your stereo speakers.
Step 4: Adjust Settings on Your Receiver or Amplifier
After connecting the cables for bi-amping your stereo speakers, the next step is to adjust the settings on your receiver or amplifier to ensure optimal performance and integration of the bi-amped setup. Here are the key steps to follow:
- Refer to the User Manual: Consult the user manual provided with your receiver or amplifier for specific instructions on configuring it for bi-amping. Different models may have unique settings or modes designed for bi-amp setups.
- Power Off Your Receiver or Amplifier: Before making any adjustments, power off your receiver or amplifier and ensure it is completely unplugged from the power source. This is necessary to prevent any electrical mishaps while handling the settings.
- Locate the Bi-Amp Settings: Locate the bi-amp settings or interface on your receiver or amplifier. This might be labeled as “Bi-Amp,” “Speaker Configuration,” or something similar. Refer to the user manual if you have trouble finding the appropriate settings.
- Assign Amplifier Channels: In the bi-amp settings, assign the respective amplifiers to each frequency range. For example, if you have a two-channel amplifier, assign one channel to the high-frequency driver and the other channel to the low-frequency driver. Follow the instructions in the user manual to ensure the appropriate configuration.
- Configure Crossover Points (if applicable): Some receivers or amplifiers with built-in crossovers allow you to adjust the crossover points. These points determine the frequency at which the audio signal is directed from one amplifier channel to another. Depending on your preference and speaker specifications, you may experiment with different crossover points to optimize the performance of your bi-amped system.
- Double-Check Connections: While adjusting the settings, ensure that all speaker and amplifier connections remain secure and properly connected. Loose or incorrect connections can compromise the effectiveness of bi-amping and result in degraded sound quality.
- Power On and Test: After adjusting the settings, power on your receiver or amplifier. Test the audio by playing various types of music or test tones. Listen for improvements in clarity, detail, and overall sound quality. Make further adjustments if necessary based on your listening preferences.
It is important to refer to the user manual and follow the manufacturer’s instructions when adjusting the settings on your receiver or amplifier for bi-amping. Proper configuration ensures that your system is optimized to take full advantage of the bi-amped setup, allowing for enhanced control and improved audio performance of your stereo speakers.
Step 5: Test the Bi-Amped Setup
After completing the bi-amping process and adjusting the settings on your receiver or amplifier, the next step is to test the bi-amped setup. Testing allows you to assess the performance and sound quality of your stereo speakers in the bi-amped configuration. Follow these steps to test the bi-amped setup:
- Select Different Audio Sources: Choose a variety of audio sources to test the capabilities of your bi-amped stereo speakers. This can include music tracks from different genres, movie soundtracks, or other audio recordings that represent various frequencies and dynamics.
- Listen for Improved Audio Performance: Pay close attention to the sound quality and performance of your speakers. Listen for improvements in clarity, detail, and overall sound reproduction. Focus on aspects such as instrument separation, vocal presence, and tonal balance. Bi-amping allows for greater control over each frequency range, which can elevate the audio experience.
- Evaluate Soundstage and Imaging: Assess the soundstage and imaging of the audio. Notice if the sound appears more spacious and three-dimensional. Instruments and vocals should be accurately positioned within the soundstage, providing a sense of depth and realism. Bi-amping can potentially enhance the soundstage and imaging capabilities of your stereo speakers.
- Check Bass Response and Control: Pay attention to the performance of the low-frequency drivers. Notice if there is improved bass response, tighter control, and articulation. Bi-amping can help optimize the reproduction of low-frequency sounds, ensuring a well-balanced and impactful bass performance.
- Make Further Adjustments if Needed: If you notice any areas that could be further improved, consider making additional adjustments to the speaker placement, room acoustics, or settings on your receiver or amplifier. Experiment with different configurations to find the optimal setup that aligns with your listening preferences and the characteristics of your audio environment.
Remember that the effectiveness of bi-amping can vary depending on factors such as the quality of your equipment, speaker design, and personal listening preferences. Some listeners may discern significant improvements, while others may experience more subtle changes. The goal is to achieve the best possible audio performance and enjoyment from your bi-amped stereo speakers.
Take the time to thoroughly test your bi-amped setup, carefully listen to various audio sources, and make adjustments as needed. Fine-tuning your system will help you fully optimize the advantages that bi-amping can bring to your audio experience.
Final Thoughts on Bi-Wiring and Bi-Amping Stereo Speakers
Bi-wiring and bi-amping are techniques that provide audio enthusiasts with the opportunity to optimize the performance of their stereo speakers. While they involve different approaches, both methods aim to enhance sound quality and control by dividing the audio signal for specific frequency ranges. Here are some final thoughts on bi-wiring and bi-amping:
Bi-Wiring: Bi-wiring can potentially improve sound clarity, reduce distortion, and enhance overall audio performance. By separating the frequencies and providing dedicated cables for the woofer and tweeter drivers, bi-wiring minimizes interference and provides a cleaner signal path to each driver. However, it is important to note that bi-wiring may not result in significant improvements for all speakers or setups. The effectiveness of bi-wiring can vary depending on speaker design and personal preferences. It is recommended to consult the speaker’s specifications and experiment with different configurations to evaluate the benefits it offers.
Bi-Amping: Bi-amping takes the concept of bi-wiring further by independently powering the high-frequency and low-frequency drivers with separate amplifiers. This method provides greater control over each driver and can result in enhanced clarity, detail, and overall sound reproduction. Bi-amping requires careful consideration of speaker and amplifier compatibility, as well as the use of active crossovers to ensure proper frequency allocation. It is worth noting that bi-amping may require additional amplifiers and cables, which can increase the overall cost and complexity of the audio setup.
Whether you choose to bi-wire or bi-amp your stereo speakers, it is important to remember that the overall audio experience is subjective. What works for one listener may not work the same for another. It is recommended to experiment and listen critically, taking note of the improvements, if any, and adjusting accordingly to find the optimal setup for your specific equipment and listening environment.
Lastly, it is crucial to carefully follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions for bi-wiring or bi-amping your speakers. This ensures that you are properly utilizing the capabilities of your equipment and minimizing the risk of damage or incorrect setup.