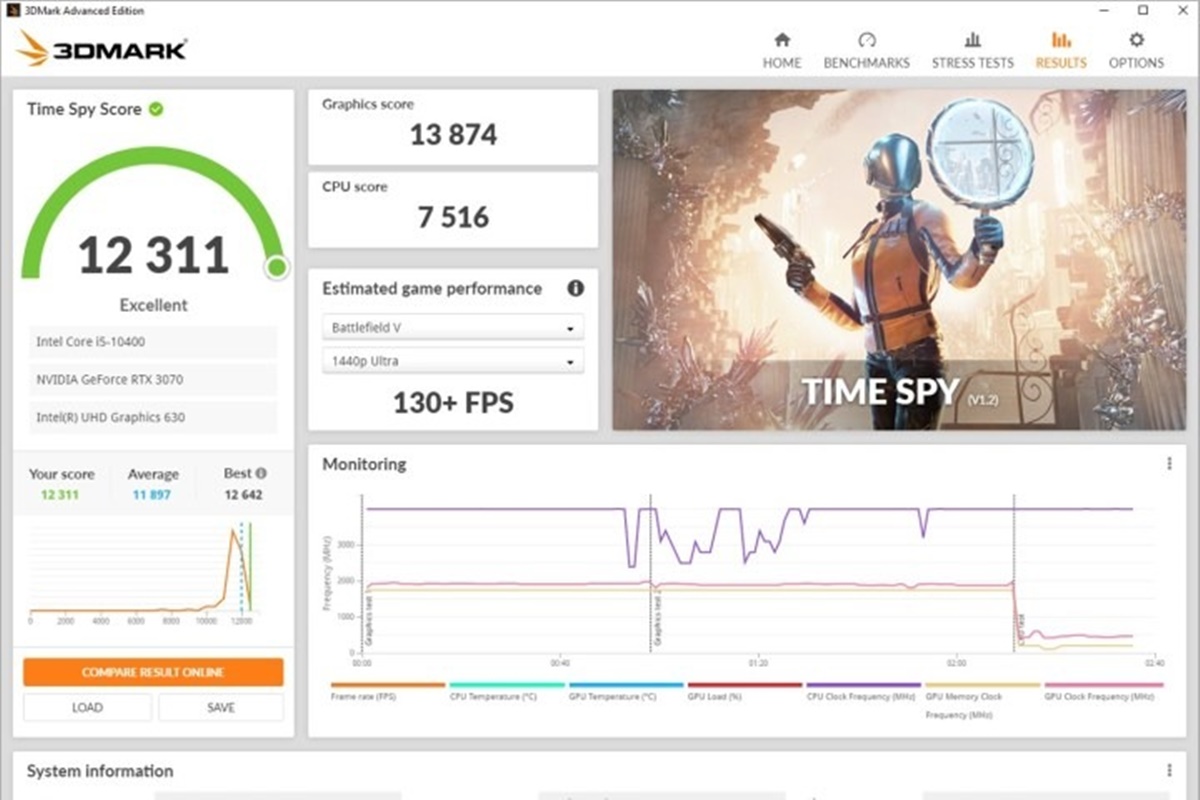
Choosing the Right Benchmarking Software
When it comes to benchmarking your graphics card, choosing the right software is crucial. The benchmarking software you select will determine the accuracy and reliability of the results. Here are some factors to consider when selecting the right benchmarking software for your needs:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the software is compatible with your graphics card and operating system. Some benchmarking tools are designed specifically for certain brands or models, so it’s essential to choose software that supports your hardware.
- Reliability: Look for benchmarking software that has a solid reputation for accuracy and consistency. Check reviews and user feedback to determine the reliability of the software.
- Features and Metrics: Consider the specific performance metrics you want to measure and ensure that the software supports those metrics. Different benchmarking software may focus on different aspects of graphics card performance, such as frame rates, GPU temperature, or memory bandwidth.
- User-Friendly Interface: Opt for software that is intuitive and user-friendly. A well-designed interface will make the benchmarking process more straightforward and efficient.
- Customization Options: Look for software that allows you to customize benchmarking settings and parameters. This will enable you to fine-tune the test conditions and tailor them to your specific needs.
- Support and Updates: Choose benchmarking software that offers regular updates and technical support. This ensures that you have access to the latest features and fixes any potential compatibility issues that may arise.
Some popular benchmarking software options for graphics cards include 3DMark, Unigine Heaven, and FurMark. Take the time to research and experiment with different software to find the one that suits your requirements best.
Remember that benchmarking is not a one-time process. As technology continues to advance, new software and updates are released regularly. It’s essential to stay up to date with the latest benchmarking tools to accurately evaluate your graphics card’s performance.
Understanding the Key Performance Metrics
When benchmarking a graphics card, it’s crucial to understand the key performance metrics that are measured. These metrics provide valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of your graphics card. Here are some of the essential performance metrics to consider:
- Frames Per Second (FPS): This metric measures the number of frames your graphics card can render per second. A higher FPS indicates smoother and more fluid gameplay.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) Clock Speed: The GPU clock speed determines how fast the graphics card processes data. Higher clock speeds generally result in improved performance.
- Memory Bandwidth: Memory bandwidth refers to the speed at which data can be transferred between the graphics card’s memory and the GPU. A higher memory bandwidth allows for faster data access and improved performance.
- Power Consumption: Power consumption indicates how much energy your graphics card consumes during operation. It’s essential to consider power efficiency to ensure optimal performance without excessive energy usage.
- Temperature: Monitoring the temperature of your graphics card is crucial to prevent overheating and maintain stable performance. Higher temperatures can lead to performance throttling and reduced lifespan of the card.
- Texture Fill Rate: The texture fill rate measures how quickly the graphics card can render textured images. Higher texture fill rates result in faster and more detailed graphics.
Understanding these metrics will help you interpret benchmark results effectively. It’s important to note that graphics card performance is not solely determined by a single metric. The combination of various metrics provides a comprehensive assessment of the overall performance of the graphics card.
When analyzing benchmark results, it’s essential to compare the metrics with the specifications of your graphics card and those of other similar cards. This comparison will help you gauge how well your card performs relative to other models and whether any upgrades are necessary.
Keep in mind that benchmarking is not just about achieving the highest numbers in all performance metrics. It’s about finding the optimal balance between various metrics based on your specific usage requirements. For gamers, a higher FPS may be crucial, while professionals focusing on rendering and 3D work may prioritize memory bandwidth and texture fill rate.
By understanding the key performance metrics and how they relate to your specific needs, you can make informed decisions about optimizing your graphics card’s performance and ensuring it meets your requirements.
Preparing Your System for Benchmarking
Before diving into benchmarking your graphics card, it’s crucial to ensure that your system is properly prepared for accurate and reliable results. Taking the time to prepare your system will help eliminate potential issues and ensure a smooth benchmarking process. Here are some essential steps to follow:
- Update Graphics Card Drivers: Ensure that you have the latest drivers installed for your graphics card. Updated drivers often include performance optimizations and bug fixes that can significantly impact benchmark results.
- Clean Your System: Remove any unnecessary files, applications, or background processes that may interfere with benchmarking. Close any running programs, especially resource-intensive applications, to ensure maximum system resources are available for benchmarking.
- Check System Temperature: Monitor your system’s temperature during benchmarking to prevent overheating. Ensure proper airflow and consider using additional cooling solutions if necessary, such as improving case ventilation or using aftermarket cooling solutions.
- Close Background Applications: Disable or close any unnecessary background applications and processes to free up system resources. This includes antivirus scans, file syncing applications, and any other programs that can consume CPU or GPU power.
- Set Power Settings: Adjust your power settings to ensure your system operates at maximum performance during benchmarking. You can set the power plan to “High Performance” in the control panel or use third-party software tools for advanced power management options.
- Monitor System Stability: Run stability tests on your system before benchmarking to ensure there are no hardware or software issues. Stress test utilities like MemTest86 or Prime95 can help identify any stability issues that could affect benchmark results.
- Disable Overclocking: If you have overclocked your graphics card, it’s recommended to reset it to the stock settings before benchmarking. Overclocking can introduce instability or inconsistent results, so it’s best to benchmark at stock speeds.
By following these steps, you can create an optimal environment for benchmarking your graphics card. Ensuring that your system is clean, running the latest drivers, and properly cooled will help provide accurate and reliable benchmark results.
Remember, benchmarking is not a one-time process. It’s a good practice to periodically repeat the benchmarking process to track any changes in your graphics card’s performance over time. Additionally, if you make any hardware or software changes to your system, it’s essential to perform benchmarking tests to evaluate the impact of those changes.
Running a Basic Graphics Card Benchmark
Running a basic graphics card benchmark is a straightforward process that allows you to assess the overall performance of your graphics card. It provides a baseline for comparison and helps identify any potential performance issues. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to run a basic graphics card benchmark:
- Select a Benchmarking Software: Choose a benchmarking software that aligns with your needs and supports the performance metrics you want to measure. Popular options include 3DMark, Unigine Heaven, and FurMark.
- Install and Configure the Software: Download and install the benchmarking software onto your system. Follow the on-screen instructions to configure any necessary settings, such as resolution and quality presets.
- Ensure System Stability: Before running the benchmark, make sure your system is stable and free from any background applications that could impact performance. Close unnecessary programs and ensure you have updated drivers installed.
- Run the Benchmark Test: Launch the benchmarking software and select the appropriate benchmark test for your graphics card. Typically, there will be different tests available, ranging from basic to more demanding benchmarks.
- Monitor the Progress: During the benchmark, monitor the progress and observe the metrics being measured. Pay attention to the frames per second (FPS), GPU temperature, and other relevant performance indicators.
- Record the Results: Once the benchmark is complete, take note of the results, including the average FPS and any other relevant metrics provided by the software. Some benchmarking tools may provide a detailed performance report.
- Compare the Results: Compare the benchmark results with the specifications of your graphics card and other similar models. This comparison will help you assess the performance of your card and identify any potential areas for improvement.
Running a basic graphics card benchmark should give you a general idea of your graphics card’s performance and how it stacks up against other similar models. It’s important to keep in mind that the performance numbers may vary depending on factors such as system configuration, drivers, and benchmarking software used.
Running benchmarks at different resolutions and quality settings can also provide additional insights into your graphics card’s performance capabilities under various conditions. This will give you a more comprehensive understanding of your card’s capabilities and its suitability for different applications and games.
Remember, benchmarking is a tool to evaluate and optimize performance, but it’s not the sole determinant of your graphics card’s capabilities. Real-world gaming and professional application performance may differ from benchmark results due to varying optimization and hardware requirements.
Running a Synthetic Graphics Benchmark
In addition to the basic graphics card benchmark, running a synthetic graphics benchmark can provide a more in-depth analysis of your graphics card’s capabilities. Synthetic benchmarks focus on stress testing specific aspects of your card, such as complex rendering algorithms, shader performance, or memory bandwidth. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to run a synthetic graphics benchmark:
- Choose a Synthetic Benchmark: Select a synthetic benchmark that emphasizes the performance metrics you want to assess. Some popular options include 3DMark Time Spy, Unigine Superposition, and Cinebench.
- Install and Configure the Software: Download and install the synthetic benchmark software onto your system. Follow the setup instructions and adjust any necessary settings, such as resolution, quality presets, or specific test parameters.
- Ensure System Stability: Similar to running a basic benchmark, ensure that your system is stable and free from any background applications that could impact performance. Close unnecessary programs and make sure you have updated drivers installed.
- Run the Synthetic Benchmark Test: Launch the synthetic benchmark software and select the appropriate test for your graphics card. Synthetic benchmarks often consist of multiple scenes or tests that stress different aspects of your card’s capabilities.
- Monitor and Analyze the Results: During the benchmark, monitor and note down the performance metrics provided by the software. These might include frames per second (FPS), shader complexity, memory bandwidth, or image quality ratings.
- Compare the Results: Compare the results with the specifications of your graphics card and other similar models. This will give you insights into how well your card performs in synthetic scenarios and how it compares to other cards in terms of performance.
- Identify Potential Bottlenecks or Performance Issues: Analyze the results to identify any bottlenecks or performance issues that may be impacting your graphics card’s performance. This can help you determine if any adjustments, optimizations, or upgrades are necessary.
Running a synthetic graphics benchmark provides a deeper understanding of your graphics card’s performance capabilities beyond basic benchmarks. It highlights specific aspects of your card’s performance and can help you identify areas for improvement or optimization.
Keep in mind that synthetic benchmarks focus on artificial, controlled scenarios and may not precisely reflect real-world usage. Therefore, it’s essential to combine synthetic benchmark results with real-world performance assessments, such as testing your card in specific applications or running benchmark tools designed for specific games or tasks.
Additionally, synthetic benchmarks may push your graphics card to its limits and result in higher temperatures or power consumption. Ensure that your system is adequately cooled and monitor temperatures during the synthetic benchmark to prevent any overheating or performance throttling.
Interpreting the Benchmark Results
Interpreting the benchmark results is crucial in understanding the performance of your graphics card and making informed decisions about optimizations or upgrades. Here are some key considerations when interpreting benchmark results:
- Comparison with Specifications: Compare the benchmark results with the specifications of your graphics card. Look for any significant deviations that may indicate performance issues or abnormalities.
- Frames Per Second (FPS): Pay attention to the average frames per second (FPS) obtained during the benchmark. Higher FPS values generally indicate smoother and more fluid gameplay or better rendering performance.
- Consistency: Consider the consistency of benchmark results across multiple runs. Look for stable and consistent performance, especially if you’re comparing the performance of different graphics cards.
- Relative Performance: Compare the benchmark results with other similar graphics cards to assess the relative performance of your card. This will give you insights into how well your card performs in relation to other models in its class.
- Bottlenecks: Identify any potential bottlenecks that could be limiting your graphics card’s performance. For example, if the GPU utilization is significantly low while other metrics like CPU usage are high, it may indicate a CPU bottleneck.
- Temperature and Power Consumption: Monitor the temperatures and power consumption of your graphics card during the benchmark. Ensure they are within safe operating limits and evaluate if any adjustments are needed, such as improving cooling or optimizing power settings.
- Real-World Performance: Remember that benchmark results provide an indication of your graphics card’s capabilities but may not reflect real-world performance in specific applications or games. Consider running additional, application-specific benchmarks or testing your card in the actual tasks you intend to perform.
- Future Upgrades: Use benchmark results to assess whether your current graphics card meets your needs. If the results fall short of your expectations or your system requirements, consider upgrading to a more powerful card that aligns with your performance goals.
It’s crucial to interpret benchmark results in the context of your specific needs and usage scenario. Consider the type of applications or games you’ll be running, the desired quality settings, and the target framerate when evaluating benchmark results.
Keep in mind that benchmarking is an ongoing process, especially as new software updates, drivers, and even games are released. Regularly benchmarking your graphics card can help you track performance changes over time and make informed decisions about optimizations or upgrades.
Comparing Different Graphics Cards
Comparing different graphics cards allows you to assess their performance capabilities and make informed decisions when choosing the right card for your needs. Here are some key factors to consider when comparing different graphics cards:
- Performance Metrics: Evaluate the performance metrics of each graphics card, such as frames per second (FPS), memory bandwidth, and GPU clock speed. Compare these metrics to determine which card offers better overall performance.
- Price-Performance Ratio: Consider the price-performance ratio of each graphics card. Calculate the cost per unit of performance and compare it among different models to identify the best value for your budget.
- Power Consumption: Compare the power consumption of different graphics cards, particularly if you’re concerned about energy efficiency. Lower power consumption can result in lower electricity bills and less heat generated by the card.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the graphics card you’re considering is compatible with your system, including the motherboard slot, power supply, and software requirements. Check the manufacturer’s specifications to verify compatibility.
- Brand and Warranty: Consider the reputation and customer support offered by different graphics card brands. Look for cards with solid warranty terms and reliable customer service in case you encounter any issues.
- Gaming or Application-Specific Performance: Assess the performance of the graphics cards in specific games or applications that you intend to use. Look for benchmarks or reviews that focus on these specific scenarios to make an informed decision.
- Future Upgrades: Consider the scalability and future upgrade potential of each graphics card. If you plan to upgrade your system’s components in the future, choose a graphics card that allows for easy integration with other hardware.
- User Reviews and Recommendations: Consider reading user reviews and seeking recommendations from trusted sources to get insights into real-world experiences with different graphics cards.
When comparing different graphics cards, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your own requirements and expectations. Determine your budget, the specific applications or games you’ll be using, and the desired quality settings to guide your decision-making process.
Remember that the “best” graphics card is subjective and depends on individual needs and preferences. A high-end card may not be necessary for casual gamers, while professionals may require a graphics card with specific features for their work. Consider your usage scenario and prioritize accordingly.
By comparing and assessing different graphics cards based on their performance, price, compatibility, and other factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the graphics card that best suits your needs and budget.
Overclocking and Benchmarking
Overclocking your graphics card can be an effective way to boost its performance beyond its stock settings. However, when it comes to benchmarking, overclocking requires careful consideration to obtain accurate and reliable results. Here are some important points to keep in mind when overclocking and benchmarking:
- Stability and Reliability: Overclocking involves increasing the clock speeds and voltages of your graphics card, which can potentially lead to instability or system crashes. Ensure that your overclocked settings are stable and reliable before proceeding with benchmarking.
- Benchmarking at Stock and Overclocked Speeds: It’s recommended to run benchmark tests both at the stock speeds and the overclocked speeds of your graphics card. This will allow you to compare the performance improvements achieved through overclocking and understand the impact on various performance metrics.
- Temperature and Power Consumption: Overclocking can increase the temperature and power consumption of your graphics card. Monitor these factors during benchmarking, as higher temperatures can impact performance and excessive power consumption may strain your system’s power supply.
- Benchmarking Overclocking Stability: After overclocking, it’s crucial to run stability tests to ensure that your graphics card can handle the increased clock speeds under prolonged stress. Unstable overclocks may lead to system instability, crashes, or even hardware damage.
- Incremental Overclocking: Instead of immediately aiming for the highest possible overclocking settings, consider an incremental approach. Gradually increase the clock speeds and test for stability. This allows you to find the optimal balance between performance and stability.
- Temperature and Cooling: Overclocking generates more heat, so adequate cooling is essential. Ensure that your system’s cooling solution, including fans and heatsinks, can handle the increased heat output caused by overclocking. Consider additional cooling methods like aftermarket coolers or liquid cooling for improved thermal management.
- Risks and Limitations: It’s important to understand that overclocking carries certain risks, including potential damage to your graphics card or voiding the warranty. Be aware of the limitations and potential consequences before proceeding with overclocking.
- Personal Experience and Research: Overclocking results can vary depending on the specific graphics card model, hardware configuration, and individual factors. Research and personal experience will help you determine the safe limits and best overclocking practices for your specific graphics card.
Remember that overclocking should be approached with caution, and it’s crucial to balance performance gains with stability and safety. Be familiar with your graphics card’s capabilities and limitations, and always monitor system stability and temperatures during benchmarking and overclocking.
It’s worth noting that not all graphics cards can be overclocked, as it depends on the manufacturer’s design and the specific model. Moreover, overclocking may void the warranty, so it’s important to review the warranty terms before proceeding.
Ultimately, overclocking and benchmarking go hand in hand, allowing you to push the performance boundaries of your graphics card while measuring its capabilities accurately. However, responsible and well-informed practices should be followed to ensure a safe and reliable experience.
Troubleshooting and Tips for Accurate Results
When benchmarking your graphics card, it’s essential to troubleshoot any issues that may arise and follow certain tips to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here are some troubleshooting steps and tips to help you achieve accurate benchmarking results:
- Check System Requirements: Make sure your system meets the minimum requirements for the benchmarking software you’re using. Inadequate system specifications can result in performance issues or inaccurate results.
- Update Drivers and Software: Ensure that you have the latest drivers installed for your graphics card and that the benchmarking software is up to date. Updated drivers and software often include performance improvements and bug fixes.
- Close Background Applications: Close any unnecessary background applications to free up system resources. Background processes can consume CPU or GPU power, affecting benchmarking accuracy.
- Monitor Temperatures: Keep an eye on your graphics card’s temperature during benchmarking. High temperatures can lead to performance throttling or system instability. Ensure proper cooling to maintain optimal temperatures.
- Perform Stability Tests: Run stability tests on your graphics card before benchmarking to ensure there are no stability issues. Stress test utilities can help identify potential problems that may affect benchmark results.
- Use Authentic and Updated Software: Stick to reliable and trusted benchmarking software to ensure accurate and consistent results. Avoid using outdated or counterfeit software that may provide inaccurate readings.
- Run Multiple Benchmark Tests: Perform multiple benchmark tests with different software or test scenes to validate the results. Running multiple tests reduces the likelihood of outliers and provides a more accurate assessment of your graphics card’s performance.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Monitor CPU, GPU, and memory usage during benchmarking. Abnormally high resource usage may indicate bottlenecks or configuration issues that need to be addressed.
- Disable Overclocking: Disable any overclocking settings before benchmarking, especially if you want to compare the performance of different graphics cards. Overclocked settings can skew results and introduce inconsistencies.
- Repeat Benchmarking: Perform benchmark tests multiple times to ensure consistency and minimize any potential variations in results. Repeating the tests helps identify anomalies and provides a more accurate average performance assessment.
By following these troubleshooting steps and implementing the recommended tips, you can increase the accuracy and reliability of your graphics card benchmarking results. Remember that benchmarking is not a one-time process and should be repeated periodically to track performance changes and evaluate system upgrades or optimizations.