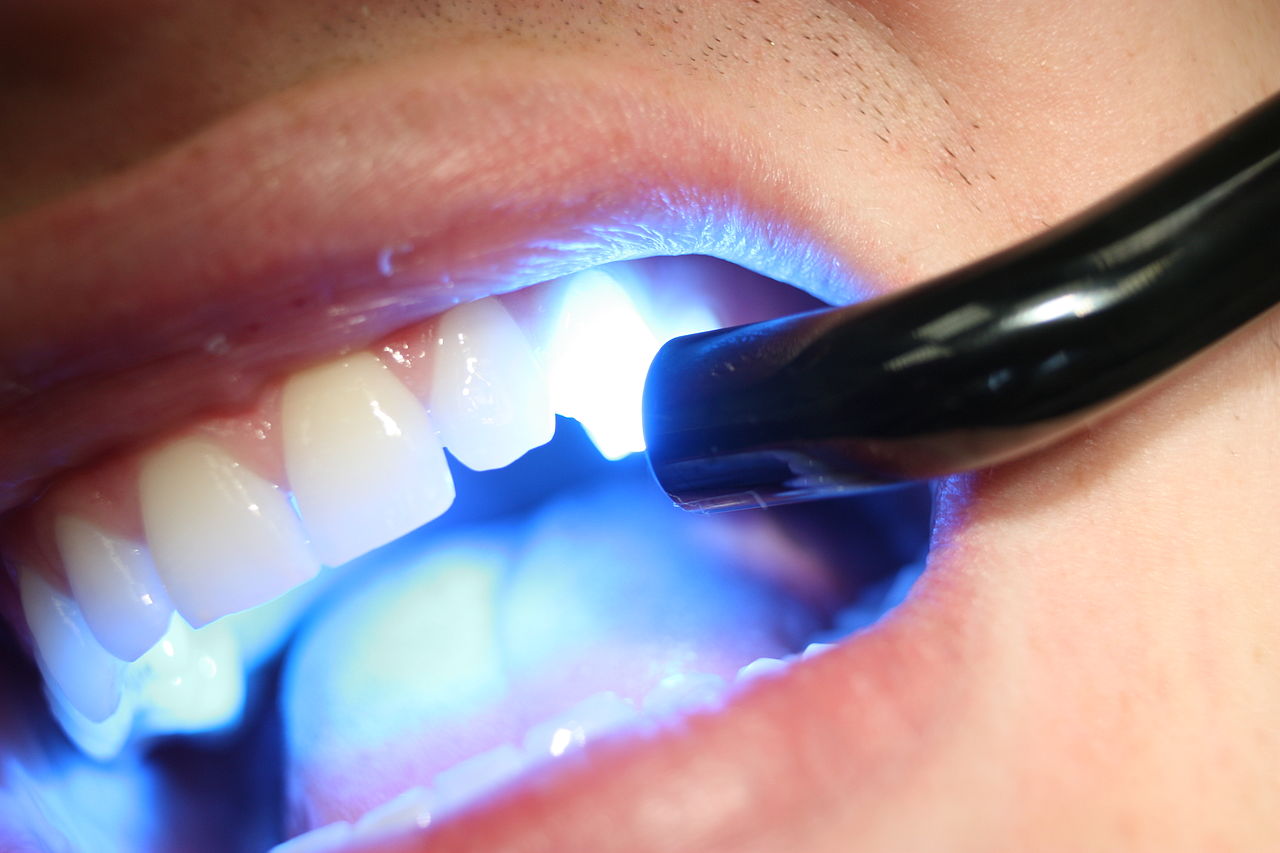
What is Dental Illumination?
Dental illumination, also known as dental curing light, is an essential tool used by dentists to cure or harden various dental materials, such as composites, sealants, and cements. This process, known as photopolymerization, involves the use of a specific wavelength of light to initiate a chemical reaction that transforms the materials from a pliable state to a hardened, durable state.
The primary type of light used in dental illumination is blue light, typically in the wavelength range of 430 to 490 nanometers. This specific range of blue light is known to activate the photoinitiators within the dental materials, allowing them to polymerize and create a strong bond with the tooth structure.
Dental illumination plays a crucial role in modern dentistry, as it enables dentists to efficiently and effectively complete various restorative and cosmetic dental procedures. The use of blue light for dental curing has revolutionized the way dental treatments are performed, leading to improved outcomes and patient satisfaction.
This technology has significantly reduced the time required for curing dental materials, allowing for quicker and more precise procedures. Additionally, the use of dental illumination has contributed to the overall durability and longevity of dental restorations, ensuring that patients can enjoy the benefits of their treatments for an extended period.
In essence, dental illumination, particularly the use of blue light, represents a cornerstone of contemporary dental practice, providing dentists with a reliable and efficient method for curing dental materials and enhancing the overall quality of patient care.
The Science Behind Blue Light
Blue light, a specific segment of the visible light spectrum, plays a pivotal role in dental illumination due to its unique properties and interactions with dental materials. Understanding the science behind blue light is essential for comprehending its effectiveness in dental procedures.
At the core of blue light’s efficacy lies its wavelength, typically ranging from 430 to 490 nanometers. This specific range of wavelengths is known to correspond with the absorption spectrum of the photoinitiators present in dental materials, such as resin-based composites. When exposed to blue light, these photoinitiators absorb the energy and undergo a photochemical reaction, initiating the polymerization process within the dental materials.
The process of photopolymerization involves the conversion of the liquid or semi-solid resin-based composite into a solid, durable material through the formation of cross-linked polymers. This transformation occurs as the photoinitiators, activated by the blue light, generate free radicals that initiate a chain reaction, leading to the formation of a stable polymer network.
Moreover, the high energy content of blue light enables it to penetrate the dental materials effectively, ensuring uniform curing throughout the restoration. This thorough polymerization is crucial for achieving optimal physical properties, such as strength, wear resistance, and color stability, in the cured dental materials.
Furthermore, blue light’s ability to activate the photoinitiators rapidly contributes to the efficiency of dental procedures, as it facilitates swift curing of the materials. This rapid curing not only saves time for both the dentist and the patient but also minimizes the risk of contamination or movement of the dental materials during the curing process.
Overall, the science behind blue light underscores its significance in dental illumination, as its specific wavelength, energy content, and rapid activation of photoinitiators collectively contribute to the successful polymerization of dental materials, ultimately enhancing the quality and longevity of dental restorations.
Benefits of Blue Light in Dentistry
The utilization of blue light in dentistry offers a myriad of benefits that significantly enhance the efficiency, efficacy, and overall patient experience during dental procedures. Understanding these advantages underscores the pivotal role of blue light in modern dental practice.
- Rapid Curing: Blue light facilitates rapid curing of dental materials, minimizing procedure time and enhancing patient comfort. The swift activation of photoinitiators expedites the polymerization process, allowing for quick and efficient completion of restorative and cosmetic treatments.
- Precision and Control: The focused delivery of blue light enables dentists to exert precise control over the curing process, ensuring uniform and thorough polymerization of dental materials. This precision contributes to the durability and longevity of dental restorations.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: The use of blue light in curing dental composites results in aesthetically pleasing outcomes, as the materials achieve optimal color stability and translucency. This contributes to natural-looking restorations that blend seamlessly with the patient’s dentition.
- Reduced Sensitivity: Efficient curing with blue light minimizes the potential for post-operative sensitivity in patients, as the thorough polymerization of dental materials contributes to the creation of restorations with minimal internal stresses, reducing the risk of discomfort.
- Improved Patient Experience: The swift and effective nature of blue light curing enhances the overall patient experience, as it reduces the time spent in the dental chair and minimizes the need for extended waiting periods during procedures. This leads to enhanced patient satisfaction and comfort.
Collectively, these benefits underscore the indispensable role of blue light in dentistry, as it not only streamlines the clinical workflow for dental professionals but also contributes to the delivery of high-quality, aesthetically pleasing, and enduring dental treatments for patients.
How Blue Light is Used in Dental Procedures
The strategic utilization of blue light in various dental procedures showcases its versatility and indispensable role in modern dentistry. From restorative treatments to cosmetic enhancements, blue light plays a pivotal role in ensuring the success and longevity of dental interventions.
Dental Bonding and Fillings: In dental bonding procedures, blue light is employed to cure the resin-based composite materials used to repair chipped, decayed, or discolored teeth. The focused application of blue light activates the photoinitiators within the composite, facilitating rapid and thorough curing to create durable, natural-looking restorations. Similarly, in dental fillings, blue light is utilized to harden the composite materials that replace decayed tooth structure, ensuring precise shaping and optimal functionality.
Dental Sealants: Blue light is instrumental in the application of dental sealants, which are used to protect the occlusal surfaces of molars and premolars from decay. After the application of the sealant material, blue light is directed onto the surface to initiate the curing process, leading to the formation of a resilient and protective seal that shields the tooth from bacterial invasion and acid erosion.
Orthodontic Treatments: In orthodontics, blue light is employed for the curing of orthodontic adhesives used to bond brackets to the teeth. This precise curing process ensures secure and reliable attachment of the brackets, contributing to the effectiveness of orthodontic treatment and the comfort of the patient.
Cosmetic Enhancements: Blue light is integral to various cosmetic dental procedures, such as teeth whitening and veneer placement. In teeth whitening treatments, the activation of whitening agents with blue light accelerates the bleaching process, leading to enhanced efficiency and superior whitening outcomes. Additionally, during veneer placement, blue light is utilized to cure the resin cement used to bond the veneers to the tooth surface, ensuring optimal adhesion and aesthetics.
Endodontic Therapy: Within endodontics, blue light is employed in the curing of root canal sealants and adhesives, contributing to the successful sealing of the root canal system and the prevention of bacterial recontamination.
By encompassing a wide array of dental procedures, the application of blue light underscores its indispensable role in facilitating efficient, durable, and aesthetically pleasing outcomes across diverse realms of dental practice.
Safety and Concerns of Blue Light in Dentistry
While the use of blue light in dentistry offers numerous benefits, it is essential to address safety considerations and potential concerns associated with its application to ensure the well-being of both dental professionals and patients.
Eye Protection: Dental practitioners and patients are required to wear appropriate eye protection, such as orange-tinted glasses or goggles, during procedures involving blue light. This precautionary measure safeguards against potential retinal damage and ensures the protection of ocular tissues from prolonged exposure to the intense blue light emitted by dental curing devices.
Skin Protection: Dental professionals must exercise caution to prevent direct skin exposure to blue light, as prolonged contact may lead to skin sensitivity or irritation. Utilizing protective barriers, such as gloves and sleeves, can mitigate the risk of skin-related concerns during the handling of blue light-emitting devices.
Precautions for Vulnerable Individuals: Special attention must be given to patients with photosensitive conditions or those who may be particularly sensitive to bright light. Dentists should inquire about any underlying medical conditions or medications that could heighten sensitivity to blue light, allowing for tailored precautions and adjustments during treatment.
Device Calibration and Monitoring: Regular calibration and monitoring of dental curing lights are imperative to ensure the consistent and safe delivery of blue light during dental procedures. Maintaining proper functionality and output intensity of the devices minimizes the potential for overexposure and ensures the optimal curing of dental materials.
Adherence to Guidelines: Dental professionals should adhere to established guidelines and best practices for the safe use of blue light in dentistry, including proper device maintenance, appropriate exposure times, and adherence to recommended safety protocols. This commitment to compliance promotes the safe and effective integration of blue light technology in dental practice.
Educational Awareness: Promoting awareness and education regarding the safe use of blue light is essential for both dental practitioners and patients. By providing comprehensive information about the potential risks and safety measures associated with blue light exposure, dental professionals empower individuals to make informed decisions and actively participate in their oral care.
By addressing these safety considerations and implementing proactive measures, dental professionals uphold a commitment to ensuring the safe and responsible integration of blue light technology in dentistry, prioritizing the well-being and comfort of both practitioners and patients.