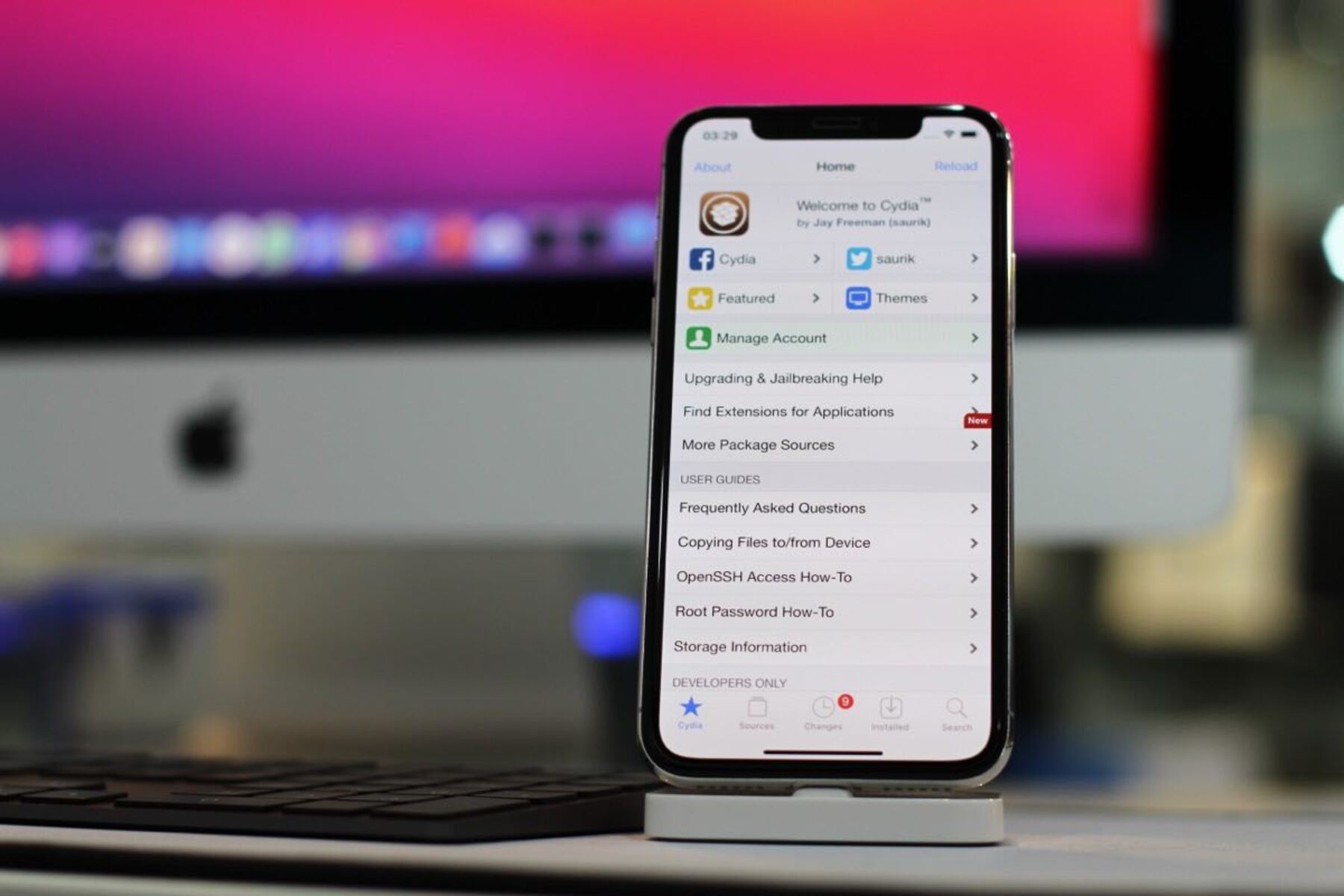
What is Rooting?
Rooting an iPhone 13 refers to the process of gaining privileged access to the device's operating system, allowing users to modify the software beyond the limitations set by the manufacturer. In essence, it grants users administrative control over the device, enabling them to customize the system, install unauthorized applications, and access features that are typically restricted.
When an iPhone 13 is rooted, users can delve into the core of the operating system, making changes that are otherwise inaccessible. This can include removing pre-installed bloatware, optimizing system performance, and even installing custom versions of the operating system, known as custom ROMs. Additionally, rooting provides the ability to tweak settings and access hidden features, offering a level of customization that is not achievable on a non-rooted device.
Rooting can also facilitate the installation of powerful applications that require elevated system permissions, allowing users to enhance the functionality of their iPhone 13 beyond what is possible with standard, non-rooted devices. This can include advanced backup and restore options, system-level automation tools, and deep customization apps that can transform the user interface and overall user experience.
However, it is important to note that rooting an iPhone 13 comes with inherent risks and can void the device's warranty. Therefore, it is crucial for users to weigh the potential benefits against the associated drawbacks before deciding to root their device. Understanding the implications of rooting is essential for making an informed decision and ensuring that the process aligns with individual needs and preferences.
Pros and Cons of Rooting the iPhone 13
Rooting the iPhone 13 offers a myriad of potential advantages and drawbacks, each of which should be carefully considered before embarking on the process. Understanding the pros and cons is crucial for individuals contemplating whether to root their device. Here's a comprehensive overview of the benefits and drawbacks associated with rooting the iPhone 13:
Pros:
-
Customization: Rooting the iPhone 13 provides unparalleled customization options, allowing users to personalize the device to their preferences. This includes the ability to install custom themes, modify system fonts, and tweak the user interface to create a truly unique user experience.
-
Performance Optimization: Rooting enables users to optimize the performance of their iPhone 13 by removing bloatware and resource-intensive background processes. This can result in improved battery life, faster operation, and a smoother overall user experience.
-
Access to Advanced Features: Rooted iPhone 13 devices can access advanced features and settings that are typically off-limits. This includes the ability to fine-tune system parameters, overclock the CPU for enhanced performance, and utilize powerful automation tools to streamline everyday tasks.
-
Installation of Custom ROMs: Rooting facilitates the installation of custom ROMs, which are modified versions of the operating system. Custom ROMs can offer enhanced functionality, improved security features, and a range of customization options that are not available on stock iOS.
-
Enhanced Backup and Restore Options: Rooted iPhone 13 devices can utilize advanced backup and restore applications that offer greater flexibility and control over data management. This includes the ability to perform full system backups, selectively restore app data, and implement comprehensive data migration strategies.
Cons:
-
Voided Warranty: Rooting the iPhone 13 can void the device's warranty, potentially leaving users without manufacturer support in the event of hardware or software issues. This can result in additional costs for repairs and maintenance.
-
Security Risks: Rooting exposes the iPhone 13 to potential security vulnerabilities, as it bypasses built-in security measures designed to protect the device and user data. This can make rooted devices more susceptible to malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
-
Risk of Bricking: Improperly executed rooting procedures can lead to "bricking" the iPhone 13, rendering it inoperable. This risk is particularly significant for inexperienced users or those who attempt to root their device without thorough understanding and preparation.
-
Limited App Compatibility: Rooted iPhone 13 devices may encounter compatibility issues with certain applications and services, as some developers restrict access to rooted devices due to security and piracy concerns.
-
Potential Instability: Modifications made to the iPhone 13's operating system through rooting can introduce instability and unpredictable behavior, leading to system crashes, app malfunctions, and overall reduced reliability.
In weighing these pros and cons, individuals considering rooting their iPhone 13 must carefully evaluate their specific needs, technical proficiency, and willingness to accept the associated risks and trade-offs. Ultimately, the decision to root an iPhone 13 should be informed by a comprehensive understanding of the potential implications and a clear assessment of the desired benefits.
How to Root the iPhone 13
Rooting the iPhone 13 involves a series of intricate steps that require careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the process. It is important to note that rooting a device carries inherent risks and can void the manufacturer's warranty, so proceeding with caution is paramount. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to root the iPhone 13:
-
Backup Data: Before initiating the rooting process, it is crucial to back up all essential data on the iPhone 13. This includes contacts, photos, videos, documents, and any other important files. Utilizing iCloud or a computer-based backup solution ensures that valuable data is safeguarded in the event of unforeseen complications during the rooting process.
-
Unlock Bootloader: In order to root the iPhone 13, the bootloader must be unlocked to allow the installation of custom software. This typically involves obtaining an unlock code from the device manufacturer or utilizing third-party tools and resources to unlock the bootloader. It is important to research and understand the implications of unlocking the bootloader, as this step is irreversible and can impact the device's security and stability.
-
Install Custom Recovery: After unlocking the bootloader, the next step is to install a custom recovery environment on the iPhone 13. This enables users to create full backups, install custom ROMs, and perform system-level modifications. Popular custom recovery options for iPhone 13 include TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project) and ClockworkMod Recovery, each offering unique features and functionality.
-
Flash Rooting Package: With the custom recovery environment in place, users can proceed to flash the rooting package onto the iPhone 13. This package typically includes the necessary files and scripts to gain root access to the device's operating system. It is essential to follow the specific instructions provided by the rooting package developer and ensure compatibility with the iPhone 13 model and software version.
-
Verify Root Access: Upon successful flashing of the rooting package, it is important to verify that root access has been attained on the iPhone 13. This can be confirmed using root management applications such as SuperSU or Magisk, which provide detailed insights into the device's root status and allow users to manage root permissions for installed applications.
-
Customize and Optimize: Once the iPhone 13 is rooted, users can explore a wide range of customization and optimization options. This includes installing root-specific applications, tweaking system settings, and exploring the full potential of the rooted device. However, it is crucial to exercise caution when making system-level modifications to avoid potential instability and security vulnerabilities.
It is important to emphasize that rooting the iPhone 13 requires a high level of technical proficiency and a thorough understanding of the associated risks. Additionally, it is essential to research and utilize reputable resources and tools when undertaking the rooting process to minimize the potential for adverse outcomes. Ultimately, individuals considering rooting their iPhone 13 should carefully weigh the benefits and drawbacks before proceeding, ensuring that the decision aligns with their specific needs and technical capabilities.
Risks and Security Concerns of Rooting
Rooting an iPhone 13 introduces a host of inherent risks and security concerns that users must carefully consider before embarking on the process. While rooting offers the allure of enhanced customization and control, it also exposes the device to potential vulnerabilities and compromises. Understanding the risks associated with rooting is essential for making an informed decision and mitigating the potential impact on the device's security and stability.
One of the primary risks of rooting the iPhone 13 is the voiding of the device's warranty. By altering the operating system and gaining root access, users effectively bypass the manufacturer's intended software configuration, which can result in the forfeiture of warranty coverage. This means that in the event of hardware or software issues, users may be left without the support of the manufacturer, potentially incurring additional costs for repairs and maintenance.
Moreover, rooting exposes the iPhone 13 to heightened security risks. By circumventing built-in security measures and gaining elevated system privileges, rooted devices are more susceptible to malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. The inherent security mechanisms designed to protect the device and user data are compromised, leaving the device more vulnerable to exploitation and compromise.
Another significant concern is the potential for "bricking" the iPhone 13 during the rooting process. Improper execution of rooting procedures, such as flashing incompatible software or making erroneous system modifications, can render the device inoperable, effectively turning it into a "brick." This risk is particularly pronounced for inexperienced users or those who attempt to root their device without a comprehensive understanding of the process.
Furthermore, rooted iPhone 13 devices may encounter compatibility issues with certain applications and services. Some developers restrict access to rooted devices due to security and piracy concerns, leading to limitations in app compatibility and functionality. This can result in a diminished user experience and may render certain applications unusable on rooted devices.
Additionally, modifications made to the iPhone 13's operating system through rooting can introduce instability and unpredictable behavior. This includes potential system crashes, app malfunctions, and reduced overall reliability. The device may exhibit erratic performance and behavior, undermining the user experience and potentially compromising essential functionality.
In light of these risks and security concerns, individuals contemplating rooting their iPhone 13 must carefully evaluate the potential implications and weigh them against the desired benefits. It is imperative to approach rooting with a thorough understanding of the associated risks and to exercise caution throughout the process to minimize the potential impact on the device's security, stability, and overall usability.
Alternatives to Rooting the iPhone 13
For individuals seeking to enhance the functionality and customization of their iPhone 13 without the inherent risks and complexities associated with rooting, several viable alternatives exist. These alternatives offer a middle ground, providing users with expanded capabilities and customization options while maintaining the integrity and security of the device's original software configuration.
1. Jailbreaking
Jailbreaking, while distinct from rooting, offers a similar avenue for customizing and expanding the capabilities of the iPhone 13. This process involves removing software restrictions imposed by Apple, allowing users to install unauthorized applications and make system-level modifications. Jailbreaking provides access to a wide array of third-party apps and tweaks, enabling users to personalize their device without fully rooting it. However, it is important to note that jailbreaking also carries inherent risks and can void the device's warranty, requiring careful consideration before proceeding.
2. Utilizing Third-Party Applications
Numerous third-party applications available on the App Store offer advanced customization and functionality without the need for rooting or jailbreaking. These applications provide features such as custom widgets, alternative keyboards, and system-wide themes, allowing users to personalize their iPhone 13 within the confines of Apple's software ecosystem. Additionally, productivity tools, automation apps, and file management utilities can significantly enhance the device's capabilities without compromising its security or stability.
3. Custom Launchers and Widgets
Custom launchers and widgets available through the App Store enable users to transform the look and feel of their iPhone 13's home screen and user interface. These tools offer extensive customization options, including unique icon packs, customizable widgets, and personalized layouts, providing a level of personalization that rivals traditional rooting without the need for system-level modifications.
4. External Accessories and Gadgets
External accessories and gadgets, such as Bluetooth-enabled controllers, smart home devices, and external storage solutions, can augment the functionality of the iPhone 13 without altering its core software. These accessories expand the device's capabilities, offering enhanced gaming experiences, improved productivity, and expanded storage options, all without the need to root the device.
5. System-Level Settings and Features
Exploring the extensive array of system-level settings and features inherent to iOS can reveal hidden customization options and advanced functionality. This includes accessibility settings, privacy controls, and advanced system configurations that can be tailored to suit individual preferences. By delving into the device's native settings, users can unlock a wealth of customization and optimization options without the need for rooting.
By leveraging these alternatives, individuals can personalize and expand the capabilities of their iPhone 13 without resorting to rooting. These options offer a balance between customization and security, providing users with a diverse array of tools and methods to tailor their device to their preferences while preserving the integrity of the original software configuration.