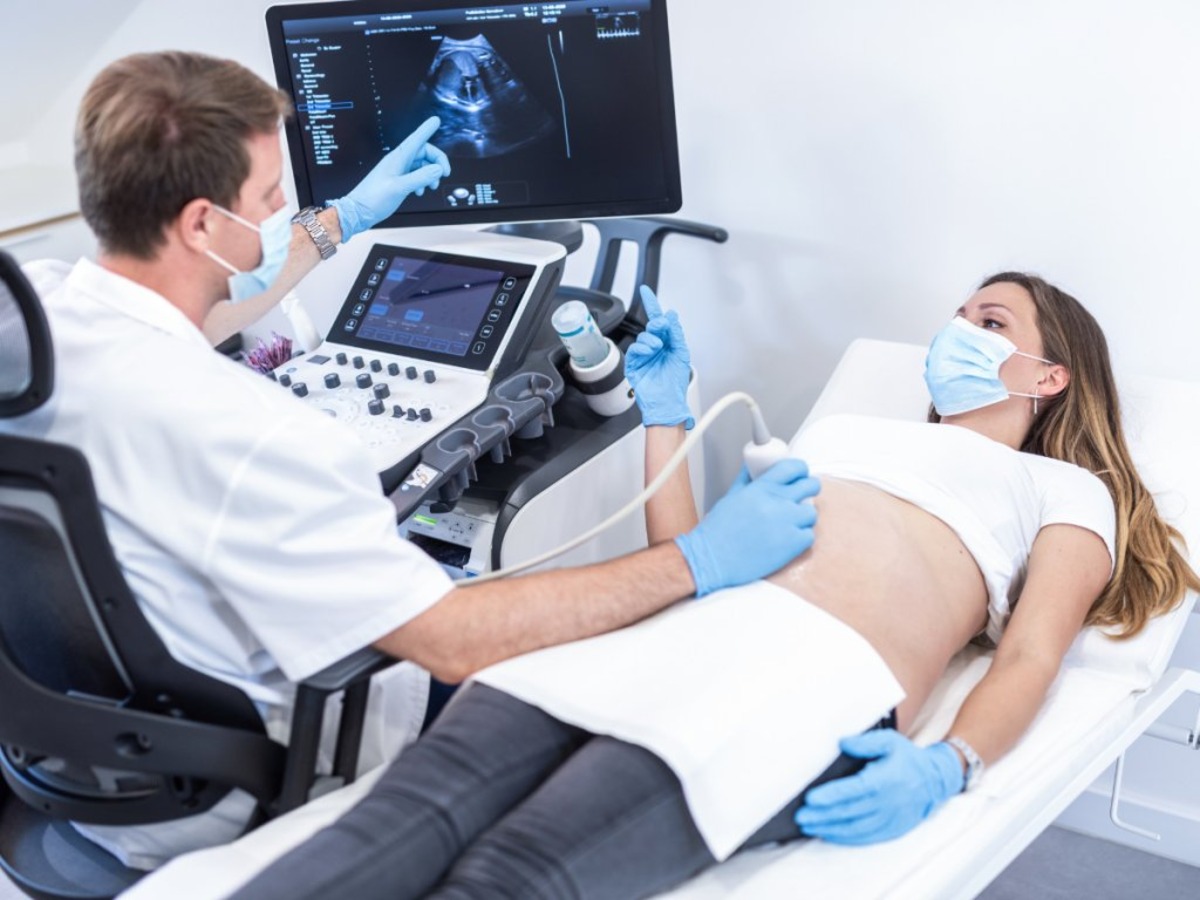
Benefits of Using a Bladder Scanner
A bladder scanner is a valuable medical device that offers numerous benefits for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Whether in hospitals, clinics, or long-term care facilities, bladder scanners play a crucial role in assessing and monitoring urinary conditions. Here are some of the key benefits of using a bladder scanner:
- Non-Invasive Procedure: One of the major advantages of using a bladder scanner is that it provides a non-invasive method for assessing bladder volume. Unlike other diagnostic methods that may require catheterization or invasive procedures, a bladder scanner uses ultrasound technology to accurately measure bladder volume externally. This reduces discomfort and eliminates the risk of infection or injury associated with invasive procedures.
- Accurate and Reliable: Bladder scanners are known for their accuracy in measuring bladder volume. By using ultrasound waves, the scanner can produce detailed and precise images of the bladder, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately determine the volume of urine inside. This information is essential in diagnosing urinary conditions, planning treatment, and monitoring the effectiveness of interventions.
- Rapid Assessment: With a bladder scanner, healthcare professionals can quickly assess a patient’s bladder volume without the need for time-consuming procedures. The scan can be completed within minutes, allowing for immediate evaluation and decision-making. This saves valuable time in the clinical setting and enables prompt interventions or adjustments to treatment plans.
- Patient Comfort: By eliminating the need for invasive procedures, bladder scanners contribute to improved patient comfort and satisfaction. Patients often experience discomfort and anxiety when undergoing catheterization or other invasive bladder assessments. With a bladder scanner, healthcare professionals can provide a more comfortable and less distressing experience for patients, leading to increased compliance and cooperation.
- Cost-Efficient: In addition to the medical benefits, bladder scanners offer cost-efficiency in healthcare settings. By accurately assessing bladder volume, healthcare professionals can avoid unnecessary catheterizations or invasive procedures, which can be costly and carry potential risks. This helps in optimizing healthcare resources, reducing expenses, and enhancing overall efficiency in patient care.
Overall, the use of a bladder scanner is a beneficial tool for healthcare professionals as it provides a non-invasive, accurate, and rapid assessment of bladder volume. Patients also benefit from increased comfort and reduced risks associated with invasive procedures. With its cost-efficiency and time-saving advantages, a bladder scanner is an essential device in healthcare settings for effective urinary condition management.
Factors Affecting the Cost of a Bladder Scanner
Bladder scanners vary in price, and several factors can influence their cost. Understanding these factors is essential when considering the purchase of a bladder scanner. Here are some key factors that can affect the cost of a bladder scanner:
- Technology and Features: The technological capabilities and features of a bladder scanner can significantly impact its cost. Advanced models may incorporate additional functionalities like wireless connectivity, touchscreen interfaces, or advanced image processing algorithms. These features enhance the user experience and diagnostic accuracy but can also contribute to a higher price point.
- Brand and Reputation: The reputation and brand name of a bladder scanner manufacturer can influence its cost. Well-established and recognized brands often charge a premium for their products due to their reputation for quality and reliability. However, it’s essential to consider both the brand and the specific model’s performance and features to ensure value for money.
- Portability: Bladder scanners come in various sizes and designs, with portable and stationary options available. Portable bladder scanners offer the advantage of mobility, allowing healthcare professionals to conduct assessments bedside or in different clinical locations. However, this convenience often comes at a higher cost compared to stationary models.
- Image Quality and Resolution: The image quality and resolution produced by a bladder scanner can affect the cost. Higher-resolution scanners with better image quality provide clearer and more detailed images of the bladder, aiding in more accurate volume measurements. However, these scanners tend to be more expensive than those with lower resolution.
- Service and Support: The level of service and support provided by the manufacturer can impact the cost of a bladder scanner. Manufacturers that offer comprehensive customer support, warranties, and regular maintenance services may charge a higher initial price for their scanners. However, this investment ensures ongoing technical assistance and reliability throughout the lifespan of the device.
It is important to consider these factors when determining the suitability and affordability of a bladder scanner for your specific needs. Evaluating the technology, features, brand, portability, image quality, and available support can help you make an informed decision that balances cost and functionality.
Types of Bladder Scanners
There are different types of bladder scanners available in the market, each with its own unique features and functionalities. Understanding the different types can help healthcare professionals choose the most suitable bladder scanner for their specific needs. Here are the main types of bladder scanners:
- Portable Bladder Scanners: Portable bladder scanners are compact and lightweight, designed for mobility and ease of use. They are often handheld devices that can be easily carried from room to room or bedside to bedside. Portable bladder scanners offer the advantage of convenience and flexibility, allowing on-the-spot assessments without the need to transport the patient to a dedicated scanning area.
- Stationary Bladder Scanners: Stationary bladder scanners are larger, bulkier devices that are typically mounted on a stand or cart. They are designed for use in dedicated scanning areas such as examination rooms or urology departments. Stationary bladder scanners offer enhanced stability and may have additional features like adjustable height and support for patient positioning.
- 3D Bladder Scanners: 3D bladder scanners use advanced technology to create three-dimensional images of the bladder. These scanners provide a more detailed and accurate assessment of bladder volume by capturing a complete image of the bladder’s shape and contours. The 3D images can assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing complex bladder conditions and optimizing treatment plans.
- Wireless Bladder Scanners: Wireless bladder scanners offer the convenience of cable-free operation. These scanners utilize wireless connectivity, allowing data transfer to a computer or mobile device without the need for physical connections. Wireless bladder scanners are highly portable and offer flexibility in data management and documentation, enabling seamless integration with electronic medical record systems.
- Handheld Bladder Scanners: Handheld bladder scanners are compact devices that can be held in the hand while conducting the assessment. These scanners usually have a probe attached, which is placed on the patient’s lower abdomen to obtain bladder measurements. Handheld bladder scanners are user-friendly and easy to maneuver, making them suitable for point-of-care applications and quick assessments.
Each type of bladder scanner has its own advantages and considerations. The choice of a bladder scanner type depends on factors such as intended use, mobility requirements, the complexity of bladder conditions being diagnosed, and personal preferences. It is important to thoroughly evaluate the features and capabilities of each type before making a decision.
Average Cost of Bladder Scanners
The cost of bladder scanners can vary significantly depending on various factors such as brand, features, technology, and additional accessories. While it is difficult to determine an exact average cost due to the wide range of options available, we can provide a general idea of the price range for bladder scanners.
Basic bladder scanners without advanced features or high-resolution imaging capabilities typically start at around $1,000 to $2,000. These scanners are often portable and handheld, offering essential bladder volume measurement functionality.
Mid-range bladder scanners with improved image quality, additional features, and wireless connectivity options range between $2,000 and $5,000. These scanners often offer better accuracy, more advanced user interfaces, and the ability to transmit data wirelessly to compatible devices.
High-end bladder scanners with advanced imaging technologies, such as 3D capabilities or high-resolution ultrasound, can cost upwards of $5,000 or more. These scanners provide enhanced diagnostic capabilities and greater accuracy in bladder volume measurements.
It is important to note that the cost of bladder scanners may also include additional expenses such as training, warranties, and maintenance agreements. These factors should be considered when budgeting for the purchase of a bladder scanner.
When determining the budget for a bladder scanner, healthcare facilities must consider their specific needs, the features required for accurate assessments, and the available financial resources. It is advisable to consult with vendors and compare different options to find the best bladder scanner that fits both the budget and the desired functionalities.
Additionally, financing options such as lease agreements or installment plans may be available to help healthcare facilities manage the upfront cost of purchasing a bladder scanner. Taking advantage of these options can provide more flexibility in acquiring the necessary equipment while spreading out the financial burden over time.
Ultimately, the cost of a bladder scanner should be viewed as an investment in improving patient care and diagnostic accuracy. It is important to consider both the upfront cost and the long-term benefits when making a purchasing decision.
Differences Between Portable and Stationary Bladder Scanners
Bladder scanners are available in different designs, including portable and stationary models. Understanding the differences between these two types can help healthcare professionals select the most suitable bladder scanner for their specific needs and clinical settings. Here are the key differences between portable and stationary bladder scanners:
Portability: Perhaps the most obvious difference is portability. Portable bladder scanners are designed to be lightweight and easy to carry, allowing healthcare professionals to conduct assessments at the patient’s bedside or in different clinical locations. They offer greater flexibility and convenience, eliminating the need to transport the patient to a dedicated scanning area. On the other hand, stationary bladder scanners are larger and typically mounted on a stand or cart. They are intended for use in specific examination rooms or urology departments.
Size and Design: Portable bladder scanners are compact and handheld devices that can be easily maneuvered. They are designed to be user-friendly and allow for quick assessments. Stationary bladder scanners, on the other hand, are larger and bulkier. They often feature a fixed probe or arm to ensure stability during scanning and might have additional features like adjustable height to accommodate different patients.
Imaging Capability: In terms of imaging capability, both portable and stationary bladder scanners can provide accurate volume measurements. However, portable bladder scanners may have limitations in terms of image resolution due to their smaller size and portability. Stationary bladder scanners, being larger and often more advanced, may offer enhanced image quality and higher resolution, allowing for more detailed assessment of the bladder.
Point-of-Care Assessment: Portable bladder scanners excel in point-of-care assessments, where immediate measurement of bladder volume is essential. Healthcare professionals can easily bring the scanner to the patient’s bedside, saving time and eliminating the need for patient transportation. Stationary bladder scanners, while not as mobile, offer stability and can be used for more comprehensive assessments in dedicated scanning areas.
Cost: Generally, portable bladder scanners tend to be more expensive than stationary ones due to their added portability and convenience features. The advanced technology and compactness of portable scanners contribute to the higher price point. Stationary bladder scanners, being larger and less portable, often come at a lower cost.
When deciding between portable and stationary bladder scanners, healthcare professionals should consider factors such as the mobility requirements of their practice, the need for immediate bedside assessments, and the level of image quality and resolution required for accurate diagnosis. Both types have their advantages, and the choice ultimately depends on the specific needs of the healthcare facility and the patients being treated.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Bladder Scanner
Choosing the right bladder scanner is a crucial decision for healthcare professionals and facilities. Considering the following factors can help ensure that the chosen bladder scanner meets the specific needs and requirements of the clinical setting:
Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy and reliability of a bladder scanner are paramount. Look for a scanner that has a proven track record of providing precise and consistent measurements. Information from user reviews, independent evaluations, and clinical studies can help assess the scanner’s accuracy and reliability.
Imaging Quality: The quality of the bladder scanner’s images directly influences the accuracy of volume measurements. High-resolution images that clearly depict the bladder’s shape and contours facilitate accurate assessment. Consider scanners that produce clear, detailed images to ensure reliable measurements.
Ease of Use: Look for a bladder scanner that is intuitive and user-friendly. It should have a simple interface and easy-to-understand controls. The scanning process should be straightforward, with clear instructions provided to the user. This ensures that healthcare professionals can easily and efficiently operate the scanner.
Portability: Depending on the clinical setting and specific use case, portability may be an important factor to consider. Portable bladder scanners offer the advantage of mobility, allowing bedside assessments and easy transport between different areas of the facility. If portability is a priority, choose a scanner that is lightweight, compact, and easy to carry.
Compatibility and Connectivity: Evaluate the compatibility of the bladder scanner with other devices and systems in your clinical setting. Look for scanners that integrate seamlessly with electronic medical record (EMR) systems, allowing for efficient data transfer and documentation. Consider scanners that offer connectivity options such as USB, Bluetooth, or wireless connections for optimal data management.
Service and Support: Good customer support and service are crucial when investing in a bladder scanner. Ensure that the manufacturer provides technical support, training resources, and regular maintenance options. Look for warranties or service agreements that can provide peace of mind and assistance if any issues or concerns arise during the scanner’s use.
Cost and Budget: Consider the budget allocation for a bladder scanner and identify the range of scanners that fit within that budget. Compare the features, functionality, and reputation of different models to find the best value for money. Balancing cost with the necessary capabilities is essential when making a purchasing decision.
User Reviews and Recommendations: Seek insights from other healthcare professionals who have experience with various bladder scanner models. User reviews and recommendations can provide valuable information about the usability, accuracy, and overall performance of different scanners.
Taking all these factors into account will help healthcare professionals make an informed decision when choosing a bladder scanner that meets their specific needs, enhances diagnostic accuracy, and ultimately provides the best outcomes for their patients.
Alternatives to Bladder Scanners
While bladder scanners are highly effective in assessing bladder volume, there are alternative methods available for evaluating urinary conditions. These alternatives may be suitable depending on the specific situation and available resources. Here are some common alternatives to bladder scanners:
Catheterization: Catheterization involves inserting a thin tube through the urethra into the bladder to drain urine and measure bladder volume directly. Although it provides accurate results, catheterization is an invasive procedure that carries a risk of infection and discomfort for the patient. It is typically reserved for cases where precise measurements are critical or when the patient cannot effectively empty their bladder naturally.
Bladder Diaries: Bladder diaries involve patients recording their voiding and fluid consumption habits over a specified period of time. This method provides valuable information about urinary patterns and volume estimation based on reported voided volumes. Although it relies on patient reporting, bladder diaries can be helpful in monitoring changes in bladder habits and identifying potential urinary issues.
Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound imaging, similar to bladder scanners, uses ultrasound waves to visualize the bladder and assess its volume. However, ultrasound imaging typically requires a dedicated ultrasound machine and a trained sonographer to perform the scan. It may be performed in situations where a bladder scanner is unavailable or if a more detailed assessment of the bladder is necessary.
Dipstick Urinalysis: Dipstick urinalysis involves using chemical test strips to analyze various parameters in the urine sample, including specific gravity, pH, and presence of white blood cells or bacteria. While dipstick urinalysis does not directly measure bladder volume, it can provide valuable information about urinary tract infections, hydration levels, and certain urinary conditions.
Bladder Palpation: Bladder palpation involves manually assessing the bladder’s size and fullness by applying gentle pressure on the lower abdomen. This technique is typically performed by healthcare professionals during physical examinations. While it is a non-invasive method, it may not provide exact measurements and relies on the skill and experience of the healthcare professional.
It is important to note that these alternatives each have their advantages and limitations. Factors such as the availability of equipment, resources, and the patient’s specific condition should be considered when choosing an alternative assessment method to bladder scanners. Additionally, the decision to use an alternative method should be made in collaboration with a healthcare professional to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Financing Options for Bladder Scanners
Investing in a bladder scanner is a significant expense for healthcare facilities. Fortunately, there are various financing options available to help manage the upfront cost and make the purchase more affordable. Here are some common financing options for bladder scanners:
Lease or Rental Agreements: Lease or rental agreements allow healthcare facilities to obtain a bladder scanner without the need for a large upfront payment. Instead, the facility pays a fixed monthly amount for the duration of the lease or rental term. This option provides flexibility, as facilities can upgrade to newer models at the end of the contract or return the scanner if it is no longer needed.
Equipment Financing: Equipment financing involves obtaining a loan specifically for purchasing medical equipment, including bladder scanners. Healthcare facilities can work with financial institutions or equipment leasing companies to secure a loan and make regular installment payments over a specified period. This option allows spreading out the cost of the bladder scanner over time.
Manufacturer Financing Programs: Many bladder scanner manufacturers offer their own financing programs to help facilitate the purchase for healthcare facilities. These programs often provide competitive interest rates, flexible repayment terms, and quick approval processes. It is recommended to inquire with the manufacturer directly to learn about their financing options.
Grants and Funding Opportunities: Healthcare facilities may be eligible for grants or funding opportunities to assist with the purchase of medical equipment, such as bladder scanners. Foundations, government entities, or other organizations may offer grants or funding programs specifically for healthcare equipment acquisition. It is advisable to research and apply for relevant opportunities that align with the facility’s needs and goals.
Vendor Financing Arrangements: Some vendors or suppliers of bladder scanners may offer financing arrangements to their customers. This can include deferred payment plans, zero-interest financing, or customized financing options tailored to the needs of the healthcare facility. It is worthwhile to discuss financing possibilities directly with the vendor when considering a bladder scanner purchase.
When exploring financing options for bladder scanners, it is important to consider factors such as interest rates, repayment terms, hidden costs, and the financial stability of the financing provider. Facility administrators should carefully evaluate each option, considering the long-term budgetary impact and choosing an option that best suits their financial circumstances and goals.
By utilizing these financing options, healthcare facilities can acquire the necessary bladder scanner equipment while effectively managing their cash flow and ensuring the best possible care for their patients.
Tips for Properly Maintaining a Bladder Scanner
Maintaining a bladder scanner is essential to ensure its longevity, accuracy, and optimal performance. Proper maintenance practices can also help prevent malfunctions, reduce downtime, and minimize the need for costly repairs. Here are some important tips for effectively maintaining a bladder scanner:
Read and Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions: Start by thoroughly reviewing the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for maintenance. Familiarize yourself with all the recommended steps, procedures, and schedules provided by the manufacturer. Following these instructions will help ensure that you are maintaining the bladder scanner correctly.
Regular Cleaning and Disinfection: Clean and disinfect the bladder scanner regularly to maintain hygiene and prevent the spread of infections. Use mild, non-abrasive cleaning solutions recommended by the manufacturer. Make sure to wipe down the external surfaces, including the interface, buttons, and probe, while avoiding getting any liquid inside the scanner.
Calibration and Quality Control: Regularly calibrate the bladder scanner as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Calibration ensures accurate and reliable measurements. Perform quality control checks according to the specified frequency to ensure the scanner is functioning within acceptable parameters. If any issues are detected during calibration or quality control checks, contact the manufacturer for support.
Inspect Cables and Probes: Regularly inspect the cables and probes for signs of wear and tear. Look for any frayed wires, loose connections, or damage to the probe’s surface. If any issues are found, contact the manufacturer for guidance on replacing or repairing the affected components. Avoid using the bladder scanner if there are visible cable or probe issues.
Keep Software and Firmware Updated: Regularly check for software or firmware updates provided by the manufacturer. Keeping the software and firmware up to date ensures that your bladder scanner benefits from the latest enhancements, bug fixes, and improvements. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for updating the software or firmware to avoid any potential issues.
Store Properly: When the bladder scanner is not in use, store it appropriately in a clean and dry location. Avoid exposing the scanner to extreme temperatures or humidity levels. Proper storage helps prolong the lifespan of the scanner and prevents damage caused by environmental factors.
Schedule Regular Maintenance and Servicing: Consider scheduling regular maintenance and servicing by the manufacturer or an authorized service provider. Routine maintenance can help identify potential issues before they become major problems and improve the overall longevity and functionality of the bladder scanner.
Train Staff: Ensure that all staff members who will be using the bladder scanner are properly trained in its operation and maintenance. This includes understanding the proper cleaning procedures, following calibration processes, and recognizing when to seek assistance or report any concerns with the scanner. Adequate training contributes to the efficient and effective use of the bladder scanner.
By following these tips for bladder scanner maintenance, healthcare facilities can maximize the lifespan and accuracy of the equipment, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients and minimizing the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Where to Purchase a Bladder Scanner
When it comes to purchasing a bladder scanner, there are several options available for healthcare professionals and facilities. Here are some common sources where you can purchase a bladder scanner:
Medical Equipment Suppliers: Medical equipment suppliers specialize in providing a wide range of medical devices and equipment, including bladder scanners. They offer a variety of brands and models to choose from and often have knowledgeable staff who can assist in selecting the most suitable scanner for your specific needs.
Online Retailers: Many online retailers, both general and specialized medical equipment stores, offer bladder scanners for purchase. Online platforms provide convenience and the ability to compare different models and prices easily. However, it is essential to ensure that the online retailer is reputable and verified to avoid potential scams or purchasing counterfeit products.
Manufacturer’s Website: Some bladder scanner manufacturers have their own official websites where they sell their products directly to customers. Purchasing directly from the manufacturer can provide the benefit of warranty coverage, customer support, and access to the latest product information.
Medical Trade Shows and Exhibitions: Medical trade shows and exhibitions are excellent platforms to explore and purchase medical equipment, including bladder scanners. These events bring together various manufacturers, suppliers, and industry professionals, providing an opportunity to see different models, ask questions, and compare features in person.
Refurbished Equipment Suppliers: If the budget is a constraint, considering refurbished bladder scanners from reputable suppliers may be an option. Refurbished equipment undergoes a thorough inspection, repair if necessary, and testing to ensure functionality and performance. This option can provide cost savings without compromising on quality. However, it is crucial to purchase from trusted suppliers who guarantee the quality and performance of the refurbished equipment.
Medical Equipment Leasing Companies: Medical equipment leasing companies specialize in offering leasing or rental options for various medical devices, including bladder scanners. These companies allow healthcare facilities to acquire the equipment through lease agreements, spreading the cost over a specified period. This option provides the advantage of flexibility and can be beneficial for facilities with budget constraints or short-term equipment needs.
When purchasing a bladder scanner, it is important to consider factors such as product quality, features, price, warranty, customer support, and the reputation of the supplier or manufacturer. Take the time to research different options, read reviews, and compare offerings to make an informed decision that aligns with the specific needs and requirements of your healthcare facility.
Remember to verify the validity of any potential supplier or retailer and ensure their adherence to safety and regulatory standards. By choosing a reliable source, healthcare professionals and facilities can procure a high-quality bladder scanner that meets their standards for accuracy, reliability, and patient care.