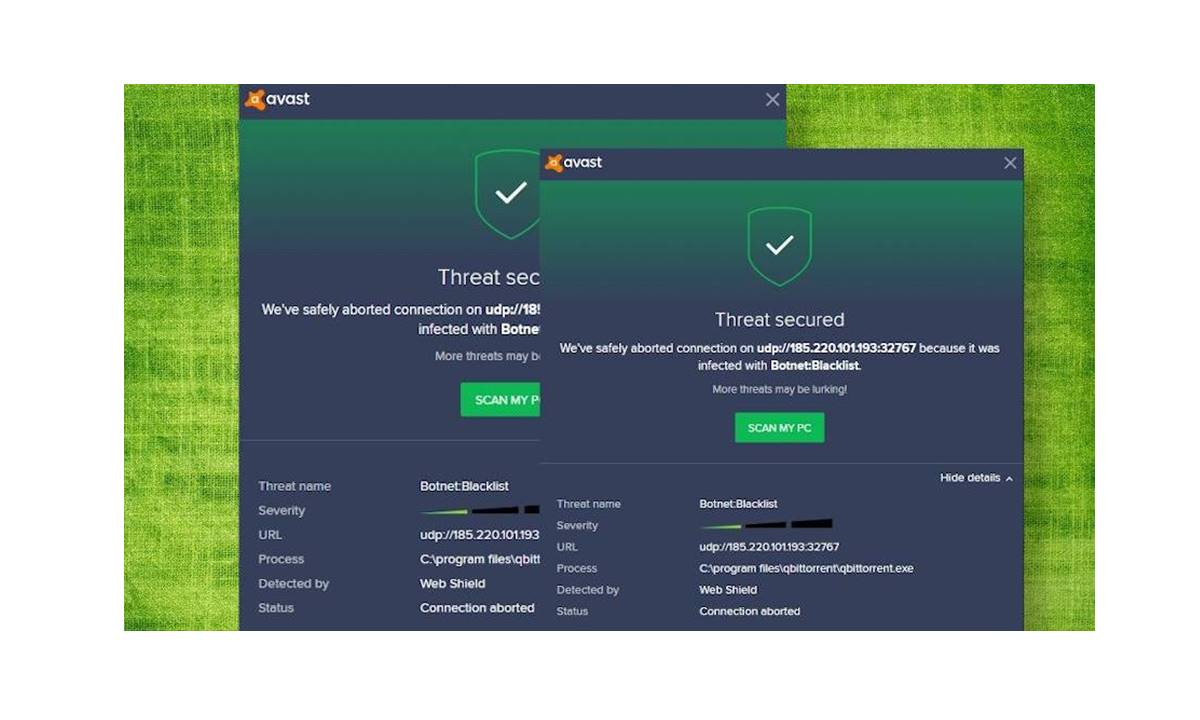
Recognizing Signs of Botnet Malware
Botnet malware is a serious threat that can compromise your devices and use them to perform malicious activities. Recognizing the signs of botnet malware early on is crucial in mitigating potential damages. Here are some common indicators to watch out for:
- Unusual Network Activity: If you notice a sudden increase in your network traffic, especially during odd hours or when your devices are idle, it could be a sign of botnet malware. Pay attention to any unusual data transfers or spikes in bandwidth usage.
- Slow Performance: Botnet malware often consumes considerable system resources, leading to slower device performance. If you find that your system is lagging or responding sluggishly, it may be a result of botnet malware running in the background.
- Unexpected Pop-ups or Advertisements: Malicious botnets often generate unwanted pop-ups or display intrusive advertisements on your browser, even when you’re not actively browsing the web. If you frequently encounter such pop-ups, it could indicate the presence of botnet malware.
- Unexplained Crashes: Frequent system crashes or unexpected restarts without any apparent reason can be a symptom of botnet malware. These activities may be initiated by the malware itself or by the command of the botnet controller.
- Mysterious Changes in Settings: If you notice unusual changes in your device’s settings, such as modified browser homepage, new toolbar installations, or unauthorized software installations, it may indicate a botnet infection. Botnet malware often manipulates these settings to gain control over your device.
It is important to remain vigilant and stay informed about the signs of botnet malware. Being able to recognize these indicators will enable you to take immediate action, protecting yourself and your devices from potential threats. In the next section, we will discuss how to identify the infected device and isolate it from the network.
Identifying the Infected Device
When dealing with botnet malware, it is crucial to identify the infected device to effectively combat the threat. Here are some steps to help you identify which device within your network has been compromised:
- Analyze Network Traffic: Start by monitoring your network traffic using network monitoring tools or firewalls. Look for any unusual or suspicious patterns that could indicate the presence of botnet activity. Abnormally high data transfers or connections to suspicious IP addresses can be a red flag.
- Review Device Logs: Examine the logs of your network devices, including routers, switches, and firewalls. Look for any entries that indicate unauthorized access attempts, unusual network behavior, or connections to known malicious domains. These logs can provide valuable clues to identify the infected device.
- Conduct Antivirus Scans: Run thorough antivirus scans on all devices connected to your network. Make sure to use reputable antivirus software that is regularly updated. The antivirus scans will help detect any malware or botnet infections on your devices.
- Observe Device Performance: Pay attention to the performance of each device on your network. If you notice significant decreases in performance or unusual behavior like high CPU usage or excessive network traffic, it may indicate that the device is infected by a botnet.
- Consider User Behavior: Evaluate the activities of the users connected to your network. Look for signs of suspicious behavior, such as downloading files from untrusted sources, visiting malicious websites, or engaging in unsafe online practices. Often, botnet infections occur due to unknowingly downloading malicious files or falling victim to social engineering attacks.
By diligently following these steps, you can identify the infected device and take the necessary measures to isolate it from your network. It is important to address the issue promptly to prevent further spread of the botnet malware. In the next section, we will discuss how to disconnect the infected device from the internet to minimize potential threats.
Disconnecting from the Internet
Once you have identified an infected device on your network, it is crucial to disconnect it from the internet immediately to prevent further harm. Taking this step will help isolate the device from the botnet and minimize the risk of spreading malware to other devices. Here’s what you should do:
- Physically Disconnect: If possible, physically disconnect the infected device from the network by unplugging the Ethernet cable or disabling the Wi-Fi connection. This will immediately cut off its access to the internet and prevent any further communication with the botnet.
- Disable Network Connections: If physical disconnection is not feasible, disable all network connections on the infected device manually. Go to the device’s network settings and turn off Wi-Fi, unplug Ethernet cables, or disable any other network interfaces. This will effectively disconnect the device from the internet.
- Disable Auto-connect Options: Some devices have auto-connect features that automatically reconnect to available networks. To ensure the infected device doesn’t reconnect to the internet, disable any auto-connect options in its network settings. This will prevent accidental reconnection to the network and further spread of malware.
- Secure the Network: After disconnecting the infected device, strengthen the security of your network by changing the Wi-Fi password and enabling network encryption. This will prevent unauthorized access attempts and ensure the safety of your network and devices.
- Notify Other Users: If the infected device is shared among multiple users, inform them about the situation and advise them to disconnect their devices from the network as a precautionary measure. This will help prevent the potential spread of the botnet malware to other devices connected to the same network.
By promptly disconnecting the infected device from the internet and taking necessary security measures, you can effectively contain the botnet malware and mitigate its impact on your network. In the next section, we will discuss how to run an antivirus scan to detect and remove the botnet malware from the infected device.
Running an Antivirus Scan
Once you have disconnected the infected device from the internet, the next step is to run a comprehensive antivirus scan to detect and remove botnet malware. Antivirus software is designed to identify and eliminate malicious programs, including botnet infections. Here are the steps to run an effective antivirus scan:
- Choose a Reliable Antivirus Software: Select a reputable antivirus software that is known for its effectiveness in detecting and removing malware. Ensure that the antivirus software is up-to-date with the latest virus definitions to maximize its detection capabilities.
- Update the Antivirus Software: Before initiating the scan, update the antivirus software to ensure it has the latest virus signatures and program updates. This will enable it to recognize and eliminate even the most recent botnet malware variants.
- Select a Full System Scan: Run a full system scan rather than a quick scan. A full scan thoroughly examines all files and folders on the infected device, leaving no room for any hidden malware. This ensures a more comprehensive detection and removal process.
- Quarantine or Remove Detected Malware: If the antivirus scan detects any infected files or botnet-related malware, follow the recommended actions provided by the antivirus software. Typically, you will have the option to quarantine or delete the detected malware. Choose the appropriate action based on the severity of the infection.
- Scan External Drives: If the infected device has any external drives like USB flash drives or external hard drives connected to it, scan them as well. Botnet malware can spread to these devices, and scanning them will help ensure that no infected files remain.
- Regularly Update and Scan: To maintain a strong defense against botnet malware, schedule regular updates and scans with your antivirus software. This proactive approach will help identify and eliminate any new threats before they can cause significant damage.
Running an antivirus scan is a crucial step in removing botnet malware from the infected device. However, it is important to remember that some advanced botnet infections may be resistant to standard antivirus solutions. In such cases, additional measures may be required, such as seeking professional help or using specialized malware removal tools. In the next section, we will discuss how to remove botnet malware effectively from the infected device.
Removing the Malware
After running an antivirus scan and identifying the presence of botnet malware on the infected device, the next crucial step is to remove it completely. Removing the malware effectively will restore the device’s functionality and prevent any further damage. Here are the steps to remove botnet malware:
- Follow Antivirus Software Recommendations: If the antivirus scan successfully detects and quarantines or removes the botnet malware, follow the recommended actions provided by the antivirus software. These actions may include deleting infected files, repairing system files, or cleaning up the registry.
- Manually Delete Suspicious Files: If the antivirus software fails to remove all traces of the botnet malware, manually deleting suspicious files is another option. However, exercise caution and only delete files that you are certain are related to the malware. Be sure to back up important files before making any changes to the system.
- Edit System Startup: Botnet malware often adds itself to the system startup process to ensure persistence. Use the “msconfig” command on Windows or the “launchctl” command on macOS to review and edit the startup programs. Disable any suspicious or unknown entries to prevent the malware from launching during system boot.
- Clear Browser Extensions and Plugins: Botnet malware can sometimes modify browser settings and install malicious extensions or plugins. Open your browser’s settings and remove any unfamiliar or suspicious extensions or plugins. Additionally, reset the browser settings to their default values to ensure any unwanted changes are reversed.
- Update and Patch Vulnerable Software: Outdated or unpatched software can leave your device vulnerable to malware attacks. To prevent future botnet infections, update all software installed on the infected device, including the operating system, web browsers, plugins, and other applications. Enable automatic updates whenever possible to stay protected against known vulnerabilities.
If you encounter difficulties in removing the botnet malware or suspect that the infection is more advanced, it is advisable to seek professional assistance from IT experts or consider using specialized malware removal tools. These tools are designed to target and remove stubborn malware that traditional antivirus software may struggle to eliminate.
By carefully following these steps and taking the necessary actions, you can effectively remove botnet malware from the infected device and restore its security and functionality. In the next section, we will discuss how to update and patch software to prevent future botnet infections.
Updating and Patching Software
Regularly updating and patching software is crucial in protecting your devices from botnet infections and other security threats. Software updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities, making it harder for botnets to exploit your system. Here are the steps to update and patch your software:
- Enable Automatic Updates: Most operating systems and software applications provide the option to enable automatic updates. Make sure this feature is enabled to ensure that your software receives the latest security patches as soon as they become available. Automatic updates reduce the risk of overlooking critical updates.
- Update the Operating System: Keep your operating system up to date by installing the latest updates and patches. These updates typically include security enhancements and bug fixes, making it more difficult for botnet malware to infiltrate your system. Regularly check for updates and install them promptly.
- Update Web Browsers and Plugins: Web browsers and their associated plugins can be targeted by botnet malware. To prevent this, regularly update your web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari) and plugins (e.g., Adobe Flash, Java). Remove any outdated or unused plugins to reduce potential security vulnerabilities.
- Update Antivirus Software: Keep your antivirus software up to date by regularly checking for updates and installing the latest virus definitions. This ensures optimal detection and protection against new forms of botnet malware and other threats. Configure the antivirus software to update automatically whenever possible.
- Patch Other Software: Apart from the operating system and web browsers, regularly update and patch other software installed on your device, such as productivity applications, media players, and messaging apps. These updates often include security fixes that add an extra layer of defense against botnet malware.
- Disable Outdated or Unused Software: If you have software that is no longer actively supported by the vendor or that you no longer use, consider disabling or uninstalling it. Outdated or unused software can pose a significant security risk as it may contain unpatched vulnerabilities that botnet malware can exploit.
By making updating and patching software a routine practice, you can significantly reduce the risk of botnet infections. Preventing vulnerabilities in your software strengthens your defenses against botnet attacks and enhances the overall security of your devices and network.
In the next section, we will discuss additional security measures you can implement to further protect your devices from botnet malware.
Enhancing Security Measures
Protecting your devices from botnet malware requires implementing robust security measures. By enhancing your security protocols, you can further safeguard your devices and network against potential threats. Here are some effective security measures to consider:
- Strong and Unique Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all your devices, online accounts, and services. Avoid using common passwords or reusing passwords across multiple accounts. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification, such as a code sent to their mobile device, in addition to a password. This greatly reduces the chances of unauthorized access to your accounts.
- Firewalls: Install and configure firewalls on your devices and network. Firewalls act as a barrier between your devices and the internet, monitoring and blocking suspicious network traffic. Configure firewalls to deny incoming connections by default and only allow necessary and trusted traffic.
- Regular Data Backups: Back up your important data regularly to an external storage device or a cloud-based service. In the event of a botnet infection or any other data loss incident, having recent backups ensures that you can quickly recover your important files without paying a ransom or succumbing to data loss.
- Software Restriction Policies: Implement software restriction policies that control the execution of applications on your devices. Allow only trusted and verified software to run, minimizing the risk of installing malicious applications or inadvertently executing malware-infected files.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate your employees or household members about online security best practices. Train them to recognize and avoid common phishing attacks, suspicious downloads, and unsafe browsing habits that can lead to botnet infections. Encourage a security-conscious culture and promote regular security awareness training.
- Regular Software and Firmware Updates: In addition to updating and patching software, keep firmware, such as the firmware on routers and IoT devices, up to date. Manufacturers often release firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities. Regularly check for firmware updates and install them promptly.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Implement network monitoring tools or Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic for any abnormal or suspicious activities. These tools alert you to any potential security breaches and help you detect and respond to botnet infection attempts in real-time.
- Limit Administrative Privileges: Limit administrative privileges to essential personnel only. Regular users should operate with standard user accounts, which have limited access rights. Administrative privileges should be reserved for system administrators or IT personnel who require elevated access for system configurations and installations.
By adopting these security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of botnet infections and enhance the overall security of your devices and network. Being proactive and vigilant in your security practices is vital in protecting against evolving threats.
In the next section, we will discuss the importance of monitoring network traffic to identify and address potential botnet infections.
Monitoring Network Traffic
Monitoring network traffic is a crucial aspect of maintaining a secure environment and preventing botnet infections. By closely monitoring the flow of data within your network, you can identify any suspicious activities or anomalies that may indicate a botnet infection. Here’s why monitoring network traffic is important and how you can do it effectively:
Identifying Botnet Activity:
Botnets rely on communication between infected devices and botnet command-and-control (C2) servers. By monitoring network traffic, you can identify unusual patterns, connections to suspicious IP addresses, or sudden increases in data transfers, which may indicate botnet activity. Monitoring network traffic allows you to detect botnet infections at an early stage and take preventive actions.
Detecting Unwanted Outgoing Connections:
Botnets often attempt to communicate with external malicious servers for command updates, data exfiltration, or launching further attacks. By monitoring outgoing network traffic, you can spot any unauthorized connections and take immediate action to prevent data breaches, data loss, or participation in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Preventing Data Leakage:
Botnets can exploit compromised devices to exfiltrate sensitive information. Monitoring network traffic allows you to detect any unusual data transfers or connections to unknown destinations, helping you identify potential data leakage attempts and mitigate the risks associated with them. Early detection can prevent severe data breaches and protect your valuable information.
Responding to Botnet Infections:
Monitoring network traffic provides valuable insights into the behavior and impact of botnet infections. By analyzing the patterns of communication, you can gain a better understanding of the infected devices, the domains or IP addresses involved, and the specific botnet variant. This information helps in formulating an effective response plan and applying targeted remediation measures.
How to Monitor Network Traffic:
To monitor network traffic effectively, you can utilize network monitoring tools or Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) that provide real-time analysis and alerting capabilities. These tools help you identify any abnormal traffic patterns, suspicious connections, or indicators of botnet activity.
Additionally, configuring firewall rules and logging settings allows you to capture and analyze network traffic within your network. A well-configured firewall can provide valuable insights into potential botnet activity.
By regularly monitoring network traffic, you can detect and respond to botnet infections in a timely manner, minimizing the potential damage and reducing the risk of further propagation within your network.
Next, we will discuss the importance of educating users about botnet malware and how to promote a proactive security mindset.
Educating Users about Botnet Malware
Education is a key component in combating botnet malware. By educating users about the dangers of botnet infections and teaching them how to recognize and prevent such threats, you can empower them to play an active role in maintaining a secure environment. Here’s why educating users about botnet malware is important and how to effectively educate them:
Understanding the Risks:
Many users may not be aware of the concept of botnet malware and its potential impact on their devices and network. By educating users about the risks associated with botnet infections, such as data theft, unauthorized access, and participation in cybercriminal activities, you can instill a sense of urgency and motivate them to take preventive measures.
Recognizing Warning Signs:
Users should be taught how to recognize the warning signs of botnet infections. This includes identifying unusual network activity, slow device performance, unexpected pop-ups or advertisements, unexplained crashes, and unauthorized changes to settings. By familiarizing users with these indicators, they can promptly report potential botnet infections and mitigate the risks.
Practicing Safe Online Behavior:
Educating users about safe online practices is crucial in preventing botnet infections. Teach them to be cautious when downloading files from untrusted sources, visiting suspicious websites, or clicking on unfamiliar links. Emphasize the importance of keeping software updated, using strong and unique passwords, and avoiding sharing personal information with unknown parties.
Phishing Awareness:
Phishing attacks are a common method used to distribute botnet malware. Educate users about the risks associated with phishing emails, text messages, and social engineering techniques. Teach them how to recognize phishing attempts and advise them to verify the authenticity of requests before providing any sensitive information.
Regular Security Awareness Training:
Implement regular security awareness training sessions to keep users informed about the latest botnet threats and prevention techniques. Cover topics such as malware detection, incident reporting procedures, and the importance of maintaining a proactive security mindset. Training should be interactive, engaging, and tailored to the specific needs and knowledge levels of the users.
Promoting a Security-Conscious Culture:
Creating a culture of security awareness is essential in preventing botnet infections. Encourage users to actively report any suspicious activities or potential botnet infections. Foster an environment where users feel comfortable asking questions, seeking guidance, and reporting incidents promptly. Utilize internal communication channels to raise awareness about botnet threats and share relevant security tips and best practices.
By educating users about botnet malware and empowering them to practice safe online behavior, you can significantly reduce the risk of botnet infections within your organization or household. Education should be an ongoing effort, with regular updates and reinforcement to ensure users stay informed and vigilant against evolving threats.
In the next section, we will discuss the importance of reporting botnet incidents to the appropriate authorities.
Reporting the Incident to Authorities
When dealing with a botnet infection, it is essential to report the incident to the appropriate authorities. Reporting botnet incidents helps law enforcement agencies take action against cybercriminals, potentially dismantling the botnet and preventing further damage to individuals and organizations. Here’s why reporting the incident to authorities is important and how to do it effectively:
Supporting Law Enforcement Efforts:
Reporting botnet incidents to authorities contributes to the collective efforts in combating cybercrime. Law enforcement agencies rely on these reports to gather intelligence, investigate botnet activities, and identify the individuals or groups responsible for operating the botnet. By reporting incidents, you support the ongoing fight against botnet malware and help protect others from falling victim to these threats.
Gathering Evidence:
Reporting botnet incidents allows law enforcement agencies to collect valuable evidence that can be used in legal proceedings. By providing detailed information about the botnet infection, such as the date and time of detection, suspicious network traffic, and any other relevant evidence, you assist the authorities in building a stronger case against the perpetrators.
Protecting Others:
Reporting botnet incidents helps protect others from falling victim to the same malware or botnet. Law enforcement agencies can use the information provided in the reports to identify and take down the botnet’s infrastructure, preventing further infections and minimizing the potential impact on individuals, organizations, and the overall cybersecurity landscape.
How to Report a Botnet Incident:
When reporting a botnet incident to authorities, follow these steps to ensure an effective and efficient reporting process:
- Document the Incident: Before reporting, gather as much information as possible about the botnet infection. Include any logs, screenshots, or details regarding the indicators of compromise or suspicious activities associated with the botnet.
- Contact Your Local Law Enforcement Agency: Begin by reaching out to your local law enforcement agency or cybercrime unit. Provide them with a clear and concise description of the botnet infection, the impact it has had on your devices or network, and any supporting evidence you have gathered.
- Report to Cybersecurity Authorities: In addition to local law enforcement, consider reporting the incident to relevant cybersecurity authorities or organizations. These may include national computer emergency response teams (CERTs), the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), or other regional cybersecurity organizations.
- Follow Reporting Instructions: Each reporting entity may have specific reporting procedures and requirements. Follow their instructions carefully, providing all the necessary details and evidence in the prescribed format. Be prepared to provide your contact information for follow-up inquiries, if required.
- Cooperate with Investigators: If contacted by law enforcement investigators, cooperate fully and provide any further details or assistance they may need. Help them understand the impact of the botnet infection and offer any insights that can aid their investigation.
By reporting botnet incidents to the appropriate authorities, you contribute to efforts in combating cybercrime, protecting others, and strengthening the overall cybersecurity ecosystem. Your actions can make a significant difference in preventing future botnet infections and holding cybercriminals accountable.
Finally, we will discuss proactive measures to prevent future botnet infections.
Preventing Future Botnet Infections
Taking proactive measures is crucial in preventing future botnet infections and safeguarding your devices and network. By implementing preventative strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to botnet malware. Here are some effective measures to consider:
Keep Software Updated:
Regularly update all software on your devices, including the operating system, web browsers, plugins, and applications. Software updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities, making it harder for botnets to exploit your system. Enable automatic updates whenever possible to stay protected against emerging threats.
Exercise Caution with Downloads:
Be cautious when downloading files from the internet. Only download files from trusted sources and verify the reliability of the website or platform before initiating any downloads. Avoid downloading files from untrusted or suspicious websites, as they may contain malware that can lead to botnet infections.
Beware of Phishing Attacks:
Stay vigilant against phishing attacks that can lead to botnet infections. Be wary of emails, messages, or websites that ask for sensitive information or encourage you to click on unknown links. Verify the authenticity of emails and websites before providing any personal or login details. Educate yourself and your users about common phishing techniques and how to spot them.
Utilize Robust Passwords:
Use strong and unique passwords for all your accounts. Avoid using easily guessable passwords or reusing passwords across different platforms. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
Secure Your Network:
Protect your network by configuring firewalls, implementing strong Wi-Fi passwords, and using encryption protocols. Separate your network into different segments to isolate potential botnet infections and limit their impact on other devices. Regularly monitor network traffic and look for any suspicious activities or connections that may indicate a botnet infection.
Educate Users:
Continuously educate and train yourself and your users about botnet threats, safe online practices, and how to identify potential risks. Promote a security-first mindset that emphasizes the importance of practicing caution, reporting suspicious activities, and following security protocols. Regularly assess the efficacy of your training program and adjust it to address emerging threats.
Implement Network Security Solutions:
Deploy network security solutions such as Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), or endpoint protection platforms. These solutions can help monitor and detect potential botnet activity, block malicious traffic, and mitigate the risks associated with botnet infections. Regularly update and maintain these security solutions to ensure they provide optimal protection.
Perform Regular Backups:
Regularly back up your important data to a secure location that is separate from your primary devices or network. This helps protect your data in case of a botnet infection or other security incidents. Verify the success and integrity of your backups to ensure easy data recovery if needed.
Stay Informed:
Keep yourself updated about the latest botnet threats, security best practices, and emerging cybersecurity trends. Stay informed through reputable sources such as cybersecurity blogs, news sites, and industry reports. Subscribe to security alerts and notifications to receive timely information about new botnet threats and necessary precautions to take.
By implementing these preventative measures and staying vigilant, you can significantly reduce the risk of future botnet infections and maintain a secure digital environment for yourself and your network. Remember that prevention is key in combating botnet threats.