History of the iPad
The iPad, a revolutionary device that changed the way we interact with technology, was first introduced by Apple Inc. in April 2010. This sleek and portable tablet computer quickly captured the attention of consumers around the world and became a symbol of innovation and cutting-edge technology.
Developed as a larger version of the iPhone, the iPad was designed to bridge the gap between smartphones and laptops. Its intuitive touch-screen interface and wide range of applications made it a versatile device that could be used for work, entertainment, and everything in between.
The first-generation iPad boasted a 9.7-inch display and was powered by Apple’s custom-designed A4 chip. It offered a seamless web-browsing experience, easy access to email and multimedia content, and support for various productivity tools. Despite initial skeptics, the iPad quickly gained traction and became a must-have gadget for tech enthusiasts.
Over the years, Apple continued to refine and improve the iPad, launching different models with enhanced features and capabilities. The introduction of the Retina display and the incorporation of the powerful A-series chips significantly boosted the performance and visual experience of the device.
The iPad also played a pivotal role in revolutionizing the publishing industry. With the launch of the iBooks app and the creation of the Apple App Store, users had access to a vast library of books, magazines, and educational materials. This not only provided a platform for authors and publishers to showcase their work but also allowed readers to embrace digital reading in an unprecedented way.
The popularity of the iPad continued to soar, with sales reaching remarkable milestones. In just one year, Apple sold over 14 million iPads, and by the end of 2013, the cumulative sales had surpassed 170 million units worldwide.
The success of the device can be attributed to several factors. The sleek and visually appealing design, the seamless integration with Apple’s ecosystem, and the extensive range of apps tailored specifically for the iPad contributed to its popularity among consumers.
Moreover, the iPad’s versatility and portability made it an ideal companion for various industries. It found its way into classrooms, transforming the education landscape by providing an interactive and engaging learning experience. It became an essential tool for artists and designers, allowing them to sketch and create digital artwork with ease.
In the competitive tablet market, the iPad has consistently led the pack, overshadowing its rivals in terms of sales and market share. Its continued success is a testament to Apple’s commitment to innovation and its understanding of consumer preferences.
As technology continues to evolve, it is fascinating to see how the iPad and other tablet devices will shape our future. With each iteration, the iPad pushes boundaries and sets new standards for what a portable computing device can accomplish.
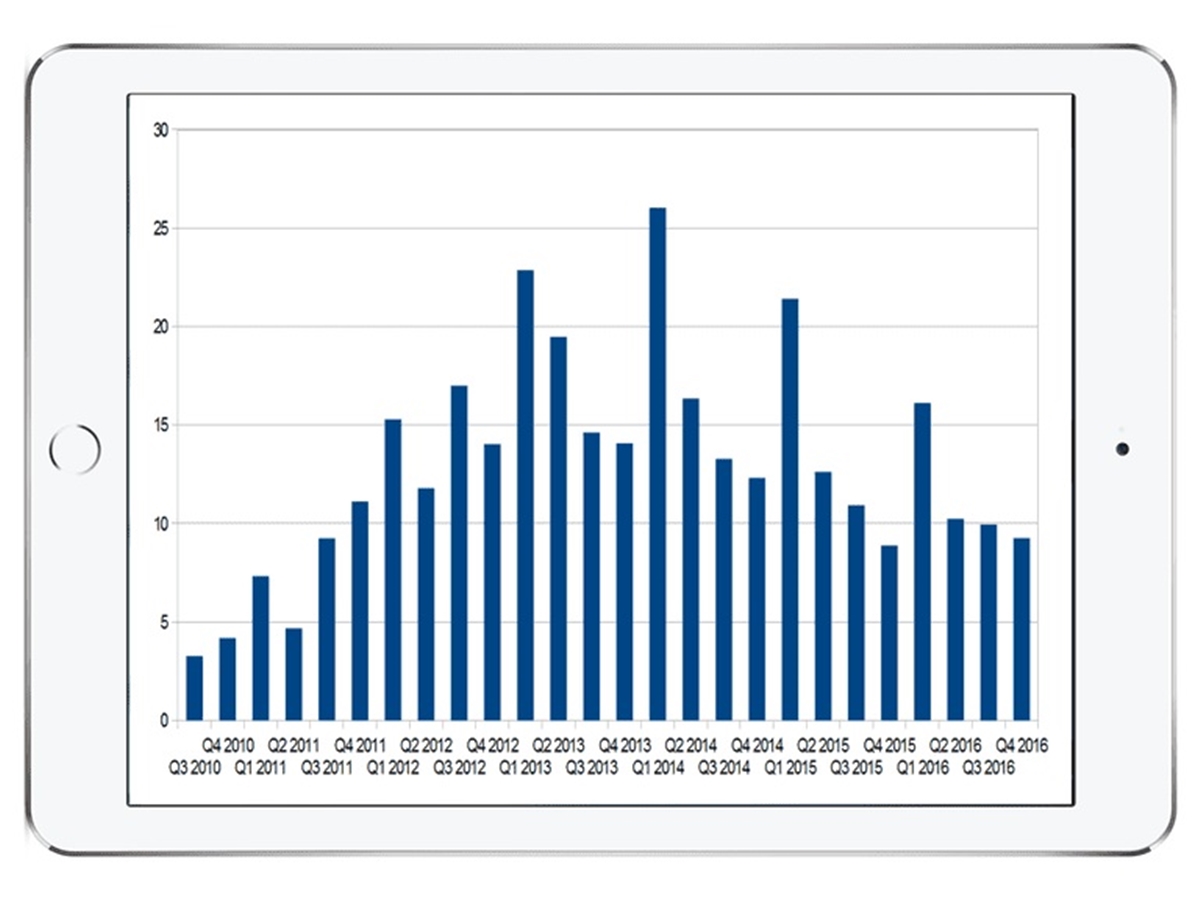
Sales figures from 2010-2013
The launch of the iPad in 2010 marked the beginning of a new era in the tablet market. With its sleek design and innovative features, the iPad quickly gained popularity among consumers worldwide. Let’s take a closer look at the sales figures from 2010 to 2013 to get a better understanding of the device’s impact.
In its first year, Apple managed to sell over 14 million iPads globally. This impressive figure was a testament to the device’s appeal and the strong demand from consumers. The sales continued to surge, reaching 32 million units sold by the end of 2011.
By 2012, the iPad had firmly established itself as the market leader, with Apple selling a staggering 58 million units. The introduction of the third-generation iPad, featuring a Retina display and improved performance, further fueled the sales momentum. The device became a must-have for tech enthusiasts and professionals alike, solidifying Apple’s position as the dominant player in the tablet market.
In 2013, Apple continued to push boundaries with the launch of the iPad Mini, a smaller and more compact version of the device. This move proved to be successful as Apple managed to sell over 71 million iPads that year, setting a new record for tablet sales.
During this period, the cumulative sales of the iPad surpassed a remarkable 170 million units worldwide. This incredible milestone further cemented Apple’s position as the industry leader in the tablet market.
The consistent high sales figures can be attributed to several factors. The iPad’s sleek design, user-friendly interface, and wide range of applications made it a desirable device for both personal and professional use. The seamless integration with Apple’s ecosystem, including iCloud and iTunes, also added value to the overall user experience.
Furthermore, the iPad’s versatility appealed to different segments of the market. It became a popular choice among students, educators, artists, and professionals in various industries. Its portability and long battery life made it an ideal companion for work, entertainment, and productivity on the go.
Overall, the sales figures from 2010 to 2013 showcased the immense popularity and success of the iPad. Apple’s continuous innovation and commitment to improving the device’s features and performance played a significant role in attracting and retaining customers.
The next section will delve into the popularity of different iPad models and how they contributed to the overall sales figures.
The popularity of different iPad models
Since its inception, the iPad has seen several iterations and model updates, each bringing new features and improvements to the table. Let’s explore the popularity of different iPad models and how they contributed to the overall sales figures.
The first-generation iPad, introduced in 2010, set the stage for the future of tablet computing. Its sleek design, intuitive interface, and extensive range of applications quickly captured the attention of consumers. This initial model laid the foundation for the iPad’s success, establishing Apple as a dominant player in the tablet market.
In 2011, the second-generation iPad, known as the iPad 2, was released. This lighter and faster model featured a dual-core processor, front and rear cameras, and a thinner design. These enhancements positioned the iPad 2 as a go-to device for multimedia consumption, communication, and productivity. Its popularity soared, and it became one of the best-selling iPads to date.
The introduction of the third-generation iPad in 2012 brought significant improvements, such as a Retina display, an upgraded processor, and enhanced graphics capabilities. This model catered to users who demanded a high-resolution display and better performance for graphics-intensive tasks. With its stunning visual experience and improved hardware, the third-generation iPad became a favorite among creatives, professionals, and media enthusiasts.
In the same year, Apple introduced the iPad Mini, a smaller and more portable version of the iPad. The iPad Mini appealed to users who preferred a more compact tablet for on-the-go tasks. Its lightweight design and affordability made it a popular choice for students and casual users alike.
With the release of the fourth-generation iPad, Apple focused on further enhancing the device’s performance and compatibility with newer technologies. This model featured a faster processor, improved camera capabilities, and lightning connector support. Although it did not bring major design changes, the fourth-generation iPad attracted users who valued increased processing power and advanced connectivity.
In 2013, Apple released the iPad Air and the second-generation iPad Mini. The iPad Air featured a significantly lighter and thinner design, making it more portable and comfortable to hold. The second-generation iPad Mini came with an improved Retina display, offering a sharper visual experience for users.
These iterations and additions to the iPad lineup showcased Apple’s commitment to meeting the diverse needs and preferences of consumers. Each model appealed to different segments of the market, offering a range of options based on size, capabilities, and price. This variety contributed to the overall popularity of the iPad and increased its market share.
Now that we have explored the popularity of different iPad models, the next section will delve into the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on iPad sales.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on iPad sales
The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020 brought unprecedented challenges and changes to various industries, including the technology sector. As people around the world adjusted to remote work, online learning, and social distancing measures, the demand for portable and versatile devices like the iPad surged.
One of the key drivers of increased iPad sales during the pandemic was the sudden shift to remote work and virtual communication. With businesses adopting work-from-home policies, professionals needed reliable devices that could support their work-related tasks. The iPad’s portability, long battery life, and compatibility with productivity apps made it an ideal choice for remote work setups. From attending virtual meetings to accessing cloud-based collaboration tools, the iPad became an essential tool for many professionals.
Similarly, the education sector witnessed a significant transformation as schools and universities moved to online learning. Students required devices that could facilitate virtual classrooms, interactive learning materials, and digital assessments. The iPad’s intuitive interface, variety of educational apps, and support for Apple Pencil enabled students to engage in remote learning effectively. Educational institutions worldwide recognized the value of iPads in facilitating distance education, leading to a surge in iPad sales for educational purposes.
Within the entertainment industry, the demand for streaming services and digital content also increased during the pandemic. With movie theaters closed and people spending more time at home, the iPad became a go-to device for consuming multimedia content. Its large, high-resolution display and immersive audio capabilities provided an enhanced viewing experience. Additionally, the iPad’s app ecosystem enabled access to a wide range of streaming platforms, gaming apps, and digital reading materials, further driving its popularity in the entertainment realm.
The impact of the pandemic on iPad sales was also fueled by consumers seeking avenues for creativity, relaxation, and personal growth. From digital art creation to fitness apps, the iPad offered a plethora of options to explore and engage in hobbies and self-improvement activities. As people sought innovative ways to stay entertained and productive while spending more time indoors, the iPad became a versatile companion for their pursuits.
Overall, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the demand for the iPad as it proved to be an adaptable, reliable, and multifunctional device for various aspects of daily life. The increased reliance on remote work, online learning, entertainment, and personal development created a favorable environment for iPad sales to soar.
In the next section, we will compare iPad sales to other tablet devices to gauge its dominance in the tablet market.
Comparing iPad sales to other tablet devices
When it comes to the tablet market, the iPad has maintained a dominant position since its launch in 2010. While other tablet devices have entered the market and gained popularity, the iPad has consistently outperformed its competitors in terms of sales and market share.
One of the key factors driving the iPad’s success is Apple’s strong ecosystem, which includes a seamless integration among its devices, services, and software. This ecosystem enables a cohesive user experience and makes it easier for consumers to transition between different Apple products. It also allows developers to create innovative and optimized apps specifically for the iPad, giving it a competitive edge.
Despite the competition, the iPad continues to hold the largest market share in the tablet industry. According to market research firm IDC, Apple accounted for around 34% of tablet shipments in 2020, making it the leading tablet vendor worldwide. This demonstrates the iPad’s popularity and market dominance.
While there are several notable competitors in the tablet market, such as Samsung, Amazon, and Lenovo, none have managed to surpass the iPad in terms of sales. Samsung, known for its Galaxy Tab series, is the closest competitor to Apple. However, Samsung’s market share lags behind Apple, with approximately 16% of tablets shipped in 2020.
Amazon’s Kindle Fire tablets have gained popularity in the budget tablet segment, primarily due to their affordability and integration with Amazon’s vast content ecosystem. However, they have not been able to rival the iPad’s market share. Lenovo, another prominent player in the tablet market, has gradually gained traction with its range of Android tablets but still falls behind Apple in terms of sales volume.
One of the key advantages that the iPad has over its competitors is its strong brand recognition and customer loyalty. Apple has a dedicated user base that eagerly awaits new product launches and upgrades. This loyal customer base, coupled with Apple’s reputation for high-quality products and customer support, gives the iPad a significant advantage in the market.
Furthermore, Apple’s focus on innovation and its ability to consistently deliver cutting-edge features and technologies have helped the iPad maintain its leadership position in the tablet market. The company’s commitment to refining and improving its products keeps consumers interested and eager to upgrade to the latest iPad model.
In summary, while other tablet devices have made their mark in the market, the iPad continues to lead in terms of sales and market dominance. Apple’s strong ecosystem, brand recognition, customer loyalty, and commitment to innovation have solidified the iPad’s position as the go-to tablet for consumers worldwide.
In the next section, we will explore iPad sales figures by region to gain a deeper understanding of its global reach.
Sales figures by region
The popularity of the iPad extends across the globe, with strong sales figures in various regions. The device’s global reach can be attributed to its innovative features, user-friendly interface, and robust app ecosystem. Let’s take a closer look at iPad sales figures by region to understand its geographical impact.
North America, particularly the United States, has consistently been a strong market for the iPad. The iPad’s early adoption and Apple’s strong presence in the region have contributed to its success. According to market research, North America accounted for a significant portion of iPad sales, with the United States being the largest market. The iPad’s versatility, performance, and strong integration within the Apple ecosystem have resonated well with North American consumers.
Europe is another key market for the iPad. Countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Italy have seen substantial iPad sales. Apple’s brand recognition, coupled with the iPad’s appeal to professionals, students, and creative individuals, has made it a popular choice across the continent. Additionally, the iPad’s compatibility with multiple languages and its extensive app selection have contributed to its success in Europe.
Asia-Pacific has emerged as a significant region for iPad sales. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia have shown a growing demand for the device. The iPad’s sleek design, advanced features, and support for regional languages and apps have made it a sought-after tablet in the Asian market. Additionally, the iPad’s compatibility with digital content services and its appeal among both young and mature consumers have contributed to its sales growth in the region.
The Latin American market has also witnessed a gradual increase in iPad sales. Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina have embraced the device for personal and educational use. The iPad’s capabilities in supporting digital learning initiatives and its robust multimedia features have made it a popular choice among students and educators in the region.
In the Middle East and Africa, the iPad has gained traction in countries like the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. The region’s growing tech-savvy population, along with a rising interest in digital content consumption and productivity tools, has fueled the demand for the iPad. Its seamless connectivity and ability to cater to various cultural and language preferences have contributed to its sales in the region.
While iPad sales figures vary by region, it is evident that the device’s appeal and market share extend globally. Apple’s strong brand presence, continuous innovation, and commitment to user experience have played a key role in driving iPad sales across different continents.
In the next section, we will explore the growing significance of iPads in the education sector and their impact on learning.
The rise of educational use of iPads
In recent years, the iPad has seen an ever-increasing presence in classrooms and educational institutions worldwide. Its intuitive interface, extensive range of educational apps, and interactive features have positioned it as a powerful tool for teaching and learning. Let’s delve into the rise of the educational use of iPads and the impact it has had on learning.
One of the primary drivers behind the adoption of iPads in education is their ability to enhance student engagement and participation. With interactive apps, multimedia content, and interactive textbooks, the iPad offers a dynamic learning experience that goes beyond traditional teaching methods. Students can explore concepts through videos, engage in interactive quizzes, and collaborate on projects, fostering a more hands-on and immersive learning environment.
The iPad’s portability and versatility also make it an excellent choice for personalized learning. With individual iPads, students can work at their own pace, access educational resources tailored to their needs, and receive immediate feedback. Adaptive learning apps and platforms allow for personalized instruction, adapting content and tasks based on individual student progress, strengths, and weaknesses.
Furthermore, iPads provide access to a vast repository of educational content, including e-books, articles, and online resources. This wealth of information empowers students to conduct research, explore different subjects, and deepen their understanding of various topics. The iPad’s digital nature also ensures that resources can be accessed anytime and anywhere, extending the learning beyond the confines of the classroom.
Teachers have also embraced iPads as a powerful teaching tool. With the ability to create and deliver interactive lessons, annotate documents, and provide real-time feedback, the iPad enables educators to enhance their instructional practices. The iPad’s versatility allows for seamless integration with other classroom technology, such as projectors and interactive whiteboards, enabling teachers to create dynamic and engaging learning experiences.
The iPad’s accessibility features have also made it an inclusive tool for students with diverse learning needs. The device offers features such as text-to-speech, voice dictation, and adjustable font sizes and colors, promoting accessibility and accommodating students with disabilities. This inclusivity ensures that all students can actively participate in the learning process and reach their full potential.
In addition to its impact on individual students and teachers, the widespread adoption of iPads has transformed the education landscape as a whole. Schools and educational institutions worldwide have embraced iPad initiatives, equipping classrooms with dedicated iPad carts or providing individual devices to students. This integration of iPads in education has not only improved teaching and learning but also fostered digital literacy skills and prepared students for the technology-driven world.
The rise of the educational use of iPads is a testament to the device’s adaptability, user-friendly interface, and versatility in catering to the diverse needs of students and educators. As the field of education continues to evolve, iPads are expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of learning.
In the next section, we will look at predictions for future iPad sales and how the device is likely to evolve in the coming years.
Predictions for future iPad sales
The iPad has experienced remarkable success since its introduction in 2010, continuously evolving and adapting to meet the changing demands of consumers. As we look to the future, several factors indicate that iPad sales will continue to thrive and reach new heights.
Firstly, the increasing integration of technology in various industries, such as healthcare, retail, and finance, presents significant opportunities for the iPad. As organizations seek more efficient and flexible solutions, the iPad’s portability, user-friendly interface, and extensive app ecosystem make it an attractive choice. From point-of-sale systems to patient management tools, the iPad has the potential to become a staple device in many professional environments.
Additionally, the ongoing digital transformation in education will drive an increased demand for iPads in schools and universities. With the shift towards blended learning models and the need for remote and personalized instruction, the iPad’s versatility and ecosystem of educational apps position it as a valuable educational tool. Integration with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies may further enhance the iPad’s role in immersive learning experiences.
The demand for tablets in emerging markets, such as India, China, and Brazil, is also expected to contribute to future iPad sales growth. As these markets continue to experience economic development and an increased focus on education and technology, more consumers will seek affordable and high-quality tablets like the iPad.
Furthermore, as Apple continues to innovate and introduce new iPad models with advanced features and capabilities, it is likely to attract both new and existing customers. Enhancements in processing power, display technology, camera capabilities, and connectivity will further solidify the iPad’s position as a premium and cutting-edge tablet option.
The ongoing advancements in 5G technology and cloud computing will also play a significant role in the future of iPad sales. These advancements will enable seamless connectivity, faster data transfer speeds, and greater storage capabilities, enhancing the iPad’s ability to handle complex tasks and enable real-time collaboration.
Lastly, the growing importance of remote work and the increased value placed on flexibility and productivity will contribute to the continued success of the iPad. As organizations adopt hybrid work models and individuals seek devices that can support their professional needs from anywhere, the iPad’s mobility, performance, and compatibility with productivity tools position it as an ideal choice.